CHAPTER 3 SECTION 3- SUMERIAN ACHIEVEMENTS Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent.
Ancient Mesopotamia Since Mesopotamia was on the fertile crescent, it was ideal for farming –...
-
Upload
hannah-george -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Ancient Mesopotamia Since Mesopotamia was on the fertile crescent, it was ideal for farming –...
Ancient Mesopotamia
Since Mesopotamia was on the fertile crescent, it was ideal for farming – fertile soil and water supply. Most all of the civilizations that developed there were polytheistic, except the Hebrews (Israelites or Jews) who were monotheistic. They also had food surpluses which led to division of labor or job specialization because everyone didn’t have to take all of their time looking for food. They could control water and they invented the first writing system, cuneiform. These civilizations were the first to keep business records. Lastly, they had Hammurabi’s Code which contained 282 laws based on everyday life.
Mesopotamia ID’s
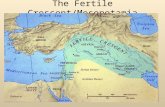
Fertile Crescent – a large arc of rich, or fertile farmland between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
Silt – a mixture of rich soil and tiny rocks…there was a lot of silt in this area because of the flooding of the rivers and that is what made this such good farm land.
Irrigation – a way of supplying water to an area of land. The civilizations here developed the first irrigation systems
Job Specialization – each worker specialized in a particular task or job. During this time was the first time humans could do this because they didn’t have to look so hard for food.
Cont’.
Levels of Civilization – Tribe Village City-State Empire
Polytheism – worshipping many gods/goddesses
Monotheism – worship of only one God
Social Hierarchy – division of society by rank or class. Ruler General Priest Scribe Artisan Peasant
Cuneiform – the world’s first system of writing
Hammurabi’s Code of Law – a set of 282 laws that dealt with almost every part of daily life.
Achievements of Ancient Mesopotamia
Vast irrigation system
Levees along banks of the rivers
Canals to direct river water into the fields
Dams to stop the flow of water
Reservoirs to store water
First cities
First governments
Specialized jobs
First written language – cuneiform
Basic algebra and geometry
Measure and calculate seasons
60 minute hour, 360 degree circle
Became merchants (trade)
First wheeled wagons and carts
Sailboat
Chariot
Stringed instruments
First Empires
First written code of laws – Hammurabi
Created iron from iron ore
Developed an alphabet
First to use coins and money
First monotheistic religions