CaenorhabditisCaenorhabditis elegans elegans (C. (C ...
Transcript of CaenorhabditisCaenorhabditis elegans elegans (C. (C ...

CaenorhabditisCaenorhabditis eleganselegans(C. (C. eleganselegans))
By:By:By:By:MajidMajid MojarradMojarrad

C. elegans timeline.
• Developed by Sydney Brenner (1963)• Mutants published by Brenner (1974)• 1976 postembryonic cell lineages determined (Sulson and Horwitz)• 1983 complete embryonic cell lineages determined (Deppe et al., Sulson et al.)
d ll d h ( i l ) b l i l• 1982 "Programmed cell death" (Horwitz et al.) Nobel Prize Brenner, Sulson, Horwitz 2002
• 1986 Complete connectivity of nervous system established (White p y y (• et al.) "The mind of a worm”• 1991-98 RNAi and miRNA discovered in worms. Nobel Prize: Fire, Mello 2006• 1998 First animal genome sequenced (97Mb, now 100.3Mb).
This is about 1/30 the size of the human genome (3 Gb). C. elegans have about 17 500 genes about half that of humans (30 000-40 000 genes) First animal to beabout 17,500 genes, about half that of humans (30,000 40,000 genes). First animal to be sequenced! Knowing the sequence allows genes of interest to be easily cloned. Also it opened opportunity for reverse genetic approach.

UnsegmentedUnsegmentedVermiformVermiformVermiformVermiformbilaterally symmetricalbilaterally symmetricalcuticle integumentcuticle integumentfour main epidermal cordsfour main epidermal cordsfour main epidermal cordsfour main epidermal cordsfluidfluid--filled filled pseudocoelomatepseudocoelomate cavitycavity

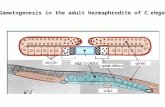
XX animals become hermaphroditesXX animals become hermaphroditesXO animals become malesXO animals become malesXO animals become males XO animals become males (chromosome non(chromosome non--disjunction)disjunction)With one less chromosome, males develop With one less chromosome, males develop Hermaphrodite produces many progeny Hermaphrodite produces many progeny 300 300 worms!worms!Adult hermaphrodites haveAdult hermaphrodites have 959959 somatic cellssomatic cellsAdult hermaphrodites have Adult hermaphrodites have 959959 somatic cells somatic cells while males have while males have 10311031
–– 79 79 more neurons and more neurons and 25 25 more muscle cells than more muscle cells than h h dith h dithermaphroditeshermaphrodites
–– used for matingused for mating

C elegansC elegansC. elegansC. elegansNon ParasiticNon Parasitic
“Bacteria Eating” Nematode“Bacteria Eating” Nematode
959959 Somatic CellsSomatic Cells959959 Somatic CellsSomatic Cells
Hermaphrodites and Hermaphrodites and Males Males
((00 0505%)%)((00..0505%)%)
Egg/Embryonic StageEgg/Embryonic Stage
j il t (Lj il t (L11 LL44))juvenile stages: (Ljuvenile stages: (L11--LL44))
? ? DauerDauer Stage (Hibernation)Stage (Hibernation)
AdultAdult

Embryonal and larval stagesEmbryonal and larval stagesEmbryonal and larval stagesEmbryonal and larval stages
Annie Lam

C elegansC elegans anatomyanatomyC. elegansC. elegans anatomyanatomy

C. Elegans morphology
Organs and tissuesOrgans and tissues
•Epidermal systemMuscles
p de a syste•Digestive system•Reproductive system•Muscular system•Excretory system•Nervous system•Nervous system
http://www.wormatlas.org

Nervous systemHermaphrodite 302 neuronsHermaphrodite 302 neurons
5000 chemical synapses2000 neuromuscular junctions
Male 381 neurones
By comparison105 neurons in flys, ~300 in worms
Interneurons and motorneurons
Major neurotransmitters:Ach -exitatoryGABA- inhibitorySerotonine (HSN neuron egg laying)Serotonine (HSN neuron- egg laying)DopamineFMRF amide peptides
Wood W.B. 1988. The Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. 1-667.

Genetic ofGenetic of C elegansC elegansGenetic of Genetic of C.elegansC.elegans
Average life span of approximately Average life span of approximately 22––33 weeks weeks Generation time of approximatelyGeneration time of approximately 44 daysdaysGeneration time of approximately Generation time of approximately 44 daysdayssequence was published in sequence was published in 19981998Genome size is approximately Genome size is approximately 100100MbpMbp55 pairs ofpairs of autosomesautosomes andand 11 pair of sexpair of sex55 pairs of pairs of autosomesautosomes and and 1 1 pair of sex pair of sex chromosomeschromosomes2000020000--2500025000 genegeneDo not have natural virusDo not have natural virusDo not have natural virusDo not have natural virus

Postembryonic cell lineage was completed first.y g p
•In the presence of food
•cell divisions resume and postembryonic developmental program begins 3 hours after hatching
•first stage larva has approximately 671 cellsg pp y
•113 undergo programmed death in the course of development
•About 10% of the remaining 558 cells in a newly hatched larva (51 in hermaphrodites 55 in the•About 10% of the remaining 558 cells in a newly hatched larva (51 in hermaphrodites, 55 in the
male), are blast cells that divide further.
•DivisionsMi ti
http://www.wormatlas.org
•Migrations•Differentiation•Death

Where do specific tissues come from?
EAB MS
Lineages do not strictly produce single tissue types.
P4DC
While intestine & germ-line come from single founder cells, the muscle, nervous system & skin cells each arise from multiple lineages This means for examplesystem & skin cells each arise from multiple lineages. This means, for example, that muscles do not have one “founder” cell early in development.

Cell death can be a genetically programmed cell fate.
Specific cells with diverse developmental origins undergo programmed cell death at specific
Indicate death event The Nematode Caenorhabditis Elegans. 1988. Editor William B. Wood ,Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Specific cells with diverse developmental origins undergo programmed cell death at specific times during development.Programmed cell death is characterized by a series of specific morphological changes.
There must be genes that control both the decision to express that fate and the execution.

How are invariant lineagesHow are invariant lineages established and maintained?
Partitioning of preexisting maternal componentspCell-autonomous programsC ll ll i t tiCell-cell interactions

WhyWhy C elegansC elegans??Why Why C. elegansC. elegans??Easy/Inexpensive To MaintainEasy/Inexpensive To MaintainEasy/Inexpensive To MaintainEasy/Inexpensive To Maintain
Lives in a Petri DishLives in a Petri Dish
Can be easily mutatedCan be easily mutatedCan be easily mutatedCan be easily mutated
Short Short Life Cycle/Can produce several generations in a short period of timeLife Cycle/Can produce several generations in a short period of time
Perfect for Genetic Perfect for Genetic ResearchResearch
Can be maintained in Can be maintained in --70 70 ºCºC
C. C. eleganselegans is transparentis transparent
Complete Cell Lineage Characterized (from zygote to adult)Complete Cell Lineage Characterized (from zygote to adult)Kathy Szeniawski
patterns of cell lineage are largely invariant between individualspatterns of cell lineage are largely invariant between individuals

Model for what?Model for what?Model for what?Model for what?

C. elegans as Model in Biomedical Research
Validated C. elegans disease models
• CNS• Depression, Psychosis
P ki ’ Al h i ’• Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s• Pain
• Metabolic• Type II diabetes• Obesity
• Other• Other• Cardiovascular (arrhythmia)• Oncology• Muscle disease

Conserved pathwaysExample: diabetesExample: diabetes
C. elegansInsulin
HumanInsulin IGF1Insulin
DAF-2/insulin receptor
Insulin, IGF1
Insulin receptor, IGF1 receptor
DAF-18AGE-1
PTENPI3 Kinase
PDK 1 PDKSHIP2
AKT-1, AKT-2 AKT/PKB
PDK-1 PDK
DAF-16 FKHR, FKHRL1, AFX
Growth, dauer bypass Growth, survival

Conserved pathwaysExample: serotonergic synapseExample: serotonergic synapse
tryptophantryptophan hydroxylase tph-1L-AAAH cofactor synthesis cat-4
5-OH-tryptophany
L-AAAD bas-1
5HT receptor
5-OH-tryptamine (5HT)
cat-1 vesicular 5HT receptor
5HT
5HT
cat 1 vesicularmonoamine transporter
5HTreuptake
5HT
5HT receptor

C elegansC elegans Worm FarmingWorm FarmingC. elegansC. elegans Worm FarmingWorm Farming
Prepare NGM agar platePrepare NGM agar plate
Grow an OPGrow an OP--50 50 E. coliE. colilawn lawn Chunk transfer or Single Chunk transfer or Single worm transferworm transferGrow at room tempGrow at room tempKathy Szeniawski
Extract eggs from AdultExtract eggs from AdultWorms can be frozen Worms can be frozen Kathy Szeniawski
Kathy Szeniawski

OP50 is a uracil auxotroph whose growth is limitedon NGM plates A limited bacterial lawn is desirableon NGM plates. A limited bacterial lawn is desirablebecause it allows for easier observation and bettermating of the wormsmating of the worms.

OPOP--5050 E coliE coliOPOP--5050 E. coliE. coli
Grow OPGrow OP--50 50 E. coliE. coliat at 3737 degrees C degrees C Kathy Szeniawski ggovernight in overnight in 22X YTB X YTB (Yeast (Yeast TryptoneTryptone Broth)Broth)(( ypyp ))Pipette onto NGM agar Pipette onto NGM agar platesplates
Kathy Szeniawski
platesplatesGrow your “Bacterial Grow your “Bacterial Lawn” forLawn” for 22 daysdaysLawn for Lawn for 22 daysdays
Kathy Szeniawski

Maintainance ofMaintainance of C elegansC elegansMaintainance of Maintainance of C .elegansC .elegansNGM (Nematode Growth Medium) plates NGM (Nematode Growth Medium) plates seeded with OPseeded with OP50 50 Esherichia coliEsherichia coli strainstrain
Worm stocks can best be maintained between Worm stocks can best be maintained between 15 15 °°C and C and 25 25 °°C i llC i ll 2020°°CC°°C, most typically at C, most typically at 2020°°C.C.
Worms grow 2.1 times faster at 25°C than at 16°C,and 1.3 times faster at 20 °C than at 16 °C

NGM (Nematode Growth Medium) agar plates :NGM (Nematode Growth Medium) agar plates :NGM (Nematode Growth Medium) agar plates :NGM (Nematode Growth Medium) agar plates :
3434 00 gg AgarAgar3434..0 0 g g AgarAgar22..5 5 g g PeptonePeptone33..0 0 g g NaClNaCl
Fill up with Fill up with 1 1 L HL H22OOInvert bottle a couple of timesInvert bottle a couple of timesAutoclave the mixture (Autoclave the mixture (2020 min at min at 121121°°C)C)(( ))Let it cool down to approximately Let it cool down to approximately 5050°°CCAdd:Add:
11 mlml Cholesterol/EthanolCholesterol/Ethanol ((55 g Cholesterol ing Cholesterol in 11 LL 9595% Ethanol)% Ethanol)11 ml ml Cholesterol/EthanolCholesterol/Ethanol ((55 g Cholesterol in g Cholesterol in 11 LL 9595% Ethanol)% Ethanol)1 1 ml ml 11M M MgSOMgSO4425 25 ml ml 11M M KPOKPO4411 ml ml 11M M CaClCaCl22
Pour NGM plates Pour NGM plates

ContaminationContaminationContaminationContamination
Maintain Sterile TechniquesMaintain Sterile Techniques
Kathy Szeniawski
Kathy Szeniawski

