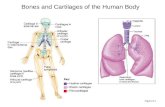
Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
-
Upload
yachiru121 -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
1/27
www.1aim.netAnatomy Tables - Bones and Cartilages of the Headand Neck - Listed Alphabetically
Bone/Cartilage Structure Description Notes
arytenoidcartilage
a pyramid shapedcartilage locatedon the superior margin of thecricoid lamina
paired; each isconnected to theepiglottis above viathe aryepiglottic m.and to the thyroidcartilage anteriorlyvia the vocalligament; pairedarytenoid cartilagesare pulled together (adducted) by thearytenoid m.
corniculatecartilage a small cartilagelocated on theapex of thearytenoidcartilage
corniculate cartilageis found in the baseof the aryepiglotticfold; it is yellowelastic cartilage
cricoidcartilage
the inferior & posterior cartilage of thelarynx; it forms a
completecartilaginousring; its arch projectsanteriorly and itslamina is broadand flat posteriorly
connected: above tothe thyroid cartilagevia the inferior hornof the thyroid
cartilage, to theconus elasticus, tothe arytenoidcartilages which sitatop the lamina;connected below tothe first trachealring via thecricotracheal
ligament
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
2/27
cuneiformcartilage
smallcartilaginousnodule located inthe aryepiglotticfold
cuneiform cartilageis yellow elasticcartilage
epiglottis the superior partof the larynx
epiglottic cartilageis covered by amucous membrane
ethmoid delicate bonelocated betweenthe two orbits
highly pneumatized bone that containsthe ethmoid air cells; forms thefragile medial wallof the orbit
cribriform plate perforated portion of ethmoid bone oneither side of thecrista galli
perforated for passage of theolfactory nerves
crista galli superior midline
projection of theethmoid boneinto the anterior cranial fossa; itarises betweenthe cribriform plates
"cock's comb";
anterior anchor point of the falxcerebri
perpendicular plate
midline process projectinginferiorly into thenasal cavity
forms the superior part of the bonynasal septum
superior nasalconcha
medial projectionof the ethmoid bone from thesuperolateralwall of the nasalcavity
forms the superior nasal meatus belowit and thesphenoethmoidalrecess above it
middle nasal portion of the forms the superior
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
3/27
concha ethmoid bonethat projectsinferomediallyfrom the lateralwall of the nasalcavity
nasal meatus aboveit and the middlenasal meatus (whichoverlies the bullaethmoidalis andhiatus semilunaris) below it
bulla ethmoidalis roundedelevation on thelateral wall of thenasal cavity
located under cover of the middle nasalconcha; middleethmoidal air cellsdrain at its apex
ethmoidal air cells pneumatizedspaces (3-18 innumber) withinthe ethmoid bone; located between theorbits
three groups may beidentified: anterior (drain into thehiatus semilunarisin the middle nasalmeatus), middle(drain onto the apexof the bullaethmoidalis in the
middle nasalmeatus), posterior (drain into thesuperior nasalmeatus)
ethmoidalforamen, anterior
opening in themedial wall of the orbit
transmits anterior ethmoidal vesselsand nerve
ethmoidalforamen, posterior
opening in themedial wall of the orbit
transmits posterior ethmoidal vesselsand nerve
hiatussemilunaris
groove in theethmoid portionof the lateralnasal wall between theuncinate process
below and bulla
receives thefrontonasal ductanterosuperiorly,opening of themaxillary sinus posteroinferiorly,
and the openings of
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
4/27
ethmoidalisabove
the anterior ethmoidal air cellsin between
frontal the anterior boneof the skullwhich underliesthe forehead
articulates with the parietal bone posteriorly;zygomatic, ethmoidand sphenoid bonesinferiorly; maxilla,nasal and lacrimal bones anteriorly; itis formed from twoossifications centerswhich normally fusein the midline - if they do not fuse, amidline "metopicsuture" is the result
orbital plate flat portion of frontal that formsthe roof of the
orbit
a very thin portionof the frontal bonewhich is like an egg
shell in thicknessforamen cecum opening near the
anterior end of the crista galli
transmits anemissary vein whichmay result intransfer of infectious materialsfrom the nasalcavity to the cranialcavity with resultingmeningitis
frontal sinus pneumatizedspace in thefrontal bone
usually paired; eachdrains through thefrontonasal ductinto the uppermost part of the hiatussemilunaris in themiddle nasal meatus
superior orbital arch of bone skin over this region
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
5/27
margin above the orbitalopening
is supplied by branches of thefrontal nerve(supraorbital andsupratrochlear nn.)
superciliary arch the ridge of boneabove the orbitalmargin
located deep to theeyebrow, blunttrauma to thisregion often resultsin cuts within theeyebrow
glabella midline point between the pairedsuperciliaryarches
supraorbitalnotch
notch in thesuperior orbitalmargin
occasionally presentas a foramen;opening for the passage of the for supraorbitalneurovascular bundle
hyoid a "U"-shaped bone consistingof several parts: body, 2 greater horns, 2 lesser horns
the hyoid boneossifies completelyin middle life; the body articulateswith the greater horns via cartilage
and with the lesser horns via fibrous joints prior toossification; animportant site for muscle attachments(suprahyoid andinfrahyoid musclegroups)
body the middle the body of the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
6/27
portion of the"U"-shaped bone
hyoid bonearticulates with thegreater horns posteriorly
greater horn(cornu)
posteriorlydirected limbs of the "U"-shaped bone
each greater hornarticulates with the body and lesser horns anteriorly;origin of middle pharyngealconstrictor m. andhyoglossus m.
lesser horn(cornu) articulates withthe greater hornat its junctionwith the body
the inferior end of the stylohyoidligament attaches tothe lesser horn
inferior nasalconcha
a separate boneon the lateralwall of the nasalcavity
it articulates withthe maxilla; formsthe inferior nasalmeatus below it andthe middle nasalmeatus above it
lacrimal small boneforming part of the medial wallof the orbit
articulates:anteriorly withfrontal process of maxilla, superiorlywith frontal bone, posteriorly withethmoid, inferiorly
with orbital processof maxilla; forms part of the canal for the nasolacrimalduct
mandible the U-shaped bone forming thelower jaw
contains the inferior teeth; formed fromthe mesenchyme of the 1st pharyngeal
arch, and its
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
7/27
muscles areinnervated by thenerve of the 1st arch(mandibular division of cranialnerve V)
body the anterior partof the mandible
paired halves arefused in the midlineat the symphysismenti
symphysis menti the midlinesymphysis between the twohalves of themandible
the two halves of the mandible fuseduring the first postnatal year
mental protuberance
the projection onthe anterior midline of themandible
the bone of the chin;mental meansrelating to the mind,a reference to theact of resting thechin on the handwhile thinking (seethe sculpture byRodin: "TheThinker")
mental spines(genial tubercles)
the spines on theinner surface of the mandible posterior to the
mental protuberance
attachment site for the genioglossusand geniohyoidmm.
mylohyoid line the ridge runningobliquely from posterosuperior to anteroinferior on the medialsurface of the body of the
mandible
attachment site for the mylohyoidmuscle; thesubmandibular gland is locatedinferior to this lineand the sublingual
gland is located
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
8/27
superior to this linemental foramen the opening on
the anterior
surface of the body of themandible inferior to the premolar teeth
transmits the mentalneurovascular
bundle; coveredsuperficially by thedepressor angulioris and depressor labii inferioris mm.
ramus the angled portion of themandible that joins the posterior portionof the body
it rises nearlyvertically from the body; thechondyloid processand the coronoid process extend fromthe superior end of the ramus; themandibular foramenis located on themedial surface of the ramus; themedial pterygoid m.
