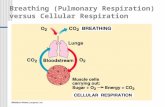
Breathing (Pulmonary Respiration) versus Cellular Respiration.
Biology 1-2. Respiration The respiratory system handles gas exchange between the body and the...
-
Upload
percival-rich -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Biology 1-2. Respiration The respiratory system handles gas exchange between the body and the...
RespirationThe respiratory system handles gas
exchange between the body and the environment.Brings in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Oxygen is for cellular respiration. Carbon dioxide is made during cellular respiration.
The Respiratory SystemOxygen enters the body through the nasal
cavity.Incoming air is warmed, filtered and sampled
for odors. Molecules land in olfactory organs, stimulating
nerve endings and sending signals to the brain. Located at the top of the nasal cavity. Brain interprets the signals as odors.
The LarynxPasses from the nasal cavity to the pharynx
and into the larynx.Sits in front of the esophagus and made of
cartilage. Cartilage-a tough, flexible connective tissue.
The Larynx cont’dThe larynx connects the pharynx to the
trachea.Contains the vocal cords.Speech occurs when air leaving the lungs
vibrates the vocal cords. The mouth, larynx and tongue shape the air,
creating different sounds.
The Trachea and LungsThe trachea
carries oxygen to the lungs.Made of rings of
cartilage.Lung-internal sac,
lined with moist epithelial tissue where gas exchange takes place.
Trachea and Lungs cont’dThe trachea splits into two bronchi (left and
right bronchus) before entering the lungs.Made of cartilage.Inside of each lung the bronchus splits
numerous times into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles.
The AlveoliEach bronchiole
ends in a cluster of air sacs called alveoli.Each alveolus is
made of a thin layer of epithelial tissue.
Alveoli cont’dThe alveolus is where
oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves.
Alveoli increase surface area without increasing lung volume.
Alveoli cont’dThe passageways and tissues of the
respiratory system are coated with mucus and lined with cilia.Mucus traps foreign particles, preventing them
from harming the lungs.Cilia-small hair-like fibers.
Beat together in a rhythmic fashion to remove particles from the lungs.
BreathingThe size of the lungs is controlled by muscles
in the chest.The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle directly
under the lungs.The intercostals are between the ribs.
Breathing cont’dInhalation begins at a signal from the brain.
Diaphragm and intercostals contract, widening and lengthening the lungs. Air pulled in.
Diaphragm and intercostals relax, lungs shrink back to normal size. Air is exhaled.
Breathing cont’dRed blood cells carry oxygen.
Red blood cells have a protein, hemoglobin, that is attracted to both oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Oxygen in the blood bonds to hemoglobin and is carried from the lungs.
Breathing cont’dOxygen enters the blood along its
concentration gradient.PO2 lungs > PO2 blood > PO2 tissuesCarbon dioxide is the reverse.
PCO2 tissues > PCO2 blood > PCO2 lungs
CO2 levels are monitored and used to adjust breathing. High CO2 levels increases breathing rate.