Ancient Egypt Part 1
description
Transcript of Ancient Egypt Part 1

Ancient Egypt
Part 1

The Nile River Valley• Between 6000 and 5000 BC,
hunter-gatherers from Africa and southwest Asia moved into the green, fertile Nile River valley
• They became the earliest Egyptians
• Egypt is warm and sunny, with little rainfall
• Relied on the Nile River

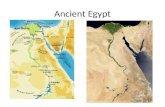
The Nile River• The world’s longest river – 4,000 miles• Begins as two separate rivers in the
mountains of eastern and central Africa• Flows NORTH to the Mediterranean• The southern part of the Nile has wild
rapids called cataracts–Make only the last 650 miles navigable by
ships• Just before it reaches the Mediterranean,
it divides into branches which fan out over an area of fertile soil called a delta


Satellite photo of northern portion of the Nile



The first of 10 cataracts along the Nile

Geography Protected the Egyptians
• On both sides of the Nile are vast, hot deserts (The Red Land)– The Sahara Desert on the west– The Eastern Desert on the east
• To the south, cataracts kept enemy boats out
• To the north, the marshy delta offered no harbor for enemy ships coming by sea
• Unlike Mesopotamia, Egypt rarely faced outside threats and the civilization was able to grow and prosper

Depending on the Nile• The Nile flooded, but in
dependable, gentle way– Egyptians didn’t have to worry about
destructive floods• Every summer, the Nile flooded
leaving behind dark, fertile soil• Egyptians call this land Kemet, or
The Black Land


Using the Nile• Egyptians were successful farmers– Grew wheat, barley, and flax
• Used irrigation and built dikes to trap the floodwaters
• Used papyrus, a reed that grows along the Nile to make baskets, rafts, and later for papermaking
• Developed geometry to measure and divide fields

Papyrus reeds growing along the Nile

Papyrus raft

Papyrus ship