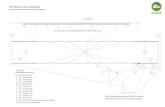
Badminton court diagram 01_A_SW_BRT_e
description
Transcript of Badminton court diagram 01_A_SW_BRT_e
-
Physical education teacher support material
Badminton
1. Using diagrams, describe the difference between a doubles and singles court.
2. Identify and describe two different types of serves.
The two different types of serves are a short serve and a long serve.
y Short serve: the player serves it really low and short, aiming for the triangle at the front of the serving box, forcing the opponent to quickly shuffle down to pick up the serve.
- Start toes facing point you want to hit to, shoulders squared, racquet perpendicular to ground.
- At point of contact, should be in front of body and soft hand.
Student work sample 1
International Baccalaureate Organization 2007 1
-
Physical education teacher support material
Student work: sample 1
y Long serve: the player serves it high and far, to the back, aiming for the triangle, forcing the player to shuffle back quickly to hit a defensive clear.
- Same technique as short serve but hit harder and point of contact more in front.
3. What are the rules concerning:
a. A player touching the net or its support with racket, person or dress?
The player who touches it looses the rally.
b. A shuttle being hit over the net and falling on the line of the outside court?
Its considered in.
c. The shuttle touching the net but still landing in your opponents service box on the service?
Re-serve.
4. When would you use the overhead clear in badminton? Describe its flight path in the air.
y When you want to push the opponent to the back of the court. y As a defensive shot, when they are under control. y When the opponent is not that good in shuffling backwards.
Not too high from net, so that you dont give the opponent much time to get under it and get settled.
2 International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
-
Physical education teacher support material
Student work sample 1
5. Describe the smash. In your answer think about the body position, when it is used and the direction and speed of the shuttlecock.
The smash is a hard, flat shot aimed at ending the rally. You should:
y Feet pointing to direction y Shoulders squared y Left hand (for right handed) point at shuttle y Knees bent y Head back y Full swing y Hit down, flat, and hard away from opponent y Follow through y Make contact a little in front of your head.
6. Suggest how the tactics of disguise could be used in a game of badminton.
For all overhead shots, you should have the same preparation stance ie racket back, knees bent, just like you are about to smash even if its about to do a drop shot to prevent the opponent from getting prepared and reading your movements. You should leave them to anticipate every movement, therefore, have the same stance at all times. This way, you can clear smash or drop shot, and the opponent can only react after you hit the shuttle.
7. What advice would you give someone in the following situations to help them improve their badminton stroke technique?
a. Their receiver is able to score a point from their serve.
Serve flatter, lower and make your opponents move. Try correcting your grip, stance, and especially your point of contact. Practice serving to the triangle of the court.
b. Overhead clear always lands mid-court.
Check stance: feet point straight, keens bent, shoulders squared, hands fully back, full swing, point of contact above your head.
c. Player is able to return their smash easily.
Check your point of contact, which should be little in front of your head, hit flat and hard, and place your shots, ie hit away from opponent and aim for the triangle.
International Baccalaureate Organization 2007
-
Physical education teacher support material
8. Your opponent keeps smashing the shuttle and winning the points. What kind of shots would you play to stop this happening and why?
You should try to drop your shots, to force your opponent to play a net clear or you can hit your clear red flat and deep, forcing them to play defensive overhead clear. You should make them move, preventing them from getting settled and use the technique of disguise to keep them anticipating.
9. What combination of shots would you use to attack an opponents backhand?
Serve it short to their backhands, eliminating any possibility for them to get prepared and change to forefront. Follow this up with an overhead clear to the backhand, this way they would be changing directions, therefore unsettled. Then depending in the quality of their return, either smash it to their backhand or drop it again. If they return it then clear it again, to the backhand and then smash/drop to the forehand since most probably you would have pushed them at the far side of the court.
Student work: sample 1
International Baccalaureate Organization 2007














![Untitled-1 [] · 2018-04-10 · THE LÄWS OF BADMINTON OF COURT SOMEPLACE WITHIN TEXT TAKEN FROM COURT & FIELD DIMENSION COURT The court shall be laid out to measurements and shall](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5eda52a2b3745412b571256d/untitled-1-2018-04-10-the-lws-of-badminton-of-court-someplace-within-text.jpg)



