Blood and Blood Vessels
Transcript of Blood and Blood Vessels

Blood & Blood Vessels
SCIENCE BIOLOGY Done by:
- Psalmy
- Joyce
- Xiao Nan
- Fahmi

Blood Contents
Functions of BloodTypes of Blood Components.Blood Components functions.

Functions of BloodIt carries oxygen to cells .

Functions of Blood
• Blood carries waste (carbon dioxide, Urea and lactic acid - via diffusion) to the kidney.

• Part of the body's self-repair mechanism (blood clotting after an open wound in order to stop bleeding - using 'Platelets')
Functions of Blood

• Regulation of body pH. Regulation of core body temperature.
Functions of Blood

Types of Blood Components.
1) Red blood cells (RBCs)2) White Blood Cells (WBCs)3) Platelets (thrombocytes) 4) Plasma

Red blood cells (RBCs / erythrocytes)
• Contains haemogoblin.
• Shaped like slightly indented, fattened disks.
• Blood gets its bright red colour when haemogoblin picks up oxygen in the lungs.
• As the blood travels through the body, the haemogoblin releases oxygen to tissues.
• It has no nucleus.

White Blood Cells (WBCs / leukocytes)
• Key part of the body’s system for defending itself against infection
• Much bigger in size than Red blood Cells• Fewer in number than Red blood cells• Colourless• Contains a nucleus

Platelets (thrombocytes
)- -> Are tiny oval-shaped cells made in the bone marrow.
->They help in the clotting process. When a blood vessel breaks, platelets gather in the area and help seal off the leak.
- -> Platelets survive only about 9 days in the bloodstream and are constantly being replaced by new cells.

Plasma
• Yellow straw coloured liquid.• Contains 90% water, but it also
contains other components such as salts, proteins, lipids and glucose.
• makes up around 55% of the total volume of blood in the human body.

Blood Vessels Content
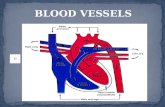
- The main blood vessels connected to the heart.
- The structures of Arteries, Veins and Capillaries.
- The function of the Arteries, Veins and Capillaries.

Main Blood Vessels connected to the heart.
• Aorta• Vena Cava• Pulmonary Vein• Pulmonary Artery

Structures of Arteries • The innermost layer, the tunica intima (also called tunica
interna), is simple squamous epithelium surrounded by a connective tissue basement membrane with elastic fibers. The middle layer, the tunica media, is primarily smooth muscle and is usually the thickest layer. It not only provides support for the vessel but also changes vessel diameter to regulate blood flow and blood pressure. The outermost layer, which attaches the vessel to the surrounding tissue, is the tunica adventitia.

Structures of Veins(:• The walls of veins have the same three layers
as the arteries. Although all the layers are present, there is less smooth muscle and connective tissue. This makes the walls of veins thinner than those of arteries, which is related to the fact that blood in the veins has less pressure than in the arteries. Because the walls of the veins are thinner and less rigid than arteries, veins can hold more blood.

Structures of Capillaries :P
• Smooth muscle cells in the arterioles where they branch to form capillaries regulate blood flow from the arterioles into the capillaries.

Functions of Blood Vessels• #1 Arteries
- Carry blood away from the heart- All arteries carry oxygenated blood except for the pulmonary artery
#2 Veins- Carry blood back to the blood.- All veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the pulmonary vein.
#3 Blood Capillaries- Carry blood from an arteriole(small artery) to a venule(small vein).- In capillaries, the blood is slowed down, giving more time for the exchange of substances.- They branch repeatedly and provide a large surface area for the
exchange of substances between the blood and arteries.

The End !PJXF_Grp_G