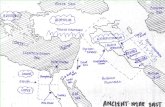
Ancient Civilizations
description
Transcript of Ancient Civilizations

Ancient CivilizationsAncient Civilizations
SOL SOL ReviewReview

Paleolithic Paleolithic EraEra
Homo Habilis, Homo Erectus, Homo Sapiens.Nomadic, hunters and gatherers
Clans, oral communications giving each group an identity
Paleolithic Era; control & use fire, used animal hides for clothing, constructed simple tools and weapons.

Mesolithic & Neolithic Mesolithic & Neolithic ErasEras
Domesticated animals constructed advanced tools, made pottery wheels, and began weaving.
Most importantly, the Neolithic Revolution, the use of seeds to grow and maintain a surplus of food, resulting in the building of civilizations.


Ancient River Valley Civ.-Egypt 3500-Ancient River Valley Civ.-Egypt 3500-1069 BC1069 BC
Nile River, current flowing north and the winds blowing south. Annual flooding left silt on the land.. Hieroglyphics were written on the papyrus culled from the Nile Delta.Egypt united under Menes (Narmer), who built the first capital at Memphis.Later the capital was moved to Thebes.Three periods of Egyptian history; Old, Middle, and New (Empire) Kingdom.Famous rulers; Rameses, Akhenaton, Hatshepsut, Thutmose.

Mesopotamia-Mesopotamia-”the land between two rivers.””the land between two rivers.”
Located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, oldest civilization in history.(4500-2300 BC).Sumer & Babylon the most
famous civilizations.Sumerian innovations; cuneiform, sun dial, ramp, arch, ziggurats, the epic poem about Gilgamesh,…Babylonian innovations; first empire, Hammurabi and the Code of Laws, zigguratsOther peoples; Jews, Persians, Assyrians, Chaldeans and Phoenicians

Indus Valley- 4000 BC-1800 Indus Valley- 4000 BC-1800 BC)BC)
Located in the Northwest portion of the Indian subcontinent. Protected by the Hindu Kush (Khyber pass) and Himalayan mts.Main cities; Harrapa and Mojenjo Daro, excavations show central planning of cities, trade with the Fertile CrescentCities disappeared after being
overwhelmed by the Aryan invasion.

Shang China – 1700-1100 BCShang China – 1700-1100 BