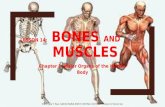
Bones & Muscles. How many bones does the human skeleton contain?
Bones, Muscles and Skin. Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis.
-
Upload
myrtle-harmon -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Bones, Muscles and Skin. Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis.
Body Organization and Homeostasis
The levels or organization in the human body consist of cells, tissues, organs and organ systems
Cells is the most basic organized part of the body
System is the most advanced
Cells
Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing
Human body contains about 100 trillion cells
Cell membrane forms on the boundary of the cell
The nucleus is the control center that directs the cells activities
The material within a cell is the cytoplasm, it is clear and jelly-like
Cells
Inside the cytoplasm are structures called organelles
Cells carry on the processes that keep the organism alive
Cells grow and reproduce They rid the organism of waste and
helps break down food to release energy
Tissues
Tissue is a group of similar cells that perform the same function
Muscular tissue can shorten and contract
Nervous tissue directs and controls the body using electrical messages
Connective tissue provides support and connects all its parts
Epithelial tissue covers you body inside and out
Organ and Organ Systems
Organ is a structure that is composed of different kinds of tissue
Organs perform a specific job like a tissue, but is more complex than a tissue
An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function
Homeostasis
The different organ systems work together and depend on one another
All the systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis, to keep the internal balance
Homeostasis is the process by which an organism’s internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment
Homeostasis
Very simply even when its cold out, your body will always have the same temp. Body temp. will drop when you are sick
Your body has various ways to maintain homeostasis When it is warm out, you sweat to help cool
off your body When it is cold, your body shivers, the
shivering helps to provide heat for your body
What the Skeletal System Does Our skeleton is our framework It is made up of all the bones in our
body The number of bones in your body
depends on how old you are. A newborn has 275 bones An adult has 206 bones As babies grow, bones in the body fuse
together.
What the Skeletal System Does Your skeleton has 5 major functions
Provides support and shape for the body Enables you to move Protects your organs Produces blood cells Stores minerals and other materials until
your body needs them
What the Skeletal System Does The backbone, or vertebral column ,
is the center of the skeleton. If you run your fingers down the
length of your back you will feel 26 vertebrae
Most of the bones in your body are associated with muscles
Bones also protect vital organs Bones also produce certain blood
cells, and store other vitamins and minerals.
Joints of the Skeleton
A joint is a place in the body where 2 bones come together
Joints allow bones to move in different ways
There are 2 different types of joints, moveable and immoveable.
Immovable are joints that allow for little or no movement The bones in the skull are held together
by immovable joints
Joints of the Skeleton
Most of the joints in the body are moveable joints.
Moveable joints allow for a wide range of motion
The joints in the body are held together by strong connective tissues called ligaments
Most joints have a second connective tissue called cartilage, which is more flexible than bone
Joints of the Skeleton
Cartilage covers the ends of the bones and keeps them from rubbing together
There is also a fluid that helps to lubricate the ends of the bones
Bones- Strong and Living
The word skeleton comes from a Greek word meaning “a dried body”
Bones are actually complex living structures that undergo growth and development
The longest bone in your body is your Femur, it is also the toughest to break.
Blood vessels and nerves enter and leave the bone through the membrane.
Bones- Strong and Living
Beneath the bone’s outer membrane is a layer of compact bone, which is hard and dense, but not solid.
These small canals carry blood vessels and nerves from the bone’s surface to the living cells within bone.
Spongy bone has many small spaces within it
This structure makes spongy bone tissue lightweight.
Bones- Strong and Living
Inside many bones contain a soft, connective tissue called marrow.
There are 2 types of marrow, red and yellow Red bone marrow produces most of the
body’s red blood cells. As a child most of your marrow is red, as
a teenager, only the ends of femurs, skull, hip bones, and sternum
Yellow marrow stores fat as an energy reserve
Bones- Strong and Living
Bones are strong and lightweight, stronger than concrete or granite rock. Only 20% of an adults weight is bone
Even when you get old, your bone tissue will continue to grow
So even when you break a bone, new bone tissue forms and the healed region will be stronger than before.
