BIOLOGY 1 WORKSHEET I Chemistry, Digestion,...
-
Upload
hoangduong -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of BIOLOGY 1 WORKSHEET I Chemistry, Digestion,...
1. What does the first law of thermodynamics state? How is this law related to the efficiencyof photosynthesis?
2. What does the second law of thermodynamics state? Give a biological example of thesecond law in action.
3. Describe the difference between potential and kinetic energy
4. Complete the following diagram:
Page 2
5. Define and give an example the following terms:Definition Example
a. Producer: __________________________________ ___________
b. Autotrophic __________________________________ ___________
c. Heterotrophic __________________________________ ___________
d. Trophic level __________________________________ ___________
e. Primary Consumer_______________________________ ___________
f. Secondary consumer______________________________ ___________
g. Omnivore __________________________________ ___________
6. Based on the information in the pyramed of biomass, would you feed a starving countryrice and beans or steak and lamb chops? Explain.
7. The charge of a proton is __________ and the weight of a proton is ________.
8. The charge of a neutron is _________ and the weight of a neutron is _______.
9. The charge of an electron is _______ and the weight of an electron is _______.
10. Atom X has 5 protons and an atomic weight of 15.
a. How many electrons does it have?_____
b. How many neutrons does it have?_____
c. How many electrons are in the:
1) first energy level?_____
2) second energy level?_____
3) third energy level?_____
Page 3
11. Atom Y has 6 protons and 6 neutrons:
a. What is the atomic weight of this atom?_______________
b. If the first orbital was full and the second orbital has 4 electrons, how manyelectrons would this atom have?______
12. The atomic number of an atom is equal to ?_________________________________
13. The weight of an atom is equal to?________________________________________
14. What types of chemical bonds form the following molecules?
a. Na + Cl ----- NaCl: ____________________________________+ -
2b. Ca + 2 Cl ---- CaCl : _________________________________+2 -
6 12 6 6 12 6 12 22 11 2c. C H O + C H O — C H O + H O: __________________
2 d. H + H----- H : ________________________________________
15. Define:a. Acid
b. Base
c. Molecule
d. Ion
e. Ionic bond
f. Covalent bond
Page 4
16. What would be the pH:
a. A strong acid?__________
b. A weak base?__________
c. Water?________________
17. Consider the following solutions:I. pH = 6II. pH = 8III. pH = 14IV. pH = 2
a. Which solution is a weak acid?________________________b. Which solution is a weak base?________________________c. Which solution is a strong base?_______________________d. Which solution is a strong acid?_______________________e. Estimate the pH of distilled water._____________________
18. What kind of bond forms between water molecules? Is this a weak or strong bond?
19. What is a buffer?
20. Sucrose = glucose + __________
21. Lactose = glucose + __________
22. Why is the shape of a protein important? What does the term denaturization mean?
23. What is the storage form of glucose in plants? In animals?___________ ___________
24. How might a protein be denatured? If an enzyme is denatured what would be theconsequence?
Page 5
25. Describe the relationship between enzymes, pH, and temperature. Include the termsprotein, denature, shape, and function in your discussion.
26. If you were the head of the MSAC cross country team would you feed them a pastadinner or prime rib the night before a race? Explain.
27. Describe the difference between starch and glycogen.
28. A triglyceride is formed by combining glycerol with three ____________________.
29. Describe the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Is there arelationship between a diet high in saturated fats and atherosclerosis? Explain.
Saturated Unsaturated
Atherosclerosis is a disease that is associated with:____________________________
30. The following questions can be answered using your book. Read the section on aminoacids and proteins.
A. Amino acids contain a chemical element not found in carbohydrates of lipids.What element is this?
B. A bond that forms between two amino acids is called a?_________________
C. A chain of amino acids is called a?____________________
D. The primary structure of a protein is its specific sequence of?_____________
E. Discuss the difference between the tertiary structure and the quaternary structureof a protein.
Page 6
31. Humans die of heat stroke when their body temperature exceeds 106 - 108 F. At theseo
temperatures human proteins start to denature. What does the term denature mean? Howdoes this relate to a person dying of heat stroke?
32. What are the functions of the following:
A. Stomach: _____________________________________________________
B. Liver: _____________________________________________________
C. Villi: _____________________________________________________
D. Lacteals: _____________________________________________________
E. Pancreas: _____________________________________________________
F. Gall Bladder: _____________________________________________________
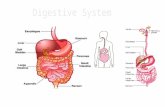
33. Label the following diagram:
Page 7
34. Matching:
a._____Initial site of starch digestion 1. Amylase
b._____Initial site of protein digestion 2. Bicarbonate or Sodium Bicarbonate
c._____Responsible for detoxification of 3. Cardiac sphincter
drugs such as alcohol 4. Duodenum
d._____Absorption of water and minerals 5. Esophagus
e._____Primary site of absorption of nutrients 6. Gall bladder
f._____Common passageway for air and food 7. HCl
g._____Site of bile production (manufacture) 8. Ileum
h._____Site of bile storage 9. Insulin
I._____Bile is secreted into the 10. Jejunum
j._____Transfer of fat droplets from the 11. Lacteals
intestine to the bloodstream 12. Large intestine
k._____Increases absorptive surface area 13. Larynx
of the small intestine 14. Lipase
l._____Enzyme responsible for protein 15. Liver
digestion in the stomach 16. Mouth
m._____Substance used to maintain the pH 17. Pancreas
of the stomach 18. Pepsin
n._____Substance used to maintain the pH 19. Pharynx
of the duodenum 20. Pyloric sphincter
o._____Enzyme used for starch digestion in 21. Small intestine
the mouth and duodenum 22. Stomach
p._____Primarily functions in storage 23. Trachea
q._____Secretes sodium bicarbonate into small intestine 24. Protease
r._____Enzyme responsible for fat digestion 25. Villi
s._____Enzyme secreted by the pancreas for
protein digestion
Page 8
35. Draw the structure of the cell membrane indicating the bilayer of phospholipids, and the
membrane proteins.
