Ancient Civilizations
description
Transcript of Ancient Civilizations

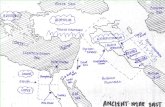
Ancient CivilizationsMesopotamia

The Start of Mesopotam
ia
• Early humans traveled to find food– When food became scarce, they moved
• As they moved they followed the coasts/rivers, to be close to water
• Soon they traveled through the area of the Middle East (5000 BCE)– Found a very fertile area known as the
“Fertile Crescent” – Present day Iraq
• Area was fertile due to 2 major rivers that emptied into the Persian Gulf

Geography of Mesopotam
ia

Characteristics of Fertile Crescent
• Two major rivers– Euphrates to the West – Tigris to the East
• Area between named Mesopotamia (c. 3100-529 BCE)– Comes from Greek term meaning
“between the rivers”• Many small cities form close to the
Persian Gulf– They later spread further away due to
growing populations


Importance of Geography
• One of the earliest known cities-states: Sumer (2900 BCE)– City-states- an area that was ruled like
separate states– Early example of an advanced civilization – Strong government, laws, economy
• Rivers provided only real water to Sumer– Positives
• Fertile land allowed crops to grow• Deposited silt- rich soil from bottom of riverbeds
– Negatives• Rivers flooded unpredictably; thousands died• Area of Sumer was small (size of
Massachusetts)• Area lacked other vital natural resources

Discussion
• What technology did the Sumerians utilize that would help lessen the negative consequences discussed previously?

Importance of Geography
• Problem Solving at Its Best– People of Sumer utilized new
technologies • Dug irrigation canals to control water
– Also spread the amount of farmable land• Built walls to protect the cities from
invaders• Traded for resources needed w/ other
cities– Traded grain and cloth for wood, metal,
and tools

River Silt and Irrigation Canals
Irrigation canal from the rivers
River silt left behind after a flood

Sumerian Cities
• All cities had their own governments and rulers– Ur- the most powerful Sumerian city– Sophisticated city w/ rigid social
classes– Buildings made of clay bricks
• Regular houses were boxlike w/ no windows
• Rich houses were two levels w/ courtyard

Examples of Ur Housing

Economy of Sum
erian Cities
• Economy based of Agriculture– Grain would be traded for
other goods• Traded for tools, metals,
and wood• Marketplace- most
important area– Used for trading of goods– Called a bazaar or open
air market• Barter –A system of
trade in which one good is traded for another

Sumerian Religion
• Sumerian Religion– Polytheism- belief in
multiple gods• Ziggurat- main religious
building (temple)– Usually protected by wall– Served many purposes
• Store grain, ceremonies, sacrifices
• Priests held high power in society– Initially had all power until
more wars broke out and military leaders took over

Sumerian Politics/Culture
• Led to dynasties – A succession of rulers from the same
family. • Society had rigid social classes
• Little Social mobility– Priests and Kings – upper class– Merchants/ Artisans – upper middle
class– Farmers/ Laborers – lower middle class– Slaves- (usually POWs, not race based)
• Women held some rights in society• Able to own land, enter low priesthood• Could not write; suggests no education

Sumerian Science & Tech
• Sumerians known for 4 major inventions– The wheel– The sail
• Both aid in travel and trade; make them faster
– The plow – The Harness
• Created calendars• Counting/ number system from 0 –
60• First to use Bronze- the Bronze Age• Created cuneiform
– Writing system of pressing into clay– Used pictographs – picture=words– Stylus- small tool for writing
• Ziggurat

Early Mesopotam
ian Conquerors
• Religious leaders held power first but wars broke out
• With more wars, military leaders come to power• Eventually leaders start taking over nearby
villages– Leads to the beginning of empires and empire
building• Empire-many areas under the rule of one leader
• First Empire builder- Sargon of Akkad• Takes power over Sumer
– Came from the city of Akkad– Adopted many of the Sumerian
practices and beliefs• Sargon dynasty unifies Sumer from
2340 – 2125 BCE– Becomes the first time Sumer was unified
• Expands empire from north of Sumer to Persian Gulf


Discussion
• Why did Sargon adopt much of the Sumerian culture?

New Group & Leader Come to Power
• Empire of Sargon begins to weaken• Amorites take power of Sumer around
2000 BCE; later known as Babylonians– Make Babylon their capital, moved it from Ur– Still kept practices of Sumer
• Babylonian Empire reaches its height under Hammurabi (1790-1750 BCE)
• Best known for creating a code of law for all people– Hammurabi’s Code; based off earlier codes– First Written Law Code; posted throughout
cities.• Hammurabi’s Code based on revenge
– Eye for an eye, tooth for tooth• Rules applied differently to rich and poor• Religion changed under Hammurabi-
Marduk main god