Bones develop from cartilage into bone, but not everywhere
Taking Care of Your Bones
A combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise are important for a lifetime of healthy bones
A healthy diet has calcium and phosphorus Meats, whole grains, leafy vegetables,
and dairy products. We try to prevent against
osteoporosis Condition in which the body’s bones
become weak and break easy.
Common Skeletal System Injuries 3 common skeletal system injuries
are fractures, dislocations, and sprains.
A fracture is a break in the bone. Simple=> cracked or completely broken
in 2 or more pieces. Compound=> the bone is sticking out of
the skin Dislocation occurs when the end of a
bone comes out of its socket Sprain is when ligaments stretch to
far
Identifying Injuries
There are 2 ways to identify injuries of the skeletal system, X-rays and MRI
X-rays are a form of energy that travels in waves A lead apron is used to protect from
unnecessary exposure The X-rays pass thru soft tissue but
not the bones One limitation is that it can not be used to
observe soft tissue damage
Identifying Injuries
An MRI, magnetic resonance imaging, is a large machine that contains magnets
The subject is exposed to short bursts of magnetic energy This causes atoms in the body to vibrate
or resonate. A computer then analyzes the vibration
patterns.
Treating Injuries
In addition to wearing a cast, 2 other ways to treat skeletal system injuries include surgical procedures such as joint replacement and arthroscopy
Joint replacement usually happens to people with arthritis, a disease of the joints.
Treating Injuries
Arthroscopic surgery Doctors make a small incision and insert
a slim, tube shaped instrument called an arthroscope.
Attached to the arthroscope is a small camera that is connected to a small monitor.
Once the problem area is found, doctors make another incision and use small instruments to make necessary repairs.
Types of Muscles
There are about 600 muscles in the human body.
Some muscles are easy to control, others are impossible to control
The beating of your heart and breathing are muscles you are unable to control, these are called involuntary muscles.
Types of Muscle
There are 3 types of muscle tissue Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac Muscle Some are voluntary, some are
involuntary
Types of Muscles
Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones of your skeleton and provide the force that moves your bones
Skeletal muscle is striated, meaning its in badns and gets tired
At the end of a skeletal muscle is a tendon A tendon is a strong connective tissue that
attaches muscle to bone Because you are able to control the
muscles in your arms and legs, they are a voluntary muscle
Types of Muscles
Smooth muscle are inside many internal organs such as the stomach and blood vessels.
Since you can not control your stomach, these muscles are involuntary
Smooth muscles tire more slowly than skeletal muscle
Types of Muscle
Cardiac muscle is found only in your heart
Cardiac muscle has some characteristics with both smooth and skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle never gets tired like skeletal muscle, but is striated.
It is also involuntary
Muscles at Work
Because muscle cells can only contract, not extend, skeletal muscles must work in pairs.
While one muscle contracts, the other muscle in the pair relaxes to its original length.
The Body’s Tough Covering
The skin protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss.
The skin also helps regulate body temperature, eliminate wastes, gather info. About the envir., and produce vitamin D.
The Epidermis
The skin is organized into 2 main layers, the epidermis and dermis.
The epidermis is the outer layer of the skin
Epidermis is usually thinner than the dermis
The epidermis does not have any blood vessel or nerves This is why shallow scratches do not
bleed or hurt
The Epidermis
Epidermal cells have a life cycle The skin cells we see, and come off
as dead skin cells, were once living when at the bottom of the epidermal layer
The Epidermis
In some ways, the cells of the epidermis are more valuable dead than alive.
Most protection is due to the layer of dead cells on the surface
Shedding of dead skin cells carries away bacteria and other substances on your skin.
Skin also produces melanin, a pigment, or colored substance that gives skin its color
The Dermis
The dermis is the inner layer of the skin.
The dermis is about a layer of fat but beneath the epidermal layer.
The fat layer helps to pad the internal organs and helps keep heat in the body.
The dermis is the layer of skin that has nerves, blood cells, sweat glands, hairs and oil glands.
The Dermis
Sweat glands produce perspiration which reach the surface through pores.
Strands of hair grow within the dermis in structures called follicles
The hair you see about the epidermal layer is made up of dead cells
Caring for your Skin
3 simple habits can help you keep your skin healthy Eat a healthy diet Keep your skin clean and dry Limit your exposure to the sun