Breastmilk as Epigenetic Medium...Australian peri/post epigenetic twin study - EBF for 4-6 m as...
Transcript of Breastmilk as Epigenetic Medium...Australian peri/post epigenetic twin study - EBF for 4-6 m as...

Breastmilk as Epigenetic Medium
NPO Conference, Portland Oct 2018 Sylvia Metzger

.
Objectives
1. Introduce the concept of epigenetics
2. Discuss epigenetic effects of breastmilk and lactation programming on infant health outcomes
3. Compare and contrast modes of feeding and its impact on microbiome and infant health outcomes
4. Discuss common breastfeeding challenges and strategies to support mother-baby breastfeeding dyads in clinical practice

.
Baby’s menu impacts DNA
Globally, only 38% of infants are exclusively breastfed
US: only 13-14% are exclusively breastfed for 6 months
Nutritional epigenetics – the diet changes the gene expression
• modulates gene expression –turns genes on/off
• later effects on health.
Verduci et al. ( 2014). Epigenetic effects of human breast milk. Nutrients, 6 : 1711-1724

.
Epigenetics Modification of gene expression without changes in DNA (the genetic code itself)

.
Basic epigenetic mechanisms1. DNA methylation
2. Histone modification
3. miRNA
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Epigenetic_mechanisms.jpg

.
1. DNA methylation – genome guardian
• A chemical cap (CH3-) binds to or near a gene
• Gene is silenced or turned off
e.g. Breastfeeding – baby LEPTIN “ I am full”
The longer she BF, the less chance that the gene
will be methylated (silenced), which sends
signals of satiety
Obermann-Borst, S.A. et al (2013). Duration of breastfeeding and gender are associated with methylation of the LEPTIN gene in very young children. Pediatric Research, 74(3):344-349.

.
2. Histone modification- access to info
• DNA hugged tightly: the info CANNOT be “read” NO PROTEIN
• Histones “loosen”, information is ACCESSED & “READ” - PROTEIN is made
e.g. DM Type 1: Altered histone methylation induced by hyperglycemia
Picascia et al. (2015). Epigenetic control of autoimmune diseases: from bench to bedside. Clinical Immunology, 157(1):1-15.

.
3. miRNAs – key regulators in maternal-fetal crosstalk
Do not code, but regulate gene expression
• Key in fetal metabolic & immune programming• Promote infant’s growth • Deficient in infant formula• Most human and bovine milk miRNAs sequences are
identical • Raw farm milk (miRNA-148s)- atopy preventive effect• Persistent consumption of pasteurized milk – increased risk
of obesity and hyperphagia
Melnik, B.C., & Schmitz, G. (2017). MicroRNAs: Milk’s epigenetic regulators. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 31:427-442.
miRNA

.
Breast Milk Microbiota
• Modulates the immunologic development via personalied microbial and immune factors
• Breastfed baby ingests up to 800,000 bacteria daily (BM 1,000 CFUs/ml)
• Seeding the infant’s gut: transfer from breastmilk to baby
• Different composition in formula fed infants
• Maternal health also alters milk microbiota (delivery mode, stress etc)
• Better Th1 responses in breastfed infants compared to formula
Le Doare, K.L., Holder, B., Bassett, A, & Pannaraj, P.S. (2018). Mothers’s Milk : A purposeful contribution to the development of the infant microbiota and immunity. Frontiers in Immunology,9(361):1-10. Pannaraj, P.S., Rollie, A. & Bailey, A. (2017). Association between breast milk bacterial communities and establishment and development of the infant gut microbiome. JAMA Pediatrics, 17(7):647-654.

.
Benefits for BABYCondition % Lower risk Breastfeeding comment
Otitis media
Recurrent OM
23%50% 77%
Any BF compared to formula>3 or 6 mon of EBF (exclusive)> 6 mon EBF compared to 4-6 BF
Upper respiratory tract infection (serious colds, ear and throat infections)
63% >6 mon (EBF)
Lower respiratory tract infection – risk of hospitalization in 1st yr of life
72%77%
>4 mon EBF> 6 mon EBF compared to BF 4-6 mon
Asthma 40%26%
>3 mon (if atopic family history)>3 mon (if no atopic family history)
RSV bronchiolitis – severity (duration of hospitalization / O2 requirements)
74% > 4 mon EBF
NEC (1 case could be prevented if 10 babies EBF)
77% NICU, preterm – exclusive human milk
Atopic dermatitis 27%42%
> 3 mon (EBF negative family history)> 3mon (EBF positive family history)
American Academy of Pediatrics (2012). Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk, 129(3)”827-841 http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/3/e827/T2.expansion.html

.
Condition % Lower risk Breastfeeding comment
Gastroenteritis (effect lasts for 2 m after BF is stopped) 64% Any BF
SIDS 36% Any BF > 1 mon
Inflammatory bowel disease (intestinal colonization is different in BF babies)
31 % Any BF
Obesity 24% Any BF
Celiac disease (if BF when exposed to gluten) 52% > 2mo
Type 1 DM 30% >3 mon EBF
Type 2 DM 40% Any BF
Leukemia (ALL)Leukemia (AML)
20%15%
> 6 mon> 6 mon
American Academy of Pediatrics (2012). Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk, 129(3)”827-841 http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/3/e827/T2.expansion.html

.
Autoimmunity
American Academy of Pediatrics (2012). Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 129(3): e827-e841 Lund-Blix et al. (2017). Infant feeding and risk of type 1 diabetes in two large Scandinavian Birth Cohorts. Diabetes Care, 40(7): 921-927
• Diabetes Type I – by 30% if exclusively BF at least 3 months
• Celiac disease – by 52% in infants breastfed when exposed to gluten
• Rheumatoid arthritis (cumulative BF > 12 m, RR 0.8, if > 24 m, RR 0.5)
• Childhood inflammatory bowel disease – by 31% (Crohn’s , Ulcerative colitis)

.
Maternal BenefitsDecreased risk of
• Breast, ovarian, & endometrial cancer
• Obesity
• Diabetes mellitus II
• Hyperlipidemia
• Hypertension
• Myocardial infarction
• Rheumatoid arthritis
• Decreased postpartum blood loss
• Postpartum depression
Schwarz, E.B., & Nothnagle, M. (2015). The Maternal Health Benefits of Breastfeeding. Am Fam Physician, 91 (9):604-4American Academy of Pediatrics (2012). Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk, 129(3):827-841 http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/3/e827/T2.expansion.html

.
Lactation as critical window of opportunity
• The First 1000 days – breastmilk as a significant early life programming medium
Cunha, A.J., Leite, A.J., & Almeida, I.S. (2015). The pediatrician’s role in the first thousand days of the child: the pursuit of healthy nutrition and development. J Pediatri (Rio J), 91(6 Suppl 1): S44-51

.
Lactational programming

.
1. IMMUNE programming
• miRNAs in breastmilk – key players in immunity
• Milk – body fluid richest in miRNA
• More in colostrum > mature milk
• Modify gene expression of distant cells• ~60% of all human genes
• Decrease inflammation (↓NEC)
• This mom-baby signaling is absent in formula
Alsaweed, M., Hartmann, P.E., Geddes, D.T., & Kakulas, F. (2015). MicroRNAs in Breastmilk and the Lactating Breast: potential immunoprotectors and developmental regulators for the infant and the mother. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(11):13981-14020.Melnik, B.C., & Schmitz. G. (2017). MicroRNAs: Milk’s epigenetic regulators. Best Practice and Research. Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 31(4):427-442.
miRNA

.
Breastfeeding & Childhood Asthma
Canadian longitudinal birth cohort (N=3296)
• Mode of feeding ~ asthma diagnosis at 3 yrs
Results
• Modes of infant feeding are associated with asthma development
• Direct BF (most protective) > expressed breastmilk> formula
• Bottled fed with BM or formula – increased risk of coughing/wheezing episodes by 1 yr compared to babies directly BF
Klopp et al. (201 7). Modes of Infant Feeding and the Risk of Childhood Asthma: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. The Journal of Pediatrics, 190:192-199.

.
2. METABOLIC programming
• Lactation period- a critical window of susceptibility to insults due to continued organ differentiation and growth
• Transient insults can have lasting effects• Metabolic tissues – sensitive to developmental stressors • Increased risk of Obesity, insulin resistance, abnormal glucose
levels, DM in offspring
Ellsworth, L., Harman, E., Padmanabhan, V., & Gregg, B. (2018). Lactational programming of glucose homeostasis: a window of opportunity. Reproduction, 156(2):R23-R42

.
Breastmilk ↓ the risk of pediatric obesity
Mischke & Plösch (2013). More than just a gut instinct- the potential interplay between a baby’s nutrition, its gut microbiome, and the epigenome.
American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative, and Comparative Physiology, 304(12):R1065-9.
Authors propose that:
• Early nutrition influences the baby epigenome via microbial metabolites
• ↑ adult obesity
• The type of feeding • Affects the composition of the early gut microbiota
• Formula feeding• different metabolites impact the epigenome of intestinal cells,
hepatocytes, and adipocytes- predisposes to obesity

.
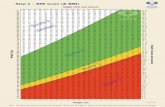
Metabolic programming & obesityAustralian peri/post epigenetic twin study
- EBF for 4-6 m as compared to 1-3 m ↓ BMI
- Infants BF less than 4m: ↑BMI, arm and abdominal circumference at 18 m
- The Early Protein Hypothesis & obesity - 55-80% higher protein in infant formulas ~ rapid weight gain in the first few months obesity
- Leptin deficiency theory & obesity- The hormone leptin “Mom, I am full” via neurological pathways -
overweight/obesity risk ↓
- Hypomethylation of the Leptin gene with longer duration of BF (hypomethylation= Leptin is awake and working) – Obermann-Borst,2013
- Leptin is absent in formula
Temples et al (2016). Breastfeeding and Growth of Children in the Peri/Postnatal Epigenetic Twins Study (PETS): Theoretical Epigenetic Mechanisms. Journal of Human Lactation, 32(3):481-488Obermann-Borst, S.A. et al (2013). Duration of breastfeeding and gender are associated with methylation of the LEPTIN gene in very young children. Pediatric Research, 74(3):344-349.

.
3. REPRODUCTIVE programming
Signals from mother to offspring continues during postnatal period (pig studies)
• Lactocrine signals 12-48 hrs from birth and colostrum are essential to support healthy uterine development of offspring
• Limited colostrum consumption or replacer feeding –alters neonatal pig uterine development via uterine gene expression & negatively impacts healthy uterine development in adult pigs
- 800 expressed, lactocrine-sensitive genes
Bartol, et al. (2017). Physiology and endocrinology symposium: Postnatal reproductive development and the lactocrine hypothesis. Journal of Animal Science, 95(5):2200-2210.

.
4. NEUROLOGIC programming
• Both mammary gland & nervous system – same origin
• Breastmilk-derived stem cells • Affect infant brain development • Can differentiate into neuron-like cells
• Gene expression of stem cell markers ↓ in• Prematurity
• ↑ Mom’ BMI

.
So, why do women stop breastfeeding?

.
Why do women stop breastfeeding?
• Formula supplementation before 72 hr
• Early postpartum - I don’t have enough milk
• Perceived or real low milk supply
• Satiety - Baby is crying a lot – must be hungry and is not satisfied
• Breast / Nipple pain
• Mastitis/plugged ducts
• Return to work/father’s attitude
• Concerns about medications
Ruowei, L, et al. (2008). Why mothers stop breastfeeding: mother’s self-reported reasons for stopping during the first yet. Pediatrics, 122;S69Newby, R.M. & Davies, P.S. (2016). Why do women stop breast-feeding? Results from a contemporary prospective study in a cohort of Australian women. European Journal of Clinical
Nutrition, . 70(12):1428-1432

.
How can we best support those who choose to breastfeed?

.
Keys to success
• Skin to skin after birth?
• Infant state optimal?
• Feeds on cue?
• Position optimal?
• Latch painless?
• Milk being transferred?

.
Skin to Skin Benefits
For babies:• Decreased crying (x12)
• More effective suckling
• HR, T, RR stable
• Increase in blood sugar
For mothers
• Less anxiety 3 days after birth
• Less breast pain at 3 days
Moore ER, Anderson GC, Bergman N, Dowswell T. Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD003519. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003519.pub3

.
Expected weight loss/gain in EBF infants
Flaherman et al. (2015). Early weight loss nomograms for exclusively breastfed newborns. Pediatrics, 135(1)Tawia, S. & McGuire, L. (2014). Early weight loss and weight gain in healthy, full-term, exclusively-breastfed infants. Breastfeeding Review, 22(1):32-42
Newborn weight loss nomogram https://www.newbornweight.org
• Loss 7-10% of birth weight is normal in the first few days of life
• Weight gain 20-20 g per day or 150-200 g per week once milk is in but this can vary
• Regain birth weight by 10-14 d

.
If medically indicated, what & how much to supplement?
Volume of Supplement
Average intake of colostrum per feeding
Birth to 24 hr 2-10 mL
24-48 hr 5-15 mL
48-72 hr 15-30 mL
72-96 hr 30-60 mL
• At 1 week – 300-450 ml of breastmilk /day
• At 1 month – 750-1050 ml of breastmilk/day
Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol #4, 2017
Choice of Supplement Expressed BMDonor Milk in the hospital Protein hydrolysate formulas

.
Possible indications for supplementation (term baby)
Maternal Indications
• Milk not in between days 3-5
• Primary glandular insufficiency
• Breast pathology, surgery with poor milk production
• Temporary cessation of BF (e.g.chemotx) or separation without expressed BM
• Intolerable & unrelieved pain
ABM Clinical Protocol #3. Supplementary Feedings in the Healthy Term Breastfed Neonate. Breastfeeding Medicine, 12 (3)
Infant Indications • Asymptomatic hypoglycemia
unresponsive to frequent BFs• Inborn errors of metabolism• Inadequate milk intake
• Evidence of dehydration• Weight loss + or > 8-10% day 5 or later or > 75th
percentile for age• Delayed bowel movement, < 4 stools on day 4,
or meconium still on day 5
• Hyperbilirubinemia• Breast milk jaundice

.
Safe Formula preparation
• Powdered formula is NOT sterile• Risk of contamination with C sakazakii – NEC, sepsis, meningitis
• FAO/WHO guidelines (2007) : Boil water to 158 F = 70 C to kill the bacteria
• Important especially in premature babies, babies < 28 d, LBW
• Use liquid formula if needed
• controversies exist – too strict vs temperature not high enough for some pathogens?
FAO/WHO. Enterobacter sakazakii and Salmonella in powdered infant formula; meeting report. Microbiological Risk Assessment Series 2006:10Losio, M.N., et al. (2018). Preparation of Powdered infant formula: could product’s safety be improved? J Pediatr Gastroengerol Nutr, 67(4):543-546

.
Common Breastfeeding Challenges
1. Nipple pain
2. Engorgement
3. Mastitis
4. Low milk supply

.
1. Nipple Pain
• Incidence of persistent nipple pain - 9.6% by day 7
• Predisposing factors:• primipara
• inappropriate positioning and latch (72.3%)
• tongue-tied (23.2%)
• oversupply (4.4%)
• Active management helps the mothers recover in 2 weeks
Puapompong, P et al. (2017). Nipple Pain Incidence, the Predisposing Factors, the Recovery Period After Care Management, and the Exclusive Breastfeeding
Outcome. Breastfeeding Medicine, 12:169-173.

.
NIPPLE PAIN – focus on the latch & positioning
For persistent pain with BF – see ABM Clinical Protocol #26
https://abm.memberclicks.net/assets/DOCUMENTS/PROTOCOLS/26-persistent-pain-protocol-english.pdf

.
Treatment of sore nipples• Positioning
• Expressed breast milk
• Lanolin (??)
• Proper suction set up on a pump
• Breastmilk + breast shells > lanolin
• Moist wound healing
• Saqez ointment (Pistacia) > breastmilk

.
Could it be yeast?
• Deep breast pain is anecdotaly linked to Candida albicans
Swedish case-control study
• Neither clinical symptoms nor microbial cultivation was reliable for making a diagnosis of C.albicans
• Refer to LC for support, focus on positioning
Kaski, K. & Kvist, L. J. (2018). Deep breast pain during lactation: a case-control study in Sweden investigating the role of Candida albicans . International Breastfeeding Journal, 13:21.

.
Berens, P., Brodribb, W., & The ABM. (2016). ABM Clinical Protocol #20: Engorgement, Revised 2016. Breastfeeding Medicine, 11 (4): 159- 163Wong, B.B., et al (2017). Application of cabbage leaves compared to gel packs for mothers with breast engorgement: Randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 76:92-99Cotterman KJ. Reverse pressure softening: A simple tool to prepare areola for easier latching during engorgement. J Hum Lact 2004;20:227–237Khosravan S. et al. The effect of Hollyhock (Althaea officinalis L) leaf compresses combined with warm and cold compress on breast engorgement in lactating women: A randomized clinical trial. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2015;pii: 2156587215617106.
• Frequent breastfeeding• Hand expression• Reverse pressure softening• TBML towards the axilla• Cabbage leaves? • Hollylock?
2. Engorgement

.
3. MASTITIS
• Inflammation of the breast, may or may not involve a bacterial infection
Risk factors
• nipple damage, infrequent, scheduled or missed feeding, poor latch, oversupply, blocked ducts, maternal stress and fatigue, oversupply, rapid feeding, illness in mom or baby
Management:
• Effective milk removal – responsive feedings, latch, positioning
• Comfort measures- rest, fluids, nutrition, heat prior to feeds, cold compress after feeds
Amir, L. H. & The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. (2014). ABM Clinical Protocol #4. Mastitis. Breastfeeding Medicine, 9(5):239-243

.
MASTITIS - Pharmacologic management
Analgesics
• Ibuprofen not detected in BM in doses up to 1.6 g/day
Antibiotics
• Mild symptoms, < 24 hr – effective milk removal/comfort measures
• No improvement within 12-24 hr- ABX 10-14 days (?)
• Dicloxacillin 500 mg PO QID for 10-14 d
• Cephalexin 500 mg PO QID for 10-14 d if suspected penicillin allergy
• Clindamycin 300 mg PO TID for 10-14 d if severe penicillin hypersensitivity or CA-MRSA
Amir, L. H. & The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Protocol Committee. (2014). ABM Clinical Protocol #4. Mastitis. Breastfeeding Medicine, 9(5):239-243

.
When milk needs to get out - TBM
• Engorgement, plugged ducts, mastitis
• Acute breast pain ~ Milk stasis
• Breast emptying is the key intervention
• In-office Therapeutic breast massage ~ 30 min
Witt, A.M., Bolman, M., Kredit, Sh., & Vanic, A. (2016). Therapeutic breast massage in lactation for the management of engorgmenet, plugged ducts, and mastitis. Journal of Human Lactation, 32 (1): 123-131.
VIDEO http://bfmedneo.com/our-services/breast-massage/Or https://vimeo.com/65196007

.
4. Low milk supply – support is critical!
• SUPPLY/DEMAND principle
• Ensure baby gets enough calories
• Frequent and thorough breast emptying
• On cue feeding
• Hand expression to stimulate milk flow
• Hands-on pumping
• Insufficient evidence to recommend increased maternal fluid intake
Ndikom, C.M., Fawole, B., & Illesanmi, R.E. (2014). Extra fluids for breastfeeding mothers for increasing milk production. Cochrane Databased of Systematic Reviews, 6:CD008758.Riddle, S.W., Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. (2017). Low milk supply and the pediatrician. Current Opionion in Pediatrics, 29:249--256

.
Low milk supply- evaluate the mom
• Obesity
• Hypothyroidism
• Labor complications – C/S? Hemorrhage?
• Insufficient glandular tissue – breast changes in pregnancy?
• PCOS?
• Breast surgery
• Medications? E.g. Decongestants/estrogen?
• Is there pain with feedings?
• What pump is she using?
• Postpartum depression
Riddle, S.W., Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. (2017). Low milk supply and the pediatrician. Current Opionion in Pediatrics, 29:249—256

.
Low milk supply – evaluate the baby
• Skin to skin?
• Does the baby feed on cue?
• Unrestricted feedings? (timing, just one breast?)
• Poor transfer?
• Latch? Positioning?
• Baby’s oral anatomy?
• Is baby feeding with a nipple shield?
• Gestational age?
Riddle, S.W., Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. (2017). Low milk supply and the pediatrician. Current Opionion in Pediatrics, 29:249—256

.
Low milk supply
• If supplementation needed - BF first
• Use a hospital-grade pump & “hands-on” pumping to drain the breasts more fully after breastfeeding if baby is not draining well
• If baby is draining well, don’t add pumping – discouraging
• BF-bottle feed-pump is exhausting- refer to LC
• Abnormalities in glucose metabolism may play a role• Delayed lactogenesis ~ maternal obesity
• Galactogogues ? • Metoclopramide – jitteriness, fatigue, EPS, depression
Lemay, D.G., et al. (2013). RNA sequencing of the human milk fat layer transcriptome reveals distinct gene expression profiles at three stages of lactation. PLoS One, 8:e67531Nommsen-Rivers, L., Riddle, S., et al. (2016). Milk production in mothers with and without signs of insulin resistance. Breastfeeding Medicine, 11 ( Supplement 1, S3-S4)Pinheiro, T.V., Goldani, M.Z, & IVAPSA group. (2018). Maternal pre-pregnancy overweight/obesity and gestational diabetes interaction on delayed breastfeeding initiation. PLoS One, 13(6):e0194879

.
What else to consider?

.
My baby is fussy, he must be hungry? Do I have enough milk?
http://purplecrying.info

.
Medications & Breastfeeding

.
MEDICATIONS while breastfeeding
• Blood levels attained in mom’s circulation
• Protein binding – choose drugs with high protein binding
• Lipid solubility – choose lower lipid soluble = less milk & CNS penetration
• Molecular weight < 300 enters milk easier; > 600 unlikely to enter milk in high conc.
• Oral bioavailability : typically < 1 % of maternal dose gets into the milk and baby
• Half-life in plasma – drugs with long half lives build up in baby’s plasma over time –choose drugs with shorter half-life
• pKa- choose drugs with a lower pKa
• Milk level is directly proportional to the maternal plasma level
Hale, T. (2018). Drug entry into human milk . Retrieved from https://www.infantrisk.com/content/drug-entry-human-milk

.
General rules when prescribing
• Is the drug absorbed from the GI tract? 3rd gen Cephalosporins (Rocephin), morphin Epsomn salts, magnesium salts, aminoglycosides, vancomycin –poorly absorbed – very little gets to the baby
• Shorter half-life drugs: wait 2-3 hr minimum after dosing before BF• Prolonged released forms: assume the drug has a long half-life (12-24hr)• Radioactive or dangerous drugs: after 5 half-lives 98% of a drug or
radioisotope is eliminated. Wait 4-5 half lives!• Topical medication on the nipple will likely be absorbed • Infants of drug abusing moms may test + for 2-4 weeks to months after
maternal exposure• Forewarn the mother - Diarrhea, constipation, sedation, weakness may
indicate neonatal absorption
Hale, T. (2018). Drug entry into human milk . Retrieved from https://www.infantrisk.com/content/drug-entry-human-milk

.
Contraception & Breastfeeding
Controversies in research!
• IUD- progestin – 6 wks pp or later• Immediate postpartum placement may lead to shorter duration of BF
• Nexplanon
• Depo-Provera
• Progestine-only pill
• Emergency contraception – postcoital copper IUD
Berens, P., & Labbok, M. &, The ABM. (2015). ABM Clinical Protocol #13: Contraception during breastfee3ding, revised 2015. Breastfeeding Medicine, 10(1): 1-10.

.
Is this medication safe while BF?
• Hale’s Medications & Mother’s Milk
• The Infant Risk Center Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center www.infantrisk.com
Helpline (806)352-2519 (M-F 8-5pm, CT)
• LactMed (A TOXNET database) https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/lactmed.htm
• Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine - protocols
• UK : The Breastfeeding Network – Drugs in Breastmilk Information(factsheets or inquiries via email)

.
Lactation support

.
RESOURCES for Breastfeeding Support • IBCLC / CLC consultants
• Hospital/community support groups
• WIC – breastfeeding as a priority• Breastfeeding peer counselors
• Breastfeeding Clinics• Breastfeeding Management Clinic at Children's Hospital
Colorado, please call 720-777-3605.
• Fathers support breastfeeding
• Colorado State Law• Employer – time to express milk up to 2 yrs
• Home visiting programs • Nurse Family Partnership-1st time moms• New Parent Support Program – military
![BM1弾 カードチェックリスト · 2020-06-17 · 1.89 d bmi-scp4[cp1 c] bmi-scp8[cp] bmi-hcpi bmi-scps[cpi a bmi cl bmi-scpi c] bmi-scp5[cp] c] bmi-cpi [cpi 12 bmi-cp2tcp]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5f0d11867e708231d43885ac/bm1-fffffff-2020-06-17-189-d-bmi-scp4cp1-c-bmi-scp8cp.jpg)