attaches to themedial surface andthe masseter m.attaches to thelateral surface of theramus
angle the posteroinferior bend formed bythe union of the body and theramus
mandibular foramen
the opening onthe medialsurface of theramus
it is the opening intothe mandibular canal; it transmitsthe inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
9/27
mandibular canal the canal thatruns through the body of themandible
it transmits theinferior alveolar neurovascular bundle from theinfratemporal fossato the mandibular teeth and gingivae
lingula the projection of bone medial tothe mandibular foramen
it is the attachmentsite of the inferior end of thesphenomandibular ligament
coronoid process the process that projectsanterosuperiorlyfrom the ramusof the mandible
it is the attachmentsite of thetemporalis m.
condylar process the rounded process that projects posterosuperiorlyfrom the ramusof the mandible
it articulates withthe mandibular fossa of thetemporal bone
mandibular notch
the notch between thecoronoid andcondylar processes
it transmits themassetericneurovascular bundle from theinfratemporal fossato the deep surface
of the masseter m.mandibular neck the constriction
below thearticular chondyle on thechondylar process of themandible
part of the lateral pterygoid m. insertsinto the pterygoidfossa of themandibular neck
pterygoid fossaof the neck
a shallowdepression on the
part of the lateral pterygoid m. inserts
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
10/27
anterior surfaceof the neck of themandible
into the pterygoidfossa of themandibular neck
maxilla bone forming themidface it forms the inferior orbital margin andcontains the teethand maxillary sinus
frontal process the part of themaxilla that projectssuperiorly medialto the orbit
it articulates withthe nasal bone, thefrontal bone and thelacrimal bone; itforms part of medialorbital wall &margin; it forms theanterior part of thecanal for thenasolacrimal duct
orbital process the part of themaxilla thatforms the floor of the orbit
also known as theorbital surface of the maxilla; itcontains theinfraorbital grooveand canal; it formsthe roof of themaxillary sinus
zygomatic process
the lateral projection of themaxilla
it articulates withthe zygomatic bone
infraorbitalgroove
groove in orbital process of themaxilla locatedin the posterior part of the orbit
transmits theinfraorbitalneurovascular bundle from theinfraorbital fissureto the infraorbitalcanal
infraorbital canal canal in orbital process of themaxilla locatedin the anterior
the directcontinuation of theinfraorbital groove;transmits the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
11/27
part of the orbit infraorbitalneurovascular bundle from theinfraorbital grooveto the infraorbitalforamen
infraorbitalforamen
opening at theanterior end of the infraorbitalcanal locatedinferior to theorbit
it transmits theinfraorbitalneurovascular bundle
alveolar process "U"-shaped process of bonethat holds themaxillary teeth
contains sockets(alveoli) for theroots of themaxillary teeth
maxillarytuberosity
the roughened posterior aspectof the body of the maxilla
the posterior superior alveolar nn. Enter themaxilla directlysuperior to thisstructure
anterior nasalspine
anterior projection of bone in themidline, inferior to the anterior nasal aperture
the cartilaginous part of the nasalseptum sits atop thisstructure
maxillary sinus pneumatizedhollow center of the body of themaxilla
paired; eachmaxillary sinusdrains through thehiatus semilunarisinto the middlenasal meatus
palatine process shelf of bone that projectshorizontally tomeet at themidline in the
paired; together,they form the roof of the oral cavity(hard palate) andthe floor of the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
12/27
intermaxillarysuture
nasal cavity
incisive foramen opening in the
midline, posterior to themaxillary incisor teeth
it transmits the
terminal branches of the nasopalatine nn.& sphenopalatineaa.; it marks the point of unionduring developmentof the primary andsecondary palate
nasal thin bone thatforms part of the bridge of thenose
articulates with thefrontal bonesuperiorly, thefrontal process of the maxilla laterallyand the contralateralnasal bone medially
occipital the bone formingthe posterior surface of theskull
it articulatessuperolaterally withthe parietal bonesthrough thelambdoid suture,anteroinferiorlywith the temporal bone and anteriorlywith the body of thesphenoid bone
pharyngeal
tubercle
projection
located anterior to the foramenmagnum
attachment site for
the superior pharyngealconstrictor m.
