Bones and the Skeletal System Advanced Biology 2013.
-
Upload
gerald-domenic-kennedy -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Bones and the Skeletal System Advanced Biology 2013.

Bones and the Skeletal System
Advanced Biology 2013

• Bones• Cartilage• Ligaments

Bones
• Osseous Tissue (Connective tissue)

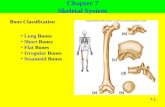
Types of Bones
• Long Bones– Longer than they are wide– Produce body movements
• Short Bones– Equal in length and width– Limited motion (Gliding)
• Flat Bones– Enclose and protect soft organs– Provide area for muscle attachment
• Irregular Bones– Vertebrae, Sphenoid, Ethmoid

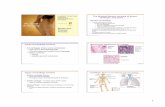
Long Bones
• Compact Bone (dense) – surrounds the medullary cavity which contains the bone marrow
• Spongy Bone (cancellous)- loosely organized form of bone tissue– Diaphysis-Shaft, provides leverage– Epiphysis-Expanded head, strengthens the joints
• Articular Cartilage-Where one bone meets another, Hyaline cartilage

Fig. 30-4
Cartilage
Spongy bone(contains redbone marrow)
Cartilage
Spongybone
Compactbone
Centralcavity
Yellowbone marrow
Bloodvessels
Fibrousconnectivetissue

Flat Bones
• 2 layers of compact bone which encloses a middle layer of spongy bone (dipole)

Bone Cells
• Osteogenic Cells- Bone producing cells• Osteoblasts-Bone forming cells• Osteocytes-Former osteoblasts-help pass
nutrients and chemical signals to each other• Osteoclasts-Bone dissolving cells, on bone
surface


Bone Marrow
• Red Marrow- Childhood, produces blood cells– In adults, Red marrow is only present in vertebrae,
ribs, sternum, and proximal heads of humerus and femur
• Yellow-Young-middle aged adults, fatty and no longer producing blood cells
• Gelatinous-Old age

Skeleton
Fig. 30-3a
Skull
Clavicle
ScapulaShouldergirdle
Sternum
Ribs
Humerus
Vertebra
Radius
Ulna
Pelvic girdle
Carpals
Phalanges
Metacarpals
Femur
Patella
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsals
Metatarsals
Phalanges

Fig. 30-3b
Intervertebraldiscs
Hipbone
7 cervicalvertebrae
12 thoracicvertebrae
5 lumbarvertebrae
Sacrum
Coccyx

Fractures

Healing of Fractures
• 1. Hematoma Formation-Clot• 2. Formation of granulation tissue• 3. Callus formation (4-6 weeks)• 4. Remodeling (3 months)

Joints
• Fibrous Joints- Sutures• Cartilaginous Joints- Vertebrae• Bony Joints- Mandible/frontal bone• Synovial Joints
– Ball and socket, Hinge, Saddle, Pivot, Gliding, and Condyloid