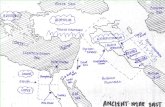
Ancient Civilizations
-
Upload
parker1220 -
Category
Education
-
view
399 -
download
0
Transcript of Ancient Civilizations

Unit 1 Notes

Day 1 - Mesopotamia

Mesopotamia (Fertile Crescent)
Area between the Tigris River and Euphrates River– unpredictable flooding– no natural boundaries– limited natural resources– women had rights
•3 General Areas– Assyria– Akkad– Sumer

Government
• City-States – a city with political and economical control over the surrounding countryside– Surrounded by walls

Ziggurat• Most prominent
building in the city and was dedicated to the chief god or goddess

Religion • Polytheistic – belief in many Gods• Theocracy – government by divine authority– Sumerians believed that the gods ruled the cities– Kings ruled the cites and derived their power from
the gods

Economy and Society
• Mesopotamians were well known for their metal work and woolen textiles
• They traded with other civilizations such as India and Egypt for fish, barley, and wheat

First Empire• Sargon of Akkad– From Akkad; a city-state north of Sumer– Long adopted most Sumerian aspects– Created 1st Empire: brings together several
peoples, nations, or previously independent states under control of one ruler.

Hammurabi’s Code• The Code of Hammurabi is one
of the oldest known set of laws in human history.
• Based on a system of strict justice
• Penalties for breaking these laws were severe and varied based on your social class
• “An Eye for an Eye”• Men have more rights than
women

Cuneiform• Cuneiform script is one of the earliest
known systems of writing distinguished by its wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets.
• Primarily used for record keeping– Scribes– Teachers

Cuneiform

Cuneiform

• The Epic of Gilgamesh, an epic poem from Mesopotamia is considered the world's first truly great work of literature.
The Epic of Gilgamesh

MesopotamiaA. Government: city-states
• like independent countries
B. Accomplishments: 1. Hammurabi’s Code2. The Wheel3. Cuneiform4. Ziggurats
C. Religion: polytheism• belief in more than one god• Theocracy – government by divine authority
D. Decline: overtaken by new groups/breaks up

Judaism
• The first monotheistic religion forms in Mesopotamia – Judaism

Judaism Develops
• Palestine: trade crossroads for many peoples• Canaan: “Promised Land” of the Hebrews (Jews)• Abraham
1. “Father” of the Hebrew people2. Torah: first 5 books of the Hebrew Bible3. Monotheism: belief in ONE god4. Covenant: promise between God and Abraham

Judaism Develops• The Exodus – Israelites
escape from slavery in Egypt
• Moses – led the Israelites out of Egypt and delivered the ten commandments
• Ten Commandments – Set of laws delivered to Moses by God

Day 2 - Egypt

Egypt• Along Nile River• Natural Desert Barriers• Upper and Lower Egypt– Upper is south– Lower is north, near Med. Sea, includes delta (100 miles
before Med. Sea, broad, marshy, triangle area, of silt at river mouth.)
• Hierarchy of classes• Women had rights

Egypt - Government
• Ruled by Pharaohs – Pharaohs received there authority to
rule from the Gods• Pharaohs were considered living
Gods• Ruled with Absolute Power• Vizier - leading government official
in ancient Egypt

Egypt - Religion
• Polytheistic – Land Gods• Osiris and Isis
– Sun Gods• Emperor – Son of Re

Egyptian History
• Divided into three eras– Old Kingdom (2700 BCE – 2200 BCE)– Middle Kingdom (2050 BCE – 1652 BCE)– New Kingdom (1567 BCE – 1085 BCE)
• Begins around 3100 BCE – Menes unites the upper and lower kingdom
creates first dynasty

Old Kingdom• Era of prosperity and splendor• Pyramids were built during the Old Kingdom– Built as burial grounds for Pharaohs – Stocked with everything that they would need in the afterlife
• Sphinx – guards the Great Pyramids of Giza– Body of a Lion– Head of a Human
• Mummification – slowly drying a body to prevent decomposition

Middle Kingdom - (2050 BCE – 1652 BCE)
• Considered the “Golden Age”• Expanded the Empire– Sent troops to Palestine and Syria
• Pharaohs were no longer seen as Gods but Shepherds
• Projects included:– Connecting Nile and Red Sea– Drained Swamplands to create more farm land

Empires Develop
New Kingdom of Egypt1. Hyksos ruled Egypt from 1640 -1570 B.C. 2. During this time, Hebrews settled Egypt3. Series of rulers began to restore power (kicked
the Hyksos out!)• Hebrews stayed and were forced into slavery in Egypt

New Kingdom - (1567 BCE – 1085 BCE)
• Most Powerful – Militaristic
• Hatshepsut 1st Women Pharaoh
• Thutmose III – Led 17 military campaigns, expanding into Mesopotamia
• King Tutankhamen• Ramses II• Cleopatra

