Bipolar transistors Two port representation of the bipolar ... › skaidres › Devices ›...
Transcript of Bipolar transistors Two port representation of the bipolar ... › skaidres › Devices ›...

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
1
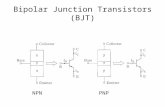
Bipolar transistors
• Two port representation of the bipolar transistor
• Models of bipolar transistors
Objectives:
Systems of r, g and h parameters of BJTs
Meanings of r, g and h parameters
Finding (calculation) of h and other parameters
Methodology of composing of the T-type equivalent circuit for a BJT in its CB
configuration
Calculation of parameters of thr equivalent circuit and application of the circuit

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
2
Two port representation of a BJT
1. I-U characteristics of BJTs are not linear. The powerfull tools of
linear circuit analysis cannot be used.
2. When transistor is used for processing of small signals, only small
parts of non-linear characteristics are used. Then the linear
approximations of the characteristics at the quiescent operating
points are possible.
3. At processing of small signals, the linear models of BJTs can
be used.

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
3
Sets of equations, describing BJTs
2121111 IZIZU +=
2221212 IZIZU +=
2121111 IrIrU +=
2221212 IrIrU +=
2121111 UYUYI +=
2221212 UYUYI +=
2121111 UgUgI +=
2221212 UgUgI +=
2121111 UHIHU += 2121111 UhIhU +=
2221212 UHIHI += 2221212 UhIhI +=
Z – impedance;
r – resistance
Y – admittance;
g – conductance
H, h – hybrid
parameters

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
4
r parameters
2121111 IrIrU +=
2221212 IrIrU +=
021
111 ==
II
Ur
012
112 ==
II
Ur
021
221 ==
II
Ur
012
222 ==
II
Ur
– the input resistance when output is open
– the reverse transfer resistance when the input is open
– the forward transfer resistance when the output is open
– the output resistance when the input is open
1. The open circuit conditions (for alternating current) must be arranged.
2. Difficulties arise when resistances r11 and r21 are measured.

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
5
g parameters
– the input conductance when the output is shortened
– the reverse transfer conductance when the input is shortened
– the forward transfer conductance when the output is shortened
– the output conductance when the input is shortened
1. The short circuit regimes (for alternating voltage) must be arranged.
2. Difficulties arise when conductances g12 and g22 are measured.
021
111 ==
UU
Ig
012
112 ==
UU
Ig
021
221 ==
UU
Ig
012
222 ==
UU
Ig
2121111 UgUgI +=
2221212 UgUgI +=

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
6
h parameters
– input resistance with shortened output
– open circuit reverse voltage gain
– short circuit forward current gain
– output conductance with input open
1. There are no difficulties to arrange output shortened and input open
conditions and measure h parameters.
2. The set of h parameters includes information about current gain:
h21B= –α, h21E = β
2121111 UhIhU +=
2221212 UhIhI +=
021
111 ==
UI
Uh
012
112 ==
IU
Uh
021
221 ==
UI
Ih
012
222 ==
IU
Ih

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
7
Parameters of BJTs
2221
1211
gg
gg
2221
1211
rr
rr
2221
1211
hh
hh
A BJT as a linear network can be represented by three sets of
parameters:
h parameters of a BJT are known. Derive formulas for calculation of
its r parameters.

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
8
2121111 UhIhU +=
2221212 UhIhI +=
2121111 IrIrU +=
2221212 IrIrU +=
Parameters of BJTs
222
122
212
1I
hI
h
hU +−=
222
121
22
2112111 )( I
h
hI
h
hhhU +−=
.1
,
,,
2212
22
2121
22
1212
22
21121111
hr
h
hr
h
hr
h
hhhr
=−=
=−=

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
9
Evaluation of h parameters
QCECEB
BE
21
1E11 const∆
∆
0 UUI
U
UI
Uh
===
==
BQB1CE3CE
BE
BCE
BE
12
1E12
∆
const∆
∆
0 IIUU
U
IU
U
IU
Uh
=−=
==
==

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
10
h parametrų skaičiavimas
QCEC1B3B
1C3C
CEB
C
21
2E21
const∆
∆
0 UUII
II
UI
I
UI
Ih
E =−
−=
==
==
Q12
222 const∆
∆
0 BBCE
CE IIU
I
IU
Ih
===
==
Evaluation of h parameters

