Carburetion. Purpose of carburetor To provide proper ratio of air and fuel under every condition for...
-
Upload
philomena-norris -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of Carburetion. Purpose of carburetor To provide proper ratio of air and fuel under every condition for...

Carburetion

Purpose of carburetor
• To provide proper ratio of air and fuel under every condition for good performance, economy and emissions

Fuel must be atomized to be vaporized

Venturi principal
• Air flowing through a tube will cause a pressure drop in that tube
• Adding a restriction or two to a tube will cause a larger decrease in pressure (increase in vacuum)
• This vacuum is used to suck or draw fuel from the float bowl

Throttle plate is used to control amount of air / fuel entering the
engine
• Limits volumetric efficiency
• Limits venturi vacuum

Multiple barrel carbs.
• Primary vs. secondary barrels
• One - two - three - four

CFM = cubic feet per minute
• What is a cubic foot?

Carburetors have 2 or 3 main parts
• Air horn, float bowl, throttle body or air horn, main body

Carb overhaul
• Chemicals
• Soak & rinse
• Blow out
• Replace all gaskets
• Perform all adjustments

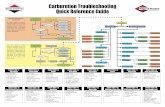
Control of fuel to air ratio is primarily controlled by seven
different circuits

Circuits
• Float circuit
• Idle circuit
• Transfer (off idle) curcuit
• Main circuit
• Power circuit
• Accelerator pump circuit
• Choke circuit


Float circuit : kind of fuel tank• Purpose: to store fuel for all other systems to work properly• Components and operation
– Float – Needle & seat– Hinge– Bowl vents internal and external– Bowl displacers – Dampening springs
• Float types– Nitrile (looks like a sponge)– Hollow brass– Hollow plastic
• Adjustments– Level
• Bending arm while using float gauges (with or without gasket)
• Adjusting seat externally adjustable (holleys)
• Sight glass with dot in the middle
– Drop adjustment eliminating float binding
• Problems with circuit– High float levels & symptoms
• Sunk floats - float inspection and weight
– Needle and seat sticking / debris on seat– Low float levels & symptoms– Binding hinges– Plugged vents or air filter
• Internal vent to compensate for dirty air filter
– Control of evaporating vapors– Bowl leaking or evaporating

Idle circuit / slow circuit
• Purpose: to supply engine with fuel at speeds too slow to operate main circuit• Starts through main jet (brief explanation)• To idle restrictor / slow jet• Fuel cut / slow cut solenoid
– Solenoid operation
• Air bleeds– Start atomization
– Air bleed jets
– Altitude compensators
• Transfer ports / work as air bleeds• Idle mixture screw
– Out to richen / in to lean
– Sometimes goes backwards adjusting air
– Do not bottom
– Spring to help maintain adjustment

Idle problems
• Plugged passages– One side of two barrel on two plane manifold
• Failing solenoids• Plugged air bleeds• Vacuum leak diagnosis
– Pinch off vacuum hoses
– Propane method
– Carb spray method

Idle adjustments• Idle speed
– Position of throttle plates in bore– Usually turning appropriate screw– Curb idle– Idle stop solenoids
• Electric or vacuum
• Idle mixture– Usually turning screw– Screw anti-tamper devises
• Plug removal• Limiter caps• Double d heads• Hex heads• Allen heads
– Preset by bottoming screw and turning out– If two / four barrel keep both screws the same– Adjust to factory recommendations
• Adjustments– Explain stoichiometrics– Idle mixture to co2– Propane enrichment methods
• 2 Speeds
– Lean drop – Pcv systems and diluted oil

Transfer / off idle circuit
• Purpose: supplies fuel at speeds too slow for main circuit
• Limited by idle restrictor
• Eliminates one idle air bleed but adds volume to idle circuit
• Used on light acceleration
• Problems– Plugging – Lean hesitation– More noticeable on smaller displacement engines– Usually older people complaints

Main circuit / main metering
• Purpose; to supply fuel to engine at cruise speeds• Components and operation
– Jet (stamped numbers on jet)– Atomizer / emulsion tube– Air bleed
• Altitude compensators• At nozzle stops dripping, possibly due to high idle speed
– Discharge nozzle– Venturi / boost venturis– Vacuum
• Problems and adjustments– Jets change / do not drill (causes swirling)– Rod changing– Float level increases
• Usually only circuit found in the secondary bore(s)

Power circuit
• Purpose: to enrichen mixture through main circuit for increased power under load
• Components and operation– Some have jet
• Calibrated size with stamp number• May incorporate spring and valve
– Manifold vacuum low at w.O.T.– Diaphragm type (holleys)– Power piston on jet– Power piston with rods– Power piston return springs
• Problems and adjustments– Vacuum piston stuck on or off
• Rod type • Valve type
– Diaphragm rupturing• Possible backfiring• Can be accessed externally
– High overlap cams causing lower intake vacuum

Accelerator pump circuit• Purpose: to supply engine with shot of fuel on moderate - heavy acceleration• Necessary because fuel is heavier than air• Components and operation
– Plunger in machined bore (hooked to linkage)– Diaphragm (hooked to linkage by cam)– Check balls, weights and springs– Pump discharge jet– Duration and return springs– Dual well accel. Pumps– Toyota’s cold accel enrichment
• Inspection of system– Look for solid stream– No external leaks
• Problems and adjustments– Plunger
• Cup material deteriorating– Rubber and oxygenated fuels– Viton– Carb cleaners swell cups– Leather
• Diaphragm– Leaking externally due to oxy. Fuels
• Check balls leaking– Pitting– Foreign material
• Duration and return springs– Weak or too stiff
• Outlet ball sticking• Adjustments by hole in arms• Adjustments by cams

Choke circuit• Purpose: to enrichen fuel mixture on cold conditions and to raise idle speeds cold• Fuel vaporizes slower cold causing much of the fuel to be wasted / vehicle not running efficiently cold needing more idle speed to run• Components and operation
– Plate or butterfly• Off centered to help opening• Draws fuel from all points when closed including air bleeds• Increases venturi vacuum under plate when closed
– Pulloff or brake• Purpose: to open choke plate a desired amount at first start to obtain a proper a/f ratio• Manifold vacuum controlled
– Vacuum can be computer controlled– Vacuum can be tvs controlled
• Can have a primary and secondary for two stages• Delay valves• Can control secondary air valve
– Coil• Electric
– Charging system output controlled– Oil pressure controlled– Computer controlled
• Heated air• Divorced• Water
– Fast idle cam• Multiple steps
• Adjustments– Choke coil
• Alignment of index marks
– Choke pulloff• Drill diameter• Angle gauge• Calibrated vacuum leaks
– Fast idle speed
• Problems– Choke coil not warming up– Plate sticking– Choke pulloff rupturing– Fast idle speed adj.

Secondary(s)
• Purpose: to increase volume of air fuel mixture under load
• Usually consists of a main type circuit• May also have idle, and accel. Pump circuits• Can be mechanical or vacuum• Can have air valves controlled by pulloffs• Usually have a lock out mechanism• Progressive vs normal