Biological Motivation Chapter 6 Key Terms: Motivation, Homeostasis, Drive Reduction Theory,...
-
Upload
scott-cummings -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Biological Motivation Chapter 6 Key Terms: Motivation, Homeostasis, Drive Reduction Theory,...

Biological MotivationChapter 6Key Terms: Motivation, Homeostasis, Drive Reduction Theory, Hypothalamus

Motivation Define the following:
Motivation Biological
What might biological motivation mean? Examples?

Homeostasis Tendency of all
organisms to correct imbalances and deviation from their normal state
Example: Fever/sweating

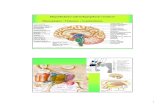
Hunger Lateral
Hypothalamus: makes us eat More active when
cold Ventromedial
Hypothalamus: makes us stop eating More active when
hot

Glucostatic Theory Hypothalamus
monitors blood glucose
BG drops, LH stimulated
Insulin released After meal: liver
secretes glucagon

Set-Point Theory Set-Point: weight
around which day-to-day weight fluctuates
If VMH is destroyed, you will not eat until you explode

Obesity Dr. Stanley
Schachter Obese people
respond to external cues for eating Cracker & Almond
experiments

Drive Reduction Theory Clark Hull (1943) All motivation
comes from physiological needs
Deprivation of Need
Random activity
Drive reduced

Pulling it Apart Not all drives have
physiological origins
Harry Harlow monkey study
Pleasure centers in the brain are drives for stimulation