Cardiovascular System – Heart and Blood Vessels
description
Transcript of Cardiovascular System – Heart and Blood Vessels

Cardiovascular System – Heart and Blood VesselsTopics in Human Pathophysiology Fall 2011Gilead Drug Safety and Public Health

Outline Heart
Conduction System and ECGs Coronary Circulation Cardiovascular Disease – diagnosis and treatment
Blood Vessels and Pressure Structure of blood vessels Blood pressure and regulation Pulmonary arterial hypertension

Figure 8.14

ECG Tracings

Figure 8.11

Ischemic Heart Disease Coronary artery disease Myocardial ischemia Myocardial hypoxia Myocardial infarct Myocardial necrosis

From wikipedia

Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
Age
Male sex
Heredity
Smoking
Diabetes mellitus
Hypertension
High cholesterol
Obesity
Lack of exercise

Diagnosis and Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
Diagnosis BP monitoring Symptoms ECG Angiogram Stress Test Nuclear myocardial
perfusion tests

Coronary Angiogram

Lexiscan (regadenoson)
For myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) A2A adenosine receptor agonist Vasodilates coronary arteries as if
exercising Injected into blood stream prior to gamma
camera scan Can give a good indication of myocardial
perfusion

Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
• Treatment– Coronary bypass surgery– Angioplasty– Stents– Cholesterol lowering
agents– Anticoagulents– Antianginal medications

Ranexa
For angina Thought to inhibit a sodium ion channel in
the cardiac muscle cells Contraction of those cells might normally
cause compression of cardiac blood vessels during diastole.
Can be taken with other anti-anginal meds Very effective

Congestive Heart Failure

Congestive Heart Failure
Heart becomes weak
Blood backs up in veins and capillaries
Fluid excess in tissues
Symptoms include shortness of breath, edema, difficulty breathing (especially when lying down,) difficulty exercising

Congestive Heart Failure
Causes: cardiomyopathy hypertension lung disease coronary artery disease previous MI valve disease

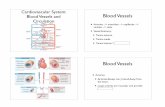
Blood Vessels and Pressure Artery structure and function
Control over smooth muscle
Vascular Disease Atherosclerosis Pulmonary arterial hypertension


Figure 8.10

Vessel Wall Structure
Tunica intima – epithelium and connective tissue
Tunica media – smooth muscle
Tunica externa– connective tissue and epithelium

Figure 8.1


Arterial blood pressure and flow
Systolic and diastolic pressure
Regulatory factors Cardiac Sympathetic nervous system from vasomotor center
of brain stimulates smooth muscle Chemical messengers – hormones, paracrines

Components of Orthe Nervous System
Figure 11.1
Organization of the Nervous System

Figure 11.12 (1 of 2)
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System

Figure 11.12 (2 of 2)
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System

Table 19.2
Hormonal Control of Blood Pressure

Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension

Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
Pulmonary arteries become narrowed causing decreased gas exchange and difficulty breathing
Causes R ventricular hypertrophy
Blood will back up in veins


Common causes of PAH
• Genetic defect
• Autoimmune diseases, such as scleroderma
• Congestive heart failure
• History of blood clot in the lung
• HIV infection
• Lung or heart valve disease
• Obstructive sleep apnea
• In many cases the cause is unknown- Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension

Symptoms of PAH
Chest pain, usually in the front of the chest
Dizziness
Fainting
Fatigue
Leg edema
Light-headedness during exercise
Shortness of breath during activity
Weakness

Treatment for PAH Letairis (ambrisentan) Flolan or other prostacyclins Bosentan (Tracleer) Calcium channel blockers Diuretics Sildenafil (Viagra) Supplemental oxygen Surgical correction of defects Lung transplant