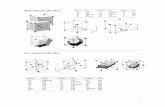
Body centered cubic
description
Transcript of Body centered cubic

Body centered cubic
Note that each corner atom is in eight cubes so only 1/8 of the corner atom is in this cell
Number of atoms = 1 center + 8 x 1/8 corners = 2
in the unit cell

Face centered cubic
Eight atoms at the corners
Six atoms at the face centers
Each face atom is in two cubes
Number of atoms =
6 x ½ faces + 8 x 1/8 corners = 4
in the unit cell

Hexagonal close packed
This unit cell has the same packing as the fcc – WHY?

Stacking of hexagonal planes
First layer is labeled A
Two ways of placing 2nd layer:
Can use only 3 of the 6 “holes”, so have two sets:
Sites B or Sites C

Stacking of hexagonal planes (2)
Alternating sites A with sites B
leads to
Hexagonal close packed

Stacking of hexagonal planes (3)
Stacking of the sequence ABC
leads to
FCC
An oblique plane shows the hexagonal planes

Scattering of radiationRadiation absorbed by atoms is re-emitted in all directions
In-phase rays reinforce
Out-of phase rays annihilate each other
Rays out of phase by an exact number of wavelengths reinforce each other

Xray Diffraction
For certain specific angles of incidence rays re-emitted from two parallel planes of a crystal are out of phase by exactly multiple wavelengths (n)
Path difference between two rays shown is SQT. If SQT equals nλ reinforcement occurs and a diffracted beam is found. SQT = 2d sin where d is separation of planes