BIOLOGY REVIEW. Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function B.5 The student knows how an...
-
Upload
scot-flynn -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of BIOLOGY REVIEW. Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function B.5 The student knows how an...

BIOLO
G
Y REVIE
W

Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function
B.5 The student knows how an organism grows and the importance of cell differentiation.
(A) describe the stages of the cell cycle, including deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms.

CELL CYCLE
Eukaryotes’ have a cell cycle which consists of
Four Phases:
1.G1:
2.S:
3.G2:
4.M:
Inte
rph
ase

INTERPHASE- S PHASE: DNA REPLICATION
Before a cell divides, it duplicates its DNA in a copying process called replication. This process, which occurs in the S phase of interphase of the cell cycle, ensures that each resulting cell has the same complete set of DNA molecules.
DNA helicase:
DNA polymerase:

M PHASEThe M phase of the cell cycle, which follows interphase, produces two daughter cells. The M phase takes its name from the processes of mitosis. During the normal cell cycle, interphase can be quite long. In contrast, the process of cell division usually takes place quickly.
The M phase occurs in two main stages.
•The first stage of the process, division of the cell nucleus is called mitosis.
•The second stage, the division of the cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.

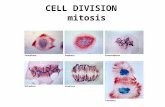
4 STAGES OF MITOSIS
P
M
A
T
Source: Drawing adapted from Mitosis, Dr. Martin Huss, Arkansas State

CYTOKINESIS
As a result of mitosis, two nuclei each with a duplicate set of chromosomes are formed. All that remains to complete the M phase of the cycle is cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm. Cytokinesis usually occurs at the same time as telophase.
Once cytokinesis is complete two new daughter cells are formed. Each new daughter cell will enter into interphase.

One division2n 2n (same number of chromosomes)
Results in 2 genetically identical cells

MITOSIS VS. MEIOSISMitosisProduces body cells(Somatic
cells for growth and repair)Daughter cells diploid(2N)Two daughter cells producedIn metaphase chromosomes
line up singlyOne nuclear divisionDaughter cells have two sets
of chromosomes(pairs)Daughter cells are genetically
identical to the parent cellInsures that all daughter cells
are genetically identical
Meiosis• Produces sex cells(Gametes for
sexual reproduction)• Daughter cells haploid(N)• Four daughter cells produced• In metaphase I chromosomes line
up as homologous pairs• Two nuclear divisions• Daughter cells have only one
member of each pair of chromosomes
• Daughter cells have one-half of the genes from the parent cell
• Generates genetic diversity through crossing over and random separation of homologous pairs of chromosomes

Reporting Category 2: Mechanisms of Genetics
The student will demonstrate an understanding of the mechanisms of genetics. (B.6) Science concepts. The student knows the mechanisms of genetics, including the role of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to (A) identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA;

DNA
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides.A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a sugar, a phosphate and one of four bases
In DNA, the bases are A, T, C, and G
DNA’s shape is a double helixThe two strands are held together by HYDROGEN bonds
A binds to TC binds with G

DNA REPLICATION• Process of DNA copying itself• Steps
•DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break)•Each side acts as a template•New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules•Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand.
• Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis)


PROTEIN SYNTHESISRemember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus
Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein
In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus
mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome
In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the protein on the ribosome.
Made of amino acids

DNA mRNA protein

CAN YOU IDENTIFY THE PARTS?1. DNA
2. mRNA
3. Nucleus
4. Cytoplasm
5. Ribosome
6. Codon
7. Anticodon
8. tRNA
9. Amino acid
10. Protein (polypeptide)

READING THE CODON CHARTBe sure to use
mRNA
You won’t have to memorize this!
What amino acid is coded for by the DNA
ATA GAGFirst convert DNA to mRNA
ATA GAGUAU CUC
UAU = tyrCUC = Leu

GENETICSThis diagram shows the cross between 2 heterozygous purple flowersCross is: Bb x Bb
Notice that 75% are purple and 25% white

We have two genes for each trait – this is our GENOTYPE
One gene came from mom, one from dad
If the genes are alike, the individual is homozygous (RR, rr)
If the genes are different , they are heterozygous (Rr)
Some genes are dominant and others are recessive
We only show a recessive trait if we have no dominant geneRR and Rr would “look” dominantrr would look recessive

GENETIC TECHNOLOGYTRANSGENIC ORGANISMS
Organisms that have 2 different kinds of DNA
Gene cloning
Uses bacteria to make human proteins like insulin
DNA FINGERPRINTING
Use gel electrophoresis to compare DNA fragments
IF DNA matches, it’s from the same individual
Evidence points to suspect 2

Reporting Category 1:Cell Structure and Function
B.5 The student knows how an organism grows and the importance of cell differentiation.
(C) describe the roles of DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and environmental factors in cell differentiation.