squamous part the flat, thin portion of theoccipital bonelocated posterior to the foramenmagnum
it articulates withthe petrous part of the temporal boneanteroinferiorly andthe parietal bonessuperolaterally at
the lambdoid suture
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
13/27
external occipital protuberance
a projection onthe externalsurface of thesquamous part of the occipital bone in themidline
it is the attachmentsite of theligamentum nuchaeand the trapeziusm.; its highest pointis called the inion
inferior nuchalline
a low ridge thatruns transverselyon the externalsurface of thesquamous part of the occipital bone inferior tothe superior nuchal line
it is an attachmentsite for deep neck muscles
superior nuchalline
a low ridge thatruns transverselyon the externalsurface of thesquamous part of
the occipital bone
it is the attachmentis the for thetrapezius andsplenius mm.
foramenmagnum
the opening inthe occipital bone posterior tothe basal part
it transmits thespinal cord, twovertebral aa., andtwo spinalaccessory nerves
basal part the portion of the
occipital bonelocated anterior to the foramenmagnum
it articulates with
the body of thesphenoid bone
lateral part the portion of theoccipital bonelocated lateral tothe foramenmagnum
paired; it is pierced by the hypoglossalcanal and thecondylar canal
hypoglossal an opening in the paired; it transmits
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
14/27
canal lateral part of theoccipital bone
the hypoglossalnerve
condylar canal an opening in the
lateral part of theoccipital bone
paired; it transmits
the condylar emissary veinoccipital condyle a low, wide
projection fromthe inferior surface of thelateral part of theoccipital bone
paired; it articulateswith the atlas
jugular notch a notch locatedon theanterolateraledge of thelateral part of theoccipital bone
it forms the posterior margin of the jugular foramen;the temporal boneforms the anterior margin of the jugular foramen
ossicles a chain of three bones in the
tympanic cavity(middle ear)connecting thetympanicmembrane to theoval window;arranged fromlateral to medial:malleus, incus,
stapes
the ossicles are joined by synovial
articulations thatmay becomearthritic in old age,resulting inconductive deafness
incus the middleossicle of themiddle ear
articulates with thehead of the malleusand the head of thestapes; incus means"anvil"
malleus the lateral ossicleof the middle ear
the manubrium isattached by itshandle to the inner surface of the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
15/27
tympanic membraneat the umbo; itshead articulateswith the incus;malleus means"hammer"
stapes the medialossicle of themiddle ear
it articulates withthe long process of the incus and its base fills thefenestra vestibuli(oval window);stapes means"stirrup"
palatine the bone thatforms the posterior part of the hard palate
paired; failure of the perpendicular platesto fuse duringdevelopment leadsto a midline defect(cleft palate)
perpendicular plate
the vertical portion of the palatine bonelocated posteriorly oneither side of thenasal cavity
it articulatesanteriorly with themaxilla; posteriorlyit forms the medialwall of the pterygopalatinefossa and the lateralwall of the nasalcavity; its posterior edge contributes to1/2 of thesphenopalatineforamen
sphenopalatinenotch
a notch at the posterosuperior margin of the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone
along with thesphenoid bone itforms thesphenopalatineforamen
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
16/27
sphenopalatineforamen
an opening in thelateral wall of thenasal cavityformed by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone andthe body of thesphenoid bone
it transmits thenasopalatine nerveand thesphenopalatinevessels
orbital process a small, superior projection fromthe perpendicular plate of the palatine bone
it forms a small partof the floor of theorbit located posteroinferiorlynear the apex
horizontal plate the portion of the palatine bonethat forms the posterior 1/3 of the hard palate
paired; the twohorizontal platesmeet at the midline
greater palatineforamen
an opening in thehard palatelocated medial tothe 3rd maxillarymolar tooth
