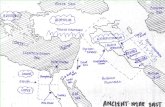
Ancient Civilizations · Ancient Civilizations Mesopotamia . ia •Early humans traveled to find...
Transcript of Ancient Civilizations · Ancient Civilizations Mesopotamia . ia •Early humans traveled to find...
The
Sta
rt of M
eso
po
tam
ia
• Early humans traveled to find food
– When food became scarce, they moved
• As they moved they followed the
coasts/rivers, to be close to water
• Soon they traveled through the area
of the Middle East (5000 BCE)
– Found a very fertile area known as the
“Fertile Crescent”
– Present day Iraq
• Area was fertile due to 2 major rivers
that emptied into the Persian Gulf
Ch
ara
cte
ristics o
f Fe
rtile C
resc
en
t
• Two major rivers
– Euphrates to the West
– Tigris to the East
• Area between named Mesopotamia
(c. 3100-529 BCE)
– Comes from Greek term meaning
“between the rivers”
• Many small cities form close to the
Persian Gulf
– They later spread further away due to
growing populations
Imp
orta
nc
e o
f Ge
og
rap
hy
• One of the earliest known cities-states: Sumer (2900 BCE)
– City-states- an area that was ruled like
separate states
– Early example of an advanced civilization
– Strong government, laws, economy
• Rivers provided only real water to Sumer – Positives
• Fertile land allowed crops to grow
• Deposited silt- rich soil from bottom of riverbeds
– Negatives • Rivers flooded unpredictably; thousands died
• Area of Sumer was small (size of Massachusetts)
• Area lacked other vital natural resources
Disc
ussio
n
• What technology did the Sumerians
utilize that would help lessen the
negative consequences discussed
previously?
Imp
orta
nc
e o
f Ge
og
rap
hy
• Problem Solving at Its Best – People of Sumer utilized new
technologies • Dug irrigation canals to control water
– Also spread the amount of farmable land
• Built walls to protect the cities from invaders
• Traded for resources needed w/ other cities
– Traded grain and cloth for wood, metal, and tools
Riv
er S
ilt an
d Irrig
atio
n C
an
als
Irrigation canal from
the rivers
River silt left behind
after a flood
Su
me
rian
Citie
s
• All cities had their own governments
and rulers
– Ur- the most powerful Sumerian city
– Sophisticated city w/ rigid social
classes
– Buildings made of clay bricks
• Regular houses were boxlike w/ no
windows
• Rich houses were two levels w/
courtyard
Ec
on
om
y o
f Su
me
rian
Citie
s
• Economy based of Agriculture – Grain would be traded
for other goods • Traded for tools, metals,
and wood
• Marketplace- most important area – Used for trading of
goods
– Called a bazaar or open air market
• Barter –A system of trade in which one good is traded for another
Su
me
rian
Re
ligio
n
• Sumerian Religion – Polytheism- belief in
multiple gods
• Ziggurat- main religious building (temple) – Usually protected by wall
– Served many purposes • Store grain, ceremonies,
sacrifices
• Priests held high power in society – Initially had all power until
more wars broke out and military leaders took over
Su
me
rian
Po
litics/C
ultu
re
• Led to dynasties
– A succession of rulers from the same
family.
• Society had rigid social classes • Little Social mobility
– Priests and Kings – upper class
– Merchants/ Artisans – upper middle class
– Farmers/ Laborers – lower middle class
– Slaves- (usually POWs, not race based)
• Women held some rights in society • Able to own land, enter low priesthood
• Could not write; suggests no education
Su
me
rian
Sc
ien
ce
& Te
ch
• Sumerians known for 4 major inventions – The wheel
– The sail • Both aid in travel and trade; make
them faster
– The plow – The Harness
• Created calendars
• Counting/ number system from 0 – 60
• First to use Bronze- the Bronze Age
• Created cuneiform – Writing system of pressing into clay
– Used pictographs – picture=words – Stylus- small tool for writing
• Ziggurat
Ea
rly M
eso
po
tam
ian
Co
nq
ue
rors
• Religious leaders held power first but wars broke out
• With more wars, military leaders come to power
• Eventually leaders start taking over nearby
villages
– Leads to the beginning of empires and empire building
• Empire-many areas under the rule of one
leader
• First Empire builder- Sargon of Akkad
• Takes power over Sumer
– Came from the city of Akkad
– Adopted many of the Sumerian
practices and beliefs
• Sargon dynasty unifies Sumer from
2340 – 2125 BCE
– Becomes the first time Sumer was unified
• Expands empire from north of Sumer to Persian Gulf
Ne
w G
rou
p &
Lea
de
r Co
me
to P
ow
er
• Empire of Sargon begins to weaken
• Amorites take power of Sumer around
2000 BCE; later known as Babylonians
– Make Babylon their capital, moved it from Ur
– Still kept practices of Sumer
• Babylonian Empire reaches its height
under Hammurabi (1790-1750 BCE)
• Best known for creating a code of law for all people – Hammurabi’s Code; based off earlier codes
– First Written Law Code; posted throughout cities.
• Hammurabi’s Code based on revenge – Eye for an eye, tooth for tooth
• Rules applied differently to rich and poor
• Religion changed under Hammurabi- Marduk main god