DNA
What is the basic structure of DNA?
What are the building blocks of DNA?
What are the parts of a nucleotide?
The sides of the DNA ladder are made up of what 2 alternating molecules?
What does it mean to have anti-parallel strands?
What makes up the steps or rungs of the ladder?
What is special about the order of the nitrogen bases?
What are the 4 nitrogen bases?
According to the base pairing rules adenine always pairs with __________ .
What type of bond hold the nitrogen bases together?

DNA VOCABULARY REVIEW

BUILDING A DNA MODEL
Match the nucleotides on the far right with the nucleotides in the box to complete the DNA strand.
Adenine - ThymineGuanine - Cytosine

PROTEIN SYNTHESISGenes carry the information needed by cells to produce proteins, and proteins determine traits such as coloration. So how are proteins made?
Protein synthesis is the process in which cells build proteins. There are 2 main steps in protein synthesis, transcription and translation.
In transcription segments of DNA serve as template to produce complementary mRNA molecules.
In translation the code carried by mRNA is fed into a ribosome "machine" and causes specific amino acids to be linked together to form a protein.

TRANSCRIPTIONIn eukaryotic cells, mRNA is produced in the cell’s nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm to play a role in the production of proteins. Transcription requires an enzyme, known as RNA polymerase is similar to DNA polymerase.
bonds A-U (Uracil not Thymine) and C-G
The genetic code is read three “letters” at a time so that each “word” is three bases long and corresponds to a single amino acid. Each three letter word is called a codon.

TRANSLATIONThe sequence of nucleotide bases in an mRNA molecule is a set of instructions that gives the order in which amino acids should be joined to produce a polypeptide. Once the polypeptide is complete, it then folds into its final shape or joins with other polypeptides to become a functional protein.
Translation uses another type of RNA known as tRNA. Each tRNA molecule carries just one kind of amino acid. In addition, each tRNA molecule has three unpaired bases, called the anticodon

AMINO ACID CHART

PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER

DNA / RNACarry genetic information
Made of a chain of nucleotides
Nucleotides contain a sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogen base

DNA / RNA
DNA
Double stranded
“Double Helix”
Four base pairs: ATGC
Sugar is Deoxyribose
Found in nucleus
RNA
Single stranded
Four base pairs:
AUCG
Sugar is Ribose

BASE PAIR RULE
In DNA,
Adenine always pairs with Thymine, and
Guanine always pairs with Cytosine

REPLICATIONMaking of an identical
strand of DNA
“semi” conservative

CENTRAL DOGMA
DNA RNA protein trait

TRANSCRIPTIONDNAmRNA
Occurs in nucleus
Complementary mRNA strand is produced from a segment of DNA

TRANSLATIONConnects amino acids in the correct order to make a protein
Occurs in the cytoplasm within the ribosomes
A- amino acidB- tRNAC- anticodonD- codonE- mRNAF- RibosomeG-polypeptide

CODONSequence of three mRNA nucleotides that code for an amino acid

MUTATIONSChange in DNA code
May cause a change in protein produced
NOT always harmful
Sickle Cell Mutation


Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
When DNA is extracted from the red algae Polyides rotundus, 32% of the nitrogen bases are guanine. Based on this information, what percentage of the bases are most likely adenine?
A. 9%B. 18%C. 36%D. 64%

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
The genetic instructions for an organism are contained in the DNA molecule. The instructions for a specific organism are determined by the —
A. number of nucleic acids in the DNA moleculeB. length of the DNA moleculeC. sequence of the nitrogen bases in the DNA moleculeD. type of nitrogen bases in the DNA molecule

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
The flow of information during gene expression is —

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
The amino acid sequence methionine, tryptophan, and aspartic acid is coded by which set of DNA bases?
A. AUGUGGGAUB. TTCTCCCTTC. UACACCGUAD. TACACCCTA

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
The genes of an organism control all its biological processes by controlling the
A. sequence of nitrogen bases in a DNA moleculeB. synthesis of proteins in each cellC. number of chromosomes in each cellD. type of nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
For a mutation to be evolutionarily significant it—
A. changes the type of protein being producedB. has a neutral effect on an organismC. provides an advantage to the speciesD. causes the loss of a gene

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
The DNA strand TAGTTGTTTTGC codes for the amino acid sequence isoleucine, aspartic acid, lysine, and threonine.
If a point mutation takes place in the DNA, and the first triplet becomes TAT, what effect will this have on the amino acid sequence?
A. The first amino acid in the sequence remains isoleucine.B. Isoleucine is replaced by methionine in the amino acid sequence.C. The amino acid sequence now includes lysine.D. The last amino acid in the sequence will become serine.

Approximately 900 people live in the small isolated village of Limone in northern Italy. About 40 of thevillagers have high levels of the bad blood cholesterol and low levels of the good cholesterol. However,thy suffer no harmful effects. Doctors have found that these villagers produce a protein that is efficient atclearing the bad type of cholesterol from arterial plaque and moving it to the liver. Which of the followingbest explains this phenomenon?A. The villagers take vitamin and mineral supplements.B. There are chemicals in the water that flush out the cholesterol.C. The villagers eat a diet consisting mostly of meat and cheese.D. There is a mutation in the genes of some villagers.
Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
Approximately 900 people live in the small isolated village of Limone in northern Italy. About 40 of the villagers have high levels of the bad blood cholesterol and low levels of the good cholesterol. However, they suffer no harmful effects. Doctors have found that these villagers produce a protein that is efficient at clearing the bad type of cholesterol from arterial plaque and moving it to the liver. Which of the following best explains this phenomenon?
A. The villagers take vitamin and mineral supplements.B. There are chemicals in the water that flush out the cholesterol.C. The villagers eat a diet consisting mostly of meat and cheese.D. There is a mutation in the genes of some villagers.

Charles A. Dana Center Science TEKS Toolkit www.sciencetekstoolkit.org
During cell division, if a chromosome breaks, a mutation occurs. Which of the following processes prevent or minimize chromosome breakage during cell division?
A The chromosomes tightly coil before the nucleus divides.B. Protein synthesis takes place during the division of the cytoplasm.C. Hydrogen bonds form between nitrogen bases.D. An enzyme rearranges the nitrogen bases in a gene.


A photomicrograph of onion root tip cells during mitosis is shown below.© iStockphoto.com/Alan John Lander PhillipsWhich phase of mitosis is occurring in the cell indicated by the arrow?F ProphaseG MetaphaseH AnaphaseJ Telophase
A photomicrograph of onion root tip cells during mitosis is shown below.
Which phase of mitosis is occurring in the cell indicated by the arrow?
F ProphaseG MetaphaseH AnaphaseJ Telophase
© iStockphoto.com/Alan John Lander Phillips

A model of a DNA molecule is shown below.
The arrow indicates —
F the bond between adjacent phosphate and deoxyribose moleculesG the junction of introns and exons in the sense strand of DNAH the hydrogen bond between complementary nucleotidesJ the junction of a codon and a DNA triplet


Characteristics such as a widow’s peak or attached earlobes are determined by the genetic code. Which components of DNA are referred to as the genetic code?
F Phosphate groupsG Nitrogenous basesH Deoxyribose sugarsJ Hydrogen bonds

In a DNA, the letters A, T, C, and G represent
A bases.B sugars.C proteins.D amino acids.

The corresponding amino acids are brought into a cell's ribosome by which type of RNA?
A messenger RNAB ribosomal RNAC transfer RNAD replication RNA

Which of these must occur during S phase of the cell cycle so that two daughter cells can be produced during M phase?
A The DNA must be replicated.B The chromosomes must be joined.C The cytoplasm must be separated.D The cell membrane must be expanded

The diagram below represents the cell cycle.
When cells leave the cell cycle, they exit during G1 phase and then enter G0 phase, a resting period. Most normal cells can leave G0 phase and reenter the cell cycle at G1 phase before entering S phase. Cancer cells are different because they cannot enter G0 phase and are likely to do which of the following?
A Fail to complete S phase C Repeat the cell cycle continuouslyB Mutate during G phase D Die after completing mitosis

The _____ contains spindle fibers, centrioles, and aster fibers.
A spindle apparatusB centromereC chromosomeD nuclear envelope

What phase of cell division comes immediately after the phase shown below?
A cytokinesis C cyclin phaseB prophase D anaphase

Which of these events does not occur during telophase?
A chromosomes arrive at cellular polesB cytoplasm splits in twoC chromosomes relaxD spindle apparatus disassembles

What structures are lined up at the center of this cell?
A cyclins C chromosomesB single chromatids D kinases