it transmits thegreater palatineneurovascular bundle; it is animportant site for oral anesthesia
lesser palatineforamen
an opening in thehard palatelocated posterior to the greater
palatine foramen
there may be morethan one; ittransmits the lesser palatine n. and
vesselsparietal a broad, flat bone
forming thelateral surface of the skull
paired; this bonearticulates with thecontralateral parietal bone in themidline at thesagittal suture; itarticulatesanteriorly with
frontal bone at
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
17/27
coronal suture; itarticulates posteriorly with theoccipital bone at thelambdoid suture; itarticulates inferiorlywith the greater wing of thesphenoid bone atthe pterion, thesquamous part of the temporal bone atthe squamous suture
and the mastoid partof the temporal bone at the parietomastoidsuture
inferior temporalline
an arching ridgeon the externalsurface of the parietal bone
it is an attachmentsite for thetemporalis muscle
superior temporal line
an arching ridgeon the externalsurface of the parietal bone
it is an attachmentsite for thetemporalis muscleand the temporalfascia
parietal foramen an opening in the parietal bonelocated near thesagittal suture
it transmits the parietal emissaryvein, a valvelessvein which connectsthe scalp to thecranial cavity
granular foveolae
small pits locatedon the inner tableof the parietal bone
for the arachnoidgranulations
thyroid
cartilage
the large anterior
cartilage of the
connected above to
the hyoid bone via
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
18/27
larynx; it hasseveral parts:laminae (2),superior horns(2), inferior horns (2),oblique line,superior thyroidnotch,
the thyrohyoidmembrane;connected below tothe cricoid cartilagevia the inferior hornof the thyroidcartilage; connected posteriorly: to thearytenoid cartilagevia the vocalligament andthyroarytenoid m.,to the epiglottic
cartilage via thethyroepiglotticligament; it tiltsanteriorly toincrease the lengthof the vocalligament and raisethe pitch of thevoice
lamina a broad flat plateof cartilageforming one sideof the thyroidcartilage; twolaminae fuseanteriorly in themidline to formthe thyroidcartilage
the laryngeal prominence is theline of fusion of thetwo laminae; eachlamina is connectedsuperiorly to thehyoid bone by thethyrohyoidmembrane
superior horn the rounded,superior projection of the posterior border of the thyroidlamina
it is connectedsuperiorly to thegreater horn of thehyoid bone by thelateral thyrohyoidligament
inferior horn the rounded,
inferior projection of the
it is connected
inferiorly to thecricoid cartilage by
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
19/27
posterior border of the thyroidlamina
the cricothyroidarticulation (asynovial joint)
oblique line ridge whichdescendsdiagonally fromsuperior toinferior on thelateral surface of the thyroidlamina
a line of muscleattachment
laryngeal prominence
the line of fusionof the thyroidlaminae
known to the lay person as the"Adam's apple"; thelaryngeal prominence is asecondary sexualcharacteristic - in postpuberal malesthe angle of thelaryngeal
prominence isapproximately 90and in females theangle isapproximately120
superior thyroidnotch
the notch at thesuperior end of the laryngeal prominence
it is connected tothe hyoid bone bythe medianthyrohyoid ligament
sphenoid an irregularlyshaped boneforming thecentral portion of the skull
it has many parts,including a body,greater wing, lesser wing and pterygoid plates
body central part of thesphenoid bone
contains thesphenoid sinuses;
attachment point for
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
20/27
the wings and pterygoid plates
sphenoid sinuses pneumatized
spaces within the body of thesphenoid bone
usually paired; it
drains into thesphenoethmoidalrecess of the nasalcavity
jugum the anterior-most portion of thesphenoid bone
articulates with thecribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
chiasmaticsulcus
the groove for the optic chiasm
located between the jugum & thetuberculum sellae
optic canal canal located atthe lateral end of the chiasmaticsulcus andmedial to theanterior clinoid process
paired; it transmitsthe optic nerve andthe ophthalmicartery from thecranial cavity to theapex of the orbit
tuberculumsellae
the anterior limitof the sellaturcica