Hieroglyphics
• Created around 3000 BCE• Used pictures and abstract forms – Highly
specific

New Kingdom Declines
• Egypt suffered invasions from “Sea Peoples”, tribes of Palestine, and Libyan raids.
• Egyptian Empire broke apart

EgyptA. Government: Theocracy/Pharaohs– Rule is based on religion; run God-kings
B. Religion: Polytheistic
C. Accomplishments:– Hieroglyphics: picture writing– Pyramids– Calendar– System of numbers/geometry (engineers and architects)– Medicine
D. Decline: Pharaohs lose power

Day 3 – Indus River Valley

Sea People
Phoenicians:• Most powerful sea traders along with the Minoans• Alphabet is their greatest legacy - Phonics

Phoenician Alphabet• Phoenicians
simplified their writing by using 22 different signs to represent the sounds of their speech
• Eventually passed on to the Greeks and eventually the Romans – which we still use today

Indo-Europeans Migrate• Indo-Europeans: group of nomadic peoples; came from the
Steppes; ancestors of many modern languages• Hittite Empire: lived in Anatolia, excelled in technology of war
(esp. chariots) – 1st civilization to use Iron
• Aryans: lived between the Caspian and Aral Seas– Vedas: four collections of prayers, magical spells, and instructions for
performing rituals– Castes: social system of Aryans

Empires Develop
Assyrian Empire• Through war, and use of iron
weapons, created empire• Glorified military strength • Peak of empire included all of the
Fertile Crescent and Egypt• Laid waste to conquered lands• Eventually falls to Chaldeans who
make Babylon their capital.

Empires Develop
Persian Empire – Unified by Cyrus the Great in 539 BCE• Over took the Babylonians and took complete control of
Mesopotamia • Cyrus allowed the Jews to return to Jerusalem• Based on tolerance and diplomacy (instead of war)
• Cyrus: King who was a military genius; controlled land from the Indus River to Anatolia• Kind towards conquered peoples • Allowed NO looting and burning• Honored local customs• Allowed Jews to return to Jerusalem

Empires Develop
• His successors would expand the Empire form the Indus River all the way into Europe and Greece and as far south as Egypt
• Darius would help strengthen the gov’t by dividing the land into 20 provinces to govern with satraps (ruled locally)
• Roads and coins promoted trade that helped hold the empire together. (Royal Road)

Decline of the Persians
• The empire weakens over time because of internal struggle over the thrown.
• Six of the nine rulers after Darius were murdered over competition for the throne
• Eventually Alexander the Great defeats the Persians and takes control of their lands.

Persian Religion
Zoroaster: Persian prophet who founded Zoroastrianism• Taught belief in one god• Earth is a battleground with a
great struggle between good and evil• Ahuramazda (the “Wise Lord”)
was supreme but not unopposed• Shares concept of Satan and
angels with Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.• Writings were written down in
the Zend Avesta the sacred book of Zoroastrianism

Indus River Valley
• Indian Subcontinent• Surrounded by mountains: Hindu Kush, Karakorum,
and Himalayan ranges • Between Indus and Ganges Rivers• Monsoons: seasonal winds from mid-June to Oct.
winds shift and blow east (from SW) bring rains

Indus River Valley
• Cities were carefully planned on a grid like pattern– Broad streets running North and South, while
smaller streets ran East and West– Cities were divided into large walled
neighborhoods– Had an advanced drainage system where waste
water was taken out of the city by underground drains and carried to sewer pits outside the city walls

Indus River Valley
• Government – Theocracy– Religion and political power were closely linked
(the royal palace and the Holy Temple were the same building)

The Aryans
• The Aryans came to the Indus River Valley from the Steppes Region and conquered the region.– They brought with them new farming techniques – The Aryans had no written language but
eventually developed the a writing system known as Sanskrit around 1000 BCE
– The Conquest of the Aryans also brought the Caste System to India

The Caste System
• The Caste System was a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person’s occupation and economic potential but also his or her position in society

Hinduism• a collection of beliefs; seeks to achieve moksha:
liberation from desires and suffering– Teach from Vedas (became Upanishads once written
down)– Reincarnation: individual soul or spirit is born again until
achieves moksha– Karma: good or bad deeds
• Strengthened caste system– Dhrma – divine law, requires people to do their duties– Brahman: world soul seen in 3 main gods

• Buddhism was founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha: enlightened one)
• Went out seeking the cure for human suffering– Became an ascetic– Eventually turned to the ideas of meditation– While sitting under a tree the Buddha reached
enlightenment as the meaning of life– Spent the rest of his life preaching his message
Buddhism

Buddhism
• Achieving wisdom is a key step to achieving Nirvana or ultimate reality
• Four Noble Truths:1. Life is filled with suffering and sorrow2. The cause of all suffering is people’s selfish desire
for the temporary pleasures of this world3. The way to end all suffering is to end all desires4. The way to overcome such desires and attain
enlightenment is to follow the Eightfold Path, which is called the Middle Way b/t desires and self-denial

Buddhism
• Eightfold Path: guide to behavior mastered one step at a time, over many lifetimes
• Originated in India, spread worldwide• Siddhartha accepted the ideas of
Reincarnation but rejected the ideas of the Caste System
• TRADE played a crucial role in the spread of Buddhism.

