Appendicular Skeleton 12/14 Allows environmental manipulation and mobility--locomotion Bones of...
-
Upload
peter-bruce -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Appendicular Skeleton 12/14 Allows environmental manipulation and mobility--locomotion Bones of...

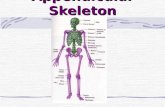
Appendicular Skeleton 12/14
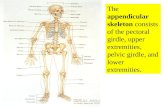
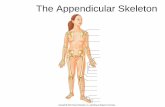
•Allows environmental manipulation and mobility--locomotion•Bones of limbs and their girdles• Pectoral or Shoulder girdle attaches upper limbs
to trunk of body• Pelvic or Hip girdle attaches lower limbs
BIO 105 Lab 6-Appendicular skeleton 1
Lab 6, BIO 105

Pectoral or Shoulder Girdle--flexible structure•Clavicles (anterior) and scapulae (posterior)• Provide attachment sites for muscles that move
upper limbs• Attach upper limbs to axial skeleton-scapulae do not
articulate with spine or ribs • muscles keep in place
• Allow movable articulation with other bones• shoulder joint is flexible and has a lot of
movement• Shoulder joint socket not deep• Easily dislocated
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 2

Clavicles•S-shaped bone•Act as brace to hold scapulae and arms out laterally; pushes shoulder posteriorly•acromial (lateral) end articulates with scapula•sternal (medial) end articulates with sternum
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 3

Scapulae•on dorsal surface of rib cage, between ribs 2 and 7•Flat and triangular shaped •Major markings:
spine acromionCoracoid process glenoid cavity or fossa
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 4

Upper Limb• Upper Arm• Humerus
• Forearm• Radius and ulna
• Hand• Wrist: carpal bones • Palm: metacarpal bones • Fingers: phalanges
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 5

Humerus•Largest, longest bone of upper limb•Articulates superiorly with glenoid cavity of scapula•Articulates inferiorly with radius and ulna•Major markings: head,
anatomical and surgical necks, greater and lesser tubercles,
deltoid tuberositycoronoid fossacapitulum, trochleaolecranon fossamedial and lateral epicondyles
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 6

Forearm Bones•Radius and Ulna• Articulate proximally with humerus and distally with
wrist bones• Articulate with each other proximally and distally at
radioulnar joints• Flat, flexible interosseous membrane connects bones
along entire length
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 7

• Ulna– Medial bone in forearm; slightly longer than radius– Forms major portion of elbow joint with humerus – Major markings: olecranon process, coronoid process,
trochlear notch, radial notch, styloid process
• Radius– Lateral bone in forearm– Head articulates with humerus capitulum and radial
notch on ulna– Major markings: head, neck, radial tuberosity, styloid
process
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 8

• Hand: Carpus--Skeleton of the hand contains carpal bones (wrist), metacarpal bones (palm), and phalanges (fingers); Bones are held together by ligaments allowing a flexible wrist
• Metacarpus (Palm)– Five metacarpal bones (#1 to #5) form palm– articulate proximally with carpals, distally with
phalanges• Phalanges
– Each finger (digit), except thumb, has three phalanges—distal, middle, and proximal
– Fingers are numbered 1–5, beginning with thumb (pollex)
– Thumb has no middle phalanx
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 9

Pelvic (Hip) Girdle•Two hip bones (also called coxal bone, os coxae, or inominate bone)• Attach lower limbs to axial skeleton with strong ligaments• Transmit weight of upper body to lower limbs• Support pelvic organs• Is more stable than shoulder because acetabulum (femur
attachment ) is deeper• Each hip bone consists of three fused bones: ilium,
ischium, and pubis (bones not fused in child—fuse in early adulthood)
•Together with sacrum and coccyx, forms pelvis
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 10

Hip Bone—3 regions1. Ilium
• Large, flaring bone which forms superior region of coxal bone• Consists of body and superior wing like portion called
“ala” • articulates with sacrum (sacroiliac joint)
– Ischium• Forms postero-inferior part of hip bone• Thick body articulates with ilium and ramus
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 11

3. Pubis• Anterior portion of hip bone• Midline pubic symphysis jointMajor pelvic markings: ramus, ilium ischiumiliac crest iliac spines (2 on each bone)acetabulum,ischial spine ischial tuberosityobturator foramen
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 12

