Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool August 2012 Training · 2017-11-06 · bighorn sheep viability...
Transcript of Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool August 2012 Training · 2017-11-06 · bighorn sheep viability...
3
Training Agenda
• Welcome and Introductions
• History/background of the project
• Conceptual model
• Questions about the history, background and model
• Input data and requirements
• Description and demonstration of the tool
• Discussion of the results
• Expectations for the tool
• Questions
Welcome
4
Melanie Woolever USFS R2 [email protected]
Clint McCarthy USFS R4 [email protected]
Chans O’Brien Payette NF [email protected]
Sanford Moss USFS R4 [email protected]
Josh O’Brien Contractor [email protected]
Stefan Orehovec Critigen [email protected]
Introductions
5
• 2005 - Forest Service Chief remands the 2003
Forest Plan decision as it pertains to bighorn
sheep and its habitat – noncompliance with NFMA
viability issues
• Requires the Regional Forester to conduct a
bighorn sheep viability analysis for the Payette NF
• Requires amendment Forest Plan to add direction
that ensures bighorn sheep viability
• Focus of the viability analysis on implications of
disease transmission between domestic sheep
and bighorn sheep as the primary concern
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
History
6
• The Payette NF focused on a way to estimate the
risk of contact between bighorn and domestic
sheep due to foray movements by bighorn sheep
• The Forest developed a methodology for
calculating the probability that bighorn sheep will
foray to land outside their home range, specifically
to domestic sheep allotments
• This methodology was applied to the home range
of the bighorn sheep herds and domestic sheep
allotments in the Payette National Forest
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
History (cont)
7
• Implications of Payette Analysis for Other Forests
– Disease transmission is a west-wide concern for
bighorn sheep populations
– Expectation that we address potential risks of
disease transmission in grazing analyses
– Species status (sensitive in three regions, 1
threatened DPS)
– Repeated and on-going die-offs (e.g. 2009/2010
winter)
– Need for consistency in assessing contact and
disease transmission potential
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
History (cont)
8
• Level/Intensity of analyses conducted for Payette
not feasible for other Forests
– Availability of data
– Complexity of analysis
– Time to complete analysis
• Use concepts of Payette analysis to formulate a
risk assessment process for multiple forests to
accommodate range NEPA analysis requisites
• Once the methodology was tested and accepted
the Forest Service contracted with Critigen LLC to
adapt the methodology into an ArcMap tool for use
in other national forests.
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
History (cont)
9
• The goal of the tool is to make the analysis of
home range, foray probability and risk of contact
easy enough that it can be carried out for other
bighorn sheep populations using available local
data and a minimum of effort on the part of the GIS
analyst
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
History (cont)
10
• Even one interspecies contact can result in a
bighorn herd die-off.
• Domestic sheep and bighorn sheep are attracted
to one another.
• Bighorn sheep carry out occasional long-distance
exploratory movements (aka ‘forays’).
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Biological Considerations
11
• No vaccines available.
• Treatment of infected animals is difficult and
ineffective.
• Minimizing contact and separating the species are
key goals. How much separation is necessary?
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Management Considerations
12
Melanie Woolever USFS R2 [email protected]
Clint McCarthy USFS R4 [email protected]
Chans O’Brien Payette NF [email protected]
Sanford Moss USFS R4 [email protected]
Josh O’Brien Contractor [email protected]
USFS Points of Contact
13
• Foray probability model has
four components:
– Estimate of herd home range
– Frequency of forays
– Distance distribution of forays
– Estimate of habitat selection
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Conceptual Model
15
• Multiple steps consolidated and automated into
single workflow with intuitive interface to generate
replicable analysis
• Integration of non-ESRI tools: R, StatconnDCOM
• Migration of standard workflow to ArcGIS 10
• ArcGIS v 10 add-in has enabled portability
• Applicable to a diversity of geographies and
National Forests
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Requirements
16
• These programs have been approved for use
on USFS computers and will be provided with
the tool distribution
– ArcMap 10.0
– R for Windows vR-2.14.2
– StatconnDCOM 3.3 – 0B2
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Software Requirements
Details on these requirements can be found in the Requirements for Running
the Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Add-In section of the user guide.