Mauryan Dynasty
• Founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 324 BCE• He helped drive out the foreign forces and
established the capital along the Ganges river • Divided the Empire into providences that were
ruled by Governors• VERY PARANIOD!!!!

Ashoka
• Grandson of Chandragupta• Considered the greatest ruler
of the Mauryan empire• Converts to Buddhism and used these ideas to
rule• After his death the empire declines into a
period of chaos

Indus River Valley
A. Government: Theocracy B. Religion: Hinduism C. Accomplishments:
• Language—Sanskirt• City-planning/grids
D. Decline: earthquakes and floods alter Indus River; trade became impossible

Day 4 - China

China• Natural Barriers isolate China
Yellow Sea, Pacific Ocean, East China Sea (East), Mt ranges and deserts dominate 2/3 of its land mass, Taklimakan Desert and Plateau of Tibet (West), Himalayas (SW), Gobi Desert and Mongolian Plateau (North)—No trade
• Huang He River (Yellow River) and Chiang Jiang River (Yangtze)
• Family more important than individual• Women have no rights; considered inferior• Hierarchy of classes

The Shang Dynasty
• 2nd Dynasty in Chinese history (1750 – 1122 BCE)• Mostly a farming civilization ruled by the
aristocracy• Built huge city walls – ruled by Kings• Practiced Ancestor worship – the practice of
burning replicas of physical objects to accompany the departed on their journey to the afterlife

The Zhou Dynasty
• Began as a revolt against the Shang rulers• Zhou rule would last for almost 900 years• Still ruled by a king– Mandate of Heaven – it was believed that order
was kept in the universe through the King, thus he ruled over all humanity

Zhou Dynasty
• The King was not a representative of Heaven• It was the King’s duty to rule the proper
“Way” called the Dao.• If a natural disaster occurred or crops failed
the King could be overthrown and replaced• Led to a “right of revolution” mentality– Only way to determine who the proper King was,
was to fight.

Life during the Zhou
• Trade was very prominent during this time• New Technologies– Irrigation was introduced into farming– Canals were built to control the flow of water– Improved farming method allowed the Zhou
dynasty to grow to 50 Million people– The most important crop grown in China was Silk• The making a silk was a highly regarded secret

The Family
• The family is the basic economic and social unit• Filial piety – it was the duty of the family to put
the needs of the elder males in front of their own

The Fall of the Zhou
• The empire was divided into territories to more easily rule
• Some of the territories became to powerful and it led to Civil War
• In 403 BCE a the “Period of Warring States” breaks out– Iron is introduced – Calvary units – Crossbow

Confucius
• China’s first teacher – up until the 20th century school children studied the saying of Confucius
• He was upset by the violence and moral decay• Traveled around China trying to convince
political leaders to follow his ways• Established Confucianism– The system of Confucian ideas

Confucianism• His whole mission became how to restore order
in China• His interest were not spiritual but political/ethical• Two elements of Confucianism– Dao or duty – people had to put the interest of the
family ahead of their own– Everyone should be governed by the Five Constant
• Parent – Child• Husband – Wife• Sibling – Younger Sibling• Older Friend – Younger Friend• Ruler - Subject

Other Philosophies– Daoism: philosophy of Laozi; taught that people
should be guided by an invisible force known as the Dao.• Tries to set proper way of living for the people
– Legalism: proposed that humans were evil by nature and they could only be controlled by harsh laws and stiff punishments.• Believed that a strong leader was needed to create an
ideal society

Qin Dynasty
• Created a new dynasty in 221 BCE• Drastically changed Chinese Philosophy – adopted
Legalism as the gov’t’s official policy• Created a gov’t where that was constantly checked
for corruption• Created a single monetary system and built roads
connecting the Empire

The Great Wall of China
• The great wall was built to keep out invaders from the North (Mongolians)

China 1. Government: Monarchy (Dynasties)
– Rule by one – Mandate of Heaven
2. Accomplishments:– Chinese characters (written language)– Roads and canals– Coined money– Cast iron weapons (not seen elsewhere until
middle ages)3. Religion: polytheism
– family spirits consulted supreme gods4. Decline: Nomads attack and kill monarch
– Enter “period of warring states”