Blood Vessels “Transport System”. Arteries Always carry blood away from the heart. The blood is...
-
Upload
alexander-bailey -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of Blood Vessels “Transport System”. Arteries Always carry blood away from the heart. The blood is...

Blood Vessels
“Transport System”

Arteries
Always carry blood away from the heart.
The blood is always oxygenated except in the pulmonary artery.
Arterioles are small arteries.

Veins
Always carries blood toward the heart
Carries deoxygenated blood except for the pulmonary veins
Venules are very small veins
Large venous spaces are called sinuses.

CapillariesMicroscopic vessels connect venules and arterioles to complete the closed circulatory system.

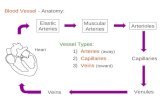
Layers of Blood Vessels
Inner layer (tunica intima)- smooth endothelium lining in arteries and forms valves in veins.
Middle layer (tunica media)- smooth muscle that allows for constriction and dilation of blood vessels.
Outer layer (tunica adeventitia)- connective tissue that offers support to prevent collapse.

Capillary Function
Capillary wall is made of simple squamous cells that accommodate only one red blood cell at a time.
This slows the blood down and allows for better exchange of gases and wastes.
Precapillary sphincters control the amount of blood flow through tissues.
Capillaries are referred to as primary exchange vessels.

Function of Veins
Veins function not only in transporting blood back to heart but also as reservoirs.
Semilunar valves in veins help to move blood back to the heart.
Pooling of blood does not cause increases in blood pressure because of veins ability to stretch or capitance.

Major Arteries
Notice that the aorta branches into many different segments.
• Ascending aorta• Aortic arch• Thoracic aorta• Abdominal aorta
Carotids are large arteries in the neck

Major VeinsThere are deep and
superficial veins.
Jugulars are the large veins in the neck
Great Saphenous vein is often used in bypass surgery
Veins from the spleen, stomach, pancreas, gall bladder and intestines first drain into the liver(hepatic portal).
This allows for excess glucose and toxins to be removed before the blood enters the general circulation.

Circulatory Routes
Systemic circulation is the movement of blood from the left ventricle through the rest of the body and back to right atrium
Pulmonary circulation is blood moving from right ventricle through lungs, gas exchange between blood and air takes place, back to left atrium.

Anastamosis
• Branches between arteries which allow for collateral circulation of blood.
• Critical in heart in case one branch is blocked there is additional routes blood can travel to tissue.

Fetal Circulation
The placenta attaches to the uterine wall is here is where the exchange of oxygen and nutrients takes place.
Blood flow in the fetal heart is diverted through a hole (forman ovale) in the septum to avoid pulmonary circulation.
After birth the umbilical veins become fibrous tissue and the forman ovule begins to close following the first breath.

Fetal Alcohol Syndrome

Cardivascular Disorders
• Heart attack (myocardial infarction)- results from occlusion of cardiac arteries. Ischemia will result followed by tissue death.
• Arteriosclerosis- hardening of the arteries, due to age and high blood pressure
• Artheriosclerosis- hardening of arteries due to excess lipids (cholesterol)
• Embolism- results from a traveling thrombus, can result in stroke.

Coronary Heart Disease
Angina — chest pain that can radiate to (or sometimes is limited to) the shoulders, arms or jaw. Angina usually lasts several minutes and may be related to activity, exercise, large meals, cold or stress. If angina lasts more than 15 minutes, there is a risk that a heart attack may be occurring.
Heart attack symptoms include severe chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating and nausea. Symptoms can be different in men and women, with women more likely to experience unusual fatigue after activity rather than chest pain.

Treatment and Prevention
Prevention• Don't smoke.
• Exercise at least 30 minutes a day.
• Keep high blood pressure, cholesterol and diabetes under control with diet, exercise and, if necessary, medications.
• Eat a diet rich in whole grains, fruits and vegetables and low in saturated fat.
• A daily aspirin can reduce the risk of heart attack, especially among men older than 50 years.