Animal cells and plant cells
-
Upload
samiran-ghosh -
Category
Education
-
view
4.012 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Animal cells and plant cells

Animal Cells and Plant Cells

Animal cells

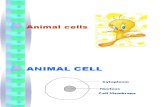
ANIMAL CELL
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane

You need to identify the different parts of a typical animal cell and relate the parts to the functions.
parts of animal cell:
• cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus

According to the cell theory, proposed over 150 years ago:
• Most cells are very tiny and can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. A human body is composed of billions of cells!
• The cells in the human body consist of blood cells, skin cells, brain cells and many others and each type of cells has different functions.
• Despite their differences, most cells in living organisms have similar structures and functions.

• A cell membrane keeps all the parts of the cell inside.
• It controls what enters and exits the cell such as water, nutrients and waste and thereby protects and supports the cell.
• It is the outermost layer in the animal cell.
Cell Membrane

• Inside the cell, there is a large fluid-filled space called the cytoplasm.
• It is a jelly-like substance composed of mainly water as well as substances like dissolved nutrients.
• The cytoplasm fills up the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane.
Cytoplasm

• The nucleus is located in the cytoplasm of the cell.
• It controls and regulates all cell activities. It is the "control center" of the cell and it contains the cell's DNA.
• It has a similar function to the brain of the body which is helping to control eating, movement, and reproduction.
Nucleus

Animal Cell - Functions
Nucleus control centre of the cell – stores information for cell functions
Cytoplasm jelly-like, where cell activities take place
Cell membrane thin, controls the substances that enter or exit the cells
Let’s summarise:

Examples of Cells found in Animals

Cheek Cells
Can you identify the parts of the cell?- cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm

Red Blood Cells

Human Muscle Cells

Plant cells

You need to identify the different parts of a typical plant cell and relate the parts to the functions.
parts of plant cell:
• cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus and chloroplasts

PLANT CELL
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
Chloroplast
Cell Wall

• A cell membrane keeps all the parts of the cell inside.
• It controls what
enters and exits the cell such as water, nutrients and waste and thereby protects and supports the cell.
• It is found just inside the cell wall in the plant cell.
Cell Membrane

• The cell wall is found in plant cells but not in animal cells.
• This is the outermost layer in the plant cell. It is stiff and rigid and helps a plant keep its shape.
• Cell walls allow materials like water and nutrients; waste, oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass to and from the cell membrane.
Cell Wall

• Chloroplasts are only found in plant cells. They are responsible for photosynthesis.
• Every green plant you see is working to convert the energy from the sun into sugars during the process of photosynthesis.
• Plants are the basis of all life on Earth. They make sugars, and the by-product of photosynthesis is the oxygen that we breathe.
• Chloroplasts are green because of the pigment chlorophyll.
Chloroplast

• Inside the cell, there is a large fluid-filled space called the cytoplasm.
• It is a jelly-like substance composed of mainly water as well as substances like dissolved nutrients.
• The cytoplasm is found in both plant and animal cells, filling the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane.
Cytoplasm

• The nucleus is found in both plant and animal cells.
• It is located in the cytoplasm of the cell.
• It controls and regulates all cell activities. It is the "control center" of the cell and it contains the cell's DNA.
• It has a similar function to the brain of the body which is helping to control eating, movement, and reproduction.
Nucleus

Nucleus control centre of the cell – stores information for cell functions
Chloroplasts contain green pigment chlorophyll, needed in photosynthesis
Cytoplasm jelly-like, where cell activities take place
Cell membrane
thin, controls the substances that enter or exit the cells
Cell wall stiff wall which gives plant cells their shape
Plant Cell - Functions
Let’s summarise:

Examples of Cells found in Plants

Hydrilla Cells

Hydrilla Cells- Magnified
Can you spot the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm and chloroplasts?

Onion Cells

Onion cell- Magnified
Can you identify the parts of the cell?

Cells in a leaf
stoma
stoma

Cells in the stem
xylem
phloem

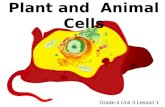
Differences between Plant and Animal Cells
Plant Cell Animal Cell•Plant cells contain chloroplasts to make food from solar energy during photosynthesis.•Underground parts of plants usually do not contain chloroplasts.
•Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts.
•Plant cells contain cell
wall.
Animal cells do not have
cell wall.