17
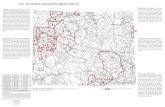
• Spatial Data
– Telemetry points or drawn home range polygon
– Biologists and State wildlife agencies
• Habitat preference raster
– T drive
• Allotment boundary polygons
– T drive or Infra Database
• Tabular Data
– Foray distance distribution
• Default provided with tool
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Data File Requirements
Details on these requirements can be found in the Data and Data Files section
in the user guide.
19
• Home Range Tool Component
– Input Points
– Animal ID
– Minimum Points per Animal
– Bandwidth Estimator
– Percent of h_ref
– Max Isopleth Quantile
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Input Data - Home Range
Details on these requirements can be found in the Data and Data Files section
in the user guide.
20
• Home Range Calculation Data
– Core Herd Home Range Output
Name
– Telemetry/Observation Layer (Point)
– Animal ID Field
– Minimum Points Per Animal
– Bandwidth Estimator
• Reference
• Plug-in
– Pecent of h_ref
– Max Isopleth Quantile
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool Component:
Home Range
Details on these requirements can be found in the Core Herd Home Range
Calculation section in the user guide.
21
• Reference (Href)
bandwidth estimator
produces a larger
rounder area estimate
• Plug-in (Hpi) bandwidth
estimator produces a
smaller narrower area
estimate
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool Component:
Bandwidth Estimator results
23
• Foray Analysis Tool Component
– Habitat Classes
– Habitat Preferences
– Ram Distance Distribution Tabular File
– Ewe Distance Distribution Tabular File
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Input Data - Foray Analysis
Details on these requirements can be found in the Data and Data Files section
in the user guide.
24
• Three habitat classes:
– ‘Habitat’
– ‘Connective habitat’
• Within 350 meters of habitat.
– ‘Non-habitat’
• Everywhere else
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Foray Analysis
25
Ewes Rams
Animals leaving CHHR at least once
6.5% (14/215) 28.8% (30/104)
Animal-years with at least one foray
1.5% (15 / 985) 14.1% (44 / 311)
Telemetry points outside of CHHR
0.2% (29 / 17258) 4.4% (160 / 3674)
(Based on ~22000 points, from 12 years and 13 Hells Canyon area herds)
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Foray Analysis
26
• Ram forays often
exceed 10 km.
• In HC telemetry data,
max ram foray: 35 km
max ewe foray: 54 km
• Observed HC foray
distances consistent
with other reports.
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Foray Analysis
27
• Foray Analysis Calculation Data
– Foray Analysis Output Name
– Core Herd Home Range Layer
(Polygon)
– Habitat Layer (Raster)
• Habit Class 1 - Relative Preference
• Habit Class 2 - Relative Preference
• Habit Class 5 - Relative Preference
– Ram Distance Distribution File
– Ewe Distance Distribution File
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool Component:
Foray Analysis
Details on these requirements can be found in the Foray Analysis Range
Calculation section in the user guide
30
• Contact Analysis Tool Component
– Allotment Polygons
– Herd Size
– Herd Sex Ratio
– Foray Probability
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Input Data - Contact Analysis
Details on these requirements can be found in the Data and Data Files section
in the user guide.
31
• Contact Analysis Calculation Data
– Contact Analysis Output Name
– Foray Analysis Output Directory
– Allotment Layer (Polygon)
– Allotment ID Field
– Herd Size
– Herd Sex Ratio
– Foray Probability
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool Component:
Contact Analysis
Details on these requirements can be found in the Contact Analysis Range
Calculation section in the user guide.
32
• Intersecting Allotments
– The model assumes that any allotment which
intersects the home range will result in contact and
therefore is not included in the analysis results.
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool Component:
Contact Analysis
36
• Discussion of Overall Results
– Tool calculates risk of contact with allotments not disease
transmission or contact with other bighorn sheep
– Probability of contact and rate of contact
– Ram vs ewe vs herd
– Calculated results seasonally
– We are not modeling attraction
– The model does not account for stray domestic sheep
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Results
37
• Expectations for Use of the Tool
– Allows a quantifiable method for assessing the risk of contact
between domestic sheep and bighorn sheep
– Consistent, repeatable methodology
– Reflects use of best available science
– August 19, 2011 national direction requires risk assessment.
– Tool is applicable at the forest planning level and for use in
project level analysis.
– Tool has utility across jurisdictional boundaries.
Bighorn Sheep Risk of Contact Tool:
Expectations