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
11
h parametrų skaičiavimasTransistor models
Equivalent circuits of a pnp transistor corresponding to
the Ebers-Moll equations

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
12
h parametrų skaičiavimasThe T-type model of a BJT in its CB configuration
2121111 UhIhU +=
2221212 UhIhI +=

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
13
2B221B212
2B121B111
UhIhI
UhIhU
+=
+=
CB22
EB22
B212
CB22
B12E
B22
B21B12B111
1I
hI
h
hU
Ih
hI
h
hhhU
+−=
+
−=
( )( )( )ECCC
CCEB2
CEBEE1
IαIrU
UIIrU
IIrIrU
+=
++=
++=
( )( ) ( )CBCBKE2
CBEEB1
rrIIrαrU
IrIrrU
+++=
++=
( )B22KB
EBB11
EB
B22B12B
1
1
...
hrr
rαrh
rr
hhr
=+
+−=
=+
=
( )B22C
EB11B
EQQE
1
025,0qk
hr
rhβr
II
T/r
E
≅
−≅
≅≅
The T-type model of a BJT in its CB configuration

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
14
h parametrų skaičiavimash parametrų skaičiavimash parametrų skaičiavimasThe T-type model of a BJT in its CB configuration
CQCQE
025,01
q
k
II
Tr ≅≅
Tπ2
1
f=ατ CB τττ α −≅ EBE / rC τ=CBC Cr=τ
( )EB11B rhr −≅ β CEB22C /1 rhr β≅≅

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
15
The T-type model of a BJT in its CB configuration
A BJT is in its CB configuration. According to I-U characteristics h
parameters were found at the given Q point (emitter current – 15 mA,
collector-base voltage – 5 V): input resistance 4 Ω, emitter current gain –
0,99, output conductance – 50 µS. Sketch the T-type model of the
transistor and find parameters of equivalent circuit elements.

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
16
The T-type model of a BJT in its CB configuration
CQCQE
025,01
q
k
II
Tr ≅≅
Tπ2
1
f=ατ KB τττ α −≅ EBE / rC τ=KBK Cr=τ
( )EB11B rhβr −≅ CEB22C /1 rβhr ≅≅

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
17
The T-type model of a BJT in its CE configuration
( )EKKK IIrU α−=
( )α−= 1KKE rr
( )
( )BKKE
BKKK
11
IIr
IIrU
βαα
α
−=
=
−
−−=

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
18
The T-type model of a BJT in its CE configuration
2E221E212
2E121E111
UhIhI
UhIhU
+=
+=
CE22
BE22
E212
CE22
E12B
E22
E21E12E111
1I
hI
h
hU
Ih
hI
h
hhhU
+−=
+
−=
( )( )( )BCCE
CCBE2
CBEBB1
IIrU
UIIrU
IIrIrU
C β−=
++=
++=
( )( ) ( )CEECBCEE2
CEBEB1
rrIIrrU
IrIrrU
++−=
++=
β
( )
E22E
E22CE
EE11B
EQE22
E12E
11
1
q/k...
hr
hr
rβhr
I
T
h
hr
≅−=
+−=
≅==
I1 = IB
rB
βΙΒ I2 = IC
U1 U2 rE rCE
IE
C B
E

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
19
The T-type model of a BJT in its CE configuration
CQCQE
025,01
q
k
II
Tr ≅≅
βωω
βββ
/j1
0
+=⇒ 0T / βff β ≅
)(, CEE KCC
)1(EE11B βrhr +−= E22CE /1 hr ≅
CCE CβC ≅
B
rB
βΙΒ
CE rE
rCE
C
E
CCE

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
20
Composing and application of the T-type equivalent
circuit of a BJT in its CE configuration
A BJT is in its CE configuration. At the given Q-point (base current 0.1 mA,
CE voltage 5 V) the input resistance is 300 Ω, the base current gain is 100, and
the output conductance is 200 µS.
Sketch the equivalent circuit of the BJT.
Find the parameters of the circuit.
Find the voltage gain at input voltage of 10 mV and load resistance of 300 Ω.

ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI 2009
VGTU EF ESK [email protected]
21
Composing and application of the T-type equivalent
circuit of a BJT in its CE configuration
CQCQE
025,0
q
k
II
1Tr ≅≅ EB11B )1( rhr +−≅ β CEB22C β/1 rhr ≅≅
I1 = IB
rB
βΙΒ I2 = IC
U1 U2 rE rCE
IE
C B
E