B2 Topic 3: Energy Flow Internal Assessment. Animal and Plant Cells Draw a labelled diagram of both...
-
Upload
esmond-allen -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
3
Transcript of B2 Topic 3: Energy Flow Internal Assessment. Animal and Plant Cells Draw a labelled diagram of both...

B2 Topic 3: Energy Flow
Internal Assessment

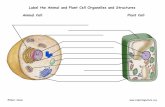
Animal and Plant Cells
• Draw a labelled diagram of both a plant and animal cell into your exercise books
– What is found inside a plant cell but not inside an animal cell?
– What do each of your labelled parts do in the cell?


• Cell membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Nucleus
• Cell wall
• Chloroplast
• Vacuole
• Contains chromosomes and controls the actions of the cell
• Controls what goes in and out of the cell
• Where photosynthesis occurs (where food is made)
• Contains cell sap• Contains all the organelles
and site of chemical reactions
• Supports the plant cell (gives it its shape)

• Complete the provided handout (B2.3 1c)

Parts of a Plant
Which part of the plant:• is the site of
photosynthesis?• absorbs water from
the ground?
• Is there any part of a plant that could be missing from this diagram?

• Make a list of factors that could affect the production of fruit on a plant. For example, on an orange plantation why do some trees produce more fruit than others?
• lack of sunlight
• soil lacking minerals
• diseases
• eaten by herbivores
• weather conditions (e.g. drought)

Recall Photosynthesis
• A plant converts carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water from the ground into oxygen and glucose
• Write this out as a word equation• What role does the glucose play?
– An energy source• Used for growth / repair• Used to grow fruit
– Stored as starch

Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
• Since photosynthesis needs the raw materials carbon dioxide, temperature, and light energy, it is clearly going to be affected by their availability. They become limiting factors
– the amount of photosynthesis that takes place is determined by whichever of these is in the shortest supply





As the light level is raised, the rate of photosynthesis increases steadily to a certain point. Beyond that, it won’t make a difference because then it’ll either e the temperature or carbon dioxide level which is the limiting factor.
The amount of carbon dioxide will only increase the rate of photosynthesis up to a point
The rate of photosynthesis is dependent on enzymes which have to be the right temperature. Above 40°C the enzymes become denatured.

Activity
1. In Biology for You; Page 206 Q2
2. Complete the provided handout (B2.3 4b)

Fertilisers
• In Biology for You; Page 203
– Make a table of the advantages and disadvantages of natural and chemical fertilisers
• In Biology for You; Page 330
– Summarize the problems that can occur if either too much fertiliser is used or if the fertiliser is added before a period of heavy rain

Farming over the Centuries…
• A hundred years ago there were many farms internationally however their numbers have been declining in the past 20 years
– Why is this?
– How have farming methods changed? In other words, what procedures are commonly used in contemporary farming?

Primary vs. Secondary Data Sources
Primary Data Sources• something that originates
from first-hand knowledge of the subject referenced in the data
(collected by the researcher themselves)– Interviews,
experimental data etc.
Secondary Data Sources• collected by others to be
"re-used" by the researcher – Internet sites,
newspapers, published statistics etc.
Complete the provided EXAMPRO Questions