Long term storage of the wormLong term storage of the wormLong term storage of the wormLong term storage of the worm
CC.. eleganselegans cancan bebe storedstored indefinitelyindefinitely atat veryvery lowlowtemperaturetemperature ((--7070 ~~ --100100 °°CC freezer)freezer)temperaturetemperature (( 7070 100100 CC freezer)freezer)
FreezingFreezing solutionsolution::SS B ffB ff [[129129 ll 00 0505 MM KK22HPOHPO44 871871 ll 00 0505 MM KHKH22POPO44 55 8585 N Cl]N Cl] ++ 3030%% l il iSS BufferBuffer [[129129 mlml 00..0505 MM KK22HPOHPO44,, 871871 mlml 00..0505 MM KHKH22POPO44,, 55..8585 gg NaCl]NaCl] ++ 3030%% glyceringlycerin11::11 withwith MM99 containingcontaining wormsworms (preferably(preferably starvedstarved LL11))
InIn thethe dauerdauer larvallarval stage,stage, itit cancanalsoalso bebe keptkept atat 1616 °°CC forfor monthsmonths

Transferring (picking) the worms from Transferring (picking) the worms from NGM agar platesNGM agar plates
PlatinumPlatinum wirewire attachedattached totoPP iiaa PasteurPasteur pippettepippette
(glass(glass isis meltedmelted withwith flame)flame)
Eyelash glued to a toothpick Eyelash glued to a toothpick
“Chunking” pieces of agar“Chunking” pieces of agarChunking pieces of agar Chunking pieces of agar

Microscopy slidesMicroscopy slidespypy

MutantsMutantsMutantsMutants
Observe under the microscopeObserve under the microscope
bliblidpydpylonlonlonlon

IsolationIsolation of dauer larvaeof dauer larvaeIsolation Isolation of dauer larvaeof dauer larvaeTheThe dauerdauer--specificspecific cuticlecuticle andand thethe lacklack ofof pharyngealpharyngeal pumpingpumpingconferconfer resistanceresistance toto manymany environmentalenvironmental insults,insults, includingincluding 11%%SDSSDSSDSSDS
Wash the daf-2 plates (20°C and 25 °C ) with M9 to collect the worms into test tubesWash the daf-2 plates (20 C and 25 C ) with M9 to collect the worms into test tubes.Centrifuge for 20-60 sec at 2000 rpm and discard excess liquid.Add 1 ml 1% SDS and wait for 15 minutes.Centrifuge for 20-60 sec at 2000 rpm and discard excess liquid.Centrifuge for 20 60 sec at 2000 rpm and discard excess liquid.Pipet the worms onto a new plate and compare the amount of survived worms.Observe dauer morphology
L4
dauerRiddle Laboratory UBC Campus Vancouver - Gallery

MakingMaking microscopy slidesmicroscopy slidesMaking Making microscopy slidesmicroscopy slides
((aa) Three microscope slides are placed in a row, with a ) Three microscope slides are placed in a row, with a 22--3 3 layers of lab tape on each of the layers of lab tape on each of the two outer slides. two outer slides. A drop of A drop of 44% agarose in M% agarose in M9 9 is placed on the center slide. is placed on the center slide. ((bb) A fourth microscope slide is rested on the lab tape on top of the two outer slides and used ) A fourth microscope slide is rested on the lab tape on top of the two outer slides and used to flatten the agarose on the center slideto flatten the agarose on the center slideto flatten the agarose on the center slide. to flatten the agarose on the center slide. ((cc) The central slide is slid out. ) The central slide is slid out. ((dd) ) 5 5 µµl of l of 20 20 mM sodium azide mM sodium azide is is pipetted onto the agarose pad and animals are picked into pipetted onto the agarose pad and animals are picked into the azide. the azide. A coverslip is placed atop the animals. A coverslip is placed atop the animals.

http://www.bio.unc.edu/faculty/goldstein/lhttp://www.bio.unc.edu/faculty/goldstein/lab/movies.htmlab/movies.html//