Comparison of Male and Female Pelves•Female pelvis• Adapted for childbearing; tilted forward • True pelvis (inferior to pelvic brim) defines birth canal• Cavity of true pelvis is broad, shallow, and has greater
capacity• Sacrum is wider, shorter, straighter• Coccyx is straighter
•Male pelvis– Tilted less forward– Adapted for support of heavier body build and stronger
muscles– Cavity of true pelvis is narrow and deep
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 13

Lower Limb•Carries weight of body•Subjected to exceptional forces with running and jumping•Three segments --thigh, leg and footFemur•Thigh bone, largest and strongest bone in body•Articulates proximally with acetabulum of hip and distally with tibia and patella•Major markings: head neck linea aspera greater and lesser trochanters lateral and medial condyles
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 14

Patella or Kneecap•Triangular bone enclosed in quadriceps tendon; anchors anterior thigh muscles to tibia•Protects knee joint anteriorly •Improves leverage of thigh muscles acting across knee•Articulates with medial and lateral condyles of distal femur and proximal tibia
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 15

Tibia• Medial leg bone• Receives weight of the body from femur and transmits it
to foot• Major markings: medial and lateral condyles, tibial
tuberosity, anterior crest, medial malleolus•Fibula
• Sticklike bone with slightly expanded ends, lateral to tibia• Not weight bearing; no articulation with femur• Site of muscle attachment • Connected to tibia by interosseous membrane• Articulates with tibia via proximal and distal tibiofibular
joints• Major markings: head, lateral malleolus
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 16

Foot: Includes tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges•Functions—support weight of body•Acts as a lever to propel body forward
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 17

Tarsals Seven tarsal bones form posterior half of foot•Body weight is primarily carried on talus and calcaneus•Talus—large, topmost bone which connects to tibia and fibula•Calcaneus• Forms heel; distal to talus• Point of attachment for Achilles (calcaneal) tendon of calf
muscles
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 18

• Metatarsals:– Five metatarsal bones (#1 to #5) that articulate with
proximal phalanges (toes) – Enlarged head of metatarsal 1 forms “ball of foot”
• Phalanges– toes– Each digit (except the hallux—great toe) has three phalanges
– Hallux has no middle phalanx
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 19

Joints (Articulations)•Articulation—site where two or more bones meet•Weakest parts of the skeleton•Functions of joints:
– Give skeleton mobility– Hold skeleton together
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 20

Joints •Classified either structurally or functionallyStructural Classification of Joints •Based on material (type of tissue) binding bones together or presence of a joint cavityStructural classifications:
– Synovial-most common, most movable– Cartilaginous-slightly movable – Fibrous-immovableFunctional Classification
•Based on amount of movement allowed•Functional classifications:-Diarthroses— freely movable (predominant in limbs)-Amphiarthroses—slightly movable -Synarthroses—immovable
Primarily in axial skeleton

Fibrous or Synarthrotic Joints•Bones joined by dense fibrous connective tissue
• Most immovable; some slightly movable• No joint cavity
Fibrous or Synarthrotic Joints: Joint held together by a ligament; Fibrous tissue can vary in length, but is longer than in sutures.--Movement varies from immovable to slightly movable;Example:
Connection between radius and ulna
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 22

Cartilaginous or Amphiarthrotic Joints: (Synchondroses or Symphyses)
– No joint cavitySynchondroses—bones connected by hyaline cartilageex: Epiphyseal plate; costal cartilage joint between first rib and sternumSymphyses--bones connected by broad, flat fibrocartilage pad intervertebral joints, pubic symphasis

Synovial or Diarthrotic Joints•freely movable •Articulating bones separated by fluid filled joint cavity
– Fluid reduces friction•Examples:
– all limb joints; – most joints of body

Reminders•ID and describe bones and bone markings presented in handout.•Describe basic kinds of joints and give examples.
BIO 105 Lab 7-Appendicular skeleton 25




![[PPT]Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle and Upper … · Web viewAPPENDICULAR SKELETON PECTORAL GIRDLE AND UPPER LIMB PECTORAL GIRDLE scapula humerus clavicle CLAVICLE sternal](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5b1c49a87f8b9a2d258f98c3/pptappendicular-skeleton-pectoral-girdle-and-upper-web-viewappendicular-skeleton.jpg)