ANDREW JACKSON and the Era of Jacksonian Democracy.
-
Upload
hilda-bryant -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of ANDREW JACKSON and the Era of Jacksonian Democracy.

ANDREWJACKSON
and the Era ofJacksonian Democracy

Transformation of American Politics
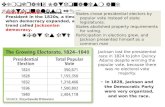
• Democratic Fervoruniversal male suffrage, electoral vote shift, nominating caucus to convention
• Election of 1824“corrupt bargain”: Adams, Jackson, Crawford and Clay
• John Quincy Adamssupported internal improvements; delegation to Latin America
• Jackson & Van Burenfrom Republican to Democrat

Election of 1828the murdering, drunken adulterer vs. the rich, silk underwear wearing pimp
• Rotation in OfficeSpoils System
• Maysville Road Bill veto• Indian Removal Act (1830)• Cherokee v. Georgia (1831)
not a foreign nation; no right to sue• Worcester v. Georgia (1832)
Georgia has no authority in tribal territory
“Old Hickory” sworn into office

Jackson vs. Calhoun
• Tariff of Abominations, 1828• Nullification Crisis South Carolina Exposition and Protest , slavery
• Peggy Eaton Affair• Olive Branch and the Sword: Compromise Tariff and Force Bill (1833)

War on the Bank
• The Bank VetoPanic of 1819, privilege and class, lending capacity, stockholders, Philly not DC
• Election of 1832Jackson 219, Clay 49 electoral votes
• Nicholas BiddlePresident of the Bank
• “Pet Banks”1836 Deposit Act; Hard-money vs. Soft-money Democrats

Capitalism DebatedWhat sort of society would the US become?
• Swift economic development at the price of allowing some people to get rich quickly while others languished?(paper money and speculation)
• Modest growth in traditional molds anchored by “honest” manual work and frugality?(specie and regulation)

Emergence of the Whig Party• Constituents:
South pro-nullification, internal improvements; North pro-reform; Anti-Masonry
• Election of 1836Van Buren 170 electoral votes; Whig split four candidates
• Panic of 1837“pet banks”; Specie Circular; Britain held specie; Independent Treasury Bill (1840)
• Election of 1840Tippencanoe and Tyler, too“Log Cabins and Hard Cider”

King Andrew?
Or “the greatest man of his age”?
“Democracy does not give people the most skillful government, but it produces what the ablest governments are frequently unable to create: namely, an all-pervading and restless activity.”
~Alexis deTocqueville Democracy inAmerica 1830-1831

Rise of Popular Religion• The Second Great Awakening
Revivals vs. Unitarians, Methodists, Burned-Over Districts(Charles Finney), Timothy Dwight (Yale Calvinists)
• MormonismJoseph Smith (Book of Mormon), Brigham Young (Salt Lake)
• ShakersMother Ann Lee

Transcendentalism
• Mystical and intuitive• Discovery of one’s inner self• Seeking the essence of God in nature
Ralph Waldo Emerson“The American Scholar”
Harvard, 1837
Henry David ThoreauWalden, 1854“On Civil Disobedience”

Brook Farm, Massachusetts, 1841
“a more natural union between intellectual and manual labor”– George Ripley
Ralph EmersonMargaret Fuller
feministNathaniel Hawthorne
novelist

Social Reform
• Temperance• Public School• Abolitionism• Women’s Rights• Penitentiaries and
Asylums• Utopian
Communities
Horace Mann
Susan B. AnthonyElizabeth Cady Stanton
Dorothea Dix
Wm Lloyd Garrison