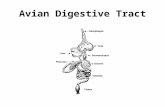
Biology 212 Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Thompson Digestive System.
-
Upload
laureen-howard -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
1
Transcript of Biology 212 Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Thompson Digestive System.
Organs
Two functional groups:
1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal tract
2. Accessory Digestive Organs
Esophagus:
Propels food from pharynx to stomachPosterior to trachea & heart
Mucosa:
Submucosa:
Muscularis Externa:
Adventitia:
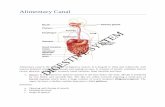
Stomach:
Storage: Highly distensible Delivers slowly to duodenum Secretion of mucous, hydrochloric acid Secretion of enzyme - Digestion of proteins Secretion of enzyme - Digestion of lipids Secretion of enzyme - Absorption of B12
Pancreas:
Produces many different digestive enzymes:
Amylases: starches & monosaccharides glycogen & disaccharides
Proteases: proteins amino acids
Lipases: diglycerides & fatty acids triglycerides & glycerol
Nucleases: nucleic acids nucleotides
Digestion:
Breakdown of food into molecules small enough to be absorbed from the lumen of the intestine into its blood vessels.
Four types of molecules = more than 95% of total:
Also: Nucleic acids Ions (electrolytes, minerals) Vitamins ? Others ?
Mechanical digestion
Chemical digestion
Absorption of nutrients electrolytes vitamins
Absorption of water








































![Digestive System Anatomy Practical [PHL 212]. The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract & accessory digestive organs: a series of hollow.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649ce35503460f949aef0e/digestive-system-anatomy-practical-phl-212-the-digestive-system-is-made.jpg)












![Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Digestive System Anatomy Practical [PHL 212]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c0031a28abf838cc3c9a/dr-mohammad-nazam-ansari-digestive-system-anatomy-practical-phl-212.jpg)