the middle clinoid processes projectfrom its lateral ends
sella turcica depression on thesuperior surfaceof the body of the sphenoid bone
"Turkish saddle";roughly equivalentto the hypophysealfossa; area betweenthe tuberculum
sellae and the posterior clinoid processes
anterior clinoid process
projection at themedial end of thelesser wing of thesphenoid bone
the internal carotidartery passes medialto this structure
lesser wing of the sphenoid
thin rim of bone projectinglaterally from the
bilateral; it formsthe posterior marginof anterior cranial
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
21/27
anterior clinoid process
fossa; it articulatesanteriorly with theorbital plate of thefrontal bone
greater wing of the sphenoid
broad plate of bone swinginglaterally from the body of thesphenoid bone
bilateral; it formsthe medial part of the floor of themiddle cranialfossa, part of temporal fossaelaterally, and the posterior part of thelateral wall of orbit;it articulatesanteriorly with thezygomatic bone,superiorly with thefrontal & parietal bones (at the pterion), posteriorlywith the squamous& petrous portionsof the temporal bone
superior orbitalfissure
slit-like opening between thelesser & greater wings of thesphenoid bone
it transmits theoculomotor nerve,the trochlear nerve,the abducens nerve, branches of ophthalmic divisionof the trigeminalnerve, the superior ophthalmic vein andlymphatics from thecranial cavity intothe orbit
foramenrotundum
opening in thefloor of themiddle cranial
fossa through thegreater wing of
it transmits themaxillary divisionof the trigeminal
nerve
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
22/27
the sphenoid bone
foramen ovale opening in the
floor of themiddle cranialfossa through thegreater wing of the sphenoid bone
it transmits the
mandibular divisionof the trigeminalnerve; it is located between theforamen rotundumand the foramenspinosum
foramenspinosum
opening in thefloor of themiddle cranialfossa through thegreater wing of the sphenoid bone
it transmits themiddle meningealartery and themeningeal br. of themandibular divisionof the trigeminalnerve (cranial nerveV)
spine of thesphenoid
process of bonethat projectsinferiorly fromundersurface of greater wing of the sphenoid
it is the superior attachment for thesphenomandibular ligament
pterygoid process
process that projectsinferiorly fromthe junction of the body &
greater wing of the sphenoid bone
it has several parts:lateral & medial pterygoid plates,hamulus, pterygoidfossa, scaphoid
fossa; the pterygoid plates are separated by the large pterygoid fossathroughout most of their length, and bythe small scaphoidfossa superiorly
lateral pterygoid
plate
thin plate of bone
that projects
it is the attachment
site of the lateral &
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
23/27
posterolaterallyfrom the pterygoid process
medial pterygoidmuscles (lateral pterygoid m. on itslateral surface,medial pterygoid m.on its medialsurface)
medial pterygoid plate
thin plate of bonethat projects posteriorly fromthe pterygoid process
it is the attachmentof the superior pharyngealconstrictor m. & the pharygobasilar fascia
scaphoid fossa an ovaldepression at thesuperior end of the lateral pterygoid plate
it is the site of origin of the tensor veli palatini m.
pterygoidhamulus
hook-like projection fromthe inferior endof the medial pterygoid plate
it acts as a pulleyfor the tendon of thetensor veli palatinim.
pterygoid canal canal that occursat the junction of the greater wing,the pterygoid process and the body of the
sphenoid bone
it transmits thenerve of the pterygoid canalfrom the pterygoidregion to the pterygopalatine
fossatemporal bone forming the
lateral side of theskull
temporal refers the passage of time,which is marked bythe appearance of gray hair on the sideof the head
petrous part the hard part of the temporal bone located in
it contains thetympanic cavity(middle ear) and the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
24/27
the floor of thecranial cavity
bony labyrinth of the inner ear
internal acoustic
meatus
the opening on
the posteromedialsurface of the petrous part of the temporal bone
it transmits the
facial n., thevestibulocochlear n., and thelabyrinthine a.
facial canal a canal whichcourses throughthe petrous partof the temporal bone
it transmits thefacial n. from theinternal acousticmeatus to thestylomastoidforamen
carotid canal a canal whichcourses throughthe petrous partof the temporal bone
it transmits theinternal carotid a.and the internalcarotid plexus of nerves into thecranial cavity
mastoid process the processlocated posteroinferior tothe externalacoustic meatus
it projects inferiorlyfrom the junction of the petrous andsquamous parts of the temporal bone;it contains themastoid air cellsthat open into
tympanic cavitythrough the mastoidantrum
tegmen tympani thin plate of boneforming the roof of the tympaniccavity
located on the floor of the middlecranial fossa
jugular fossa a depression onthe posterior surface of the
it forms the anterior margin of the jugular foramen; the
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
25/27
petrous part of the temporal bone
occipital bone formsthe posterior marginof the jugular foramen
styloid process the spike of bonethat projectsinferiorly fromthe petrous partof the temporal bone
it is the attachmentsite for thestylohyoid,styloglossus andstylopharyngeusmm. and thestylomandibular andstylohyoidligaments
tympanic part the part of thetemporal boneconsisting of theexternal acousticmeatus and thetympanic ring
the medial 1/3 of the external acousticmeatus is bony andthe lateral 2/3 isformed by cartilage
external acousticmeatus
the opening inthe lateralsurface of thetemporal bone
it extends mediallyfrom the surface tothe tympanicmembrane; it allowssound to reach thetympanicmembrane; themedial 1/3 of theexternal acousticmeatus is bony andthe lateral 2/3 isformed by cartilage
tympanic ring the rim of bonesurrounding themedial end of theexternal acousticmeatus
it is the attachmentsite of the tympanicmembrane
squamous part the thin flat portion of the
temporal bone
it articulates withthe parietal bone
and the greater wing
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
26/27
that constitutesthe side of theskull above theear
of the sphenoid bone at thesquamous suture
zygomatic process
the projection of bone that arisesanterior to theexternal acousticmeatus
it articulates withthe temporal process of thezygomatic bone toform the zygomaticarch
mandibular fossa the depressionlocated medial tothe origin of thezygomatic process
it articulates withthe condylar processof the mandible
articular tubercle an inferior projectionlocated anterior to the mandibular fossa
dislocations of thetemporomandibular joint result when themandibular condyleslides anterior tothis structure
vomer thin plate of boneforming the posteroinferior part of the nasalseptum
articulatessuperiorly with the perpendicular plateof the ethmoid boneand the body of thesphenoid bone;articulates inferiorlywith the palatine
processes of themaxilla and thehorizontal plate of the palatine bone
wormian bone small irregular bone that occurs between suturesof the skull
wormian bones arevariable inoccurrence and areespecially commonat the junction of
the squamous suture
-
7/31/2019 Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck.doc
27/27
and the lambdoidsuture
zygomatic the bone that
forms the cheek
the zygomatic bone
is frequentlyfractured in blowsto the side of theorbit; the temporalfascia attaches tothe zygomatic arch
temporal process the portion of thezygomatic bonethat projects posteriorly
it articulates withthe zygomatic process of thetemporal bone toform the zygomaticarch
frontal process the portion of thezygomatic bonethat projectssuperiorly andmedially
it forms the inferior part of the lateralorbital margin andthe anteroinferior part of the lateralorbital wall; itarticulates with thefrontal boneanteriorly and thegreater wing of thesphenoid bone posteriorly
maxillary process
the part of thezygomatic bone
that projectsmedially
it forms the lateral part of the inferior
orbital margin andthe anterolateral part of the orbitalfloor; it articulateswith the maxilla
zygomaticofacialforamen
a small openingon the lateralsurface of thezygomatic bone
it transmits thezygomaticofacial n.