36. Red Blood cells are placed in the following solutions:
I: Distilled water II: 25% NaCl III: 0.9% NaCl
a. Which solution is hyposmotic?_________________________
b. Which solution is isosmotic?__________________________
c. Which solution is hyperosmotic?_______________________
d. In which solution would you expect the cell to burst?___
e. In which solution would you expect the cell to lose water?___
37. The diagram shows a plant cell after it was placed in a hyperosmotic solution. Identify 1-5.
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
4. ____________________
5. ____________________
Page 9
38. Matching:
a._____Site of protein synthesis 1. Atomic weight
b._____Site of DNA replication 2. Charge
c._____Site of aerobic energy production 3. Chloroplast
d._____Site of detoxification of drugs in the cell 4. Cristae
e._____Packages protein vesicles pinched 5. Eukaryotic
off from rough endoplasmic reticulum
6. Golgi apparatus
f._____The building blocks of cilia and
flagella 7. Stroma
g._____Fluid in the chloroplast 8. Kinetic energy
h._____Fluid in the mitochondria 9. Lysosomes
I._____Inner membrane of the mitochondria 10. Matrix
j._____Cells without a nucleus 11. Microtubules
k._____Cells with a nucleus 12. Mitochondria
l._____ #Protons + #Neutrons = _____ 13. Smooth ER
m._____ #Protons - #Electrons = _____ 14. Nucleus
n._____Contains digestive enzymes 15. Rough ER
o._____Site of photosynthesis 16. Ribosomes
17. Centrioles
18. Prokaryotic
Page 10
40. Draw the following cellular organelles and list their functions:
a. Nucleus with nucleolus
b. Chloroplast with stroma and granum
c. Mitochondria with cristae and matrix
d. Plant cell showing cell wall, cell membrane, chloroplast, and vacuole.
41. Label the diagram below:
Page 12
42. Define the following terms:
a. Hydrophobic
b. Cytoplasm
c. Hydrophilic
d. Hyposmotic solution
e. Hyperosmotic solution
f. Osmosis
g. Brownian movement
h. Active transport
i. Phagocytosis
j. Pseudopod
k. Cytoplasmic streaming
l. Flagella
m. Passive transport
n. Exosytosis
Page 13
43. Questions from chapter 4 (pp 14 - 20)
----------a. Still Layer of air that surrounds any object 1. Boundary Layer
----------b. Primary source of body temperature is metabolism 2. Conduction
----------c. Low body temperature 3. Convection
----------d. Primary source of body temperature is environment 4. Desert Iguana
----------e. Heat loss from body to cold air 5. Eccritic
----------f. Heat loss due to wind currents 6. Evaporation
----------g. Animal with a fluctuating body temperature 7. Ectothermic
----------h. Animal that maintains a constant body temperature 8. Endothermic
----------I. To get through a cold night small endotherms allow 9. Horned lizard
their metabolism and body temperature to drop 10. Chuckwalla
----------j. This animal can absorb water from its urinary bladder 11. Increase
----------k. This small desert endotherm is poikilothermic 12. Hypothermia
----------l. This desert lizards has melanophores which allow 13. Decrease
it to change color 14. Homeothermic
----------m. Lowering of metabolic rate during the winter 15. Antelope ground squirrel
----------n. The most effective mode of heat loss in the desert 16. Desert tortoise
----------o. Lizard with a very high critical thermal maximum 17. Desert spiny lizard
----------p. Fish with a very high critical thermal maximum 18. Torpor
----------q. Range of temperatures in which energy 19. Hibernation
expended in thermoregulation is minimal 20. Bass
21. Pupfish
22. Trout
23. Radiation
24. Poikilothermic
44. Is behavior important to thermoregulation? Explain.
45. Define torpor. How does torpor differ from hibernation?
Page 14
46. Define the following terms:
A. Radiation ____________________________________________________
B. Conduction ____________________________________________________
C. Convection ____________________________________________________
D. Evaporation ____________________________________________________
E. Ectothermic ____________________________________________________
F. Endothermic ____________________________________________________
G. Poikilothermic ____________________________________________________
47. Why is a lizard able to maintain a fairly constant body temperature in nature, yet its body
temperature is equal to cage temperature in the laboratory.
48. Give at least two reasons why it an advantage to be an ectotherm in a desert
environment? Explain.
Page 15
49. List adaptations found in the following desert animals that enable existence in such a
harsh environment.
Animal Adaptation
Horned lizard ______________________________________________
Kangaroo rat ______________________________________________
Kit fox ______________________________________________
Antelope ground squirrel ___________________________________________
Desert tortoise ______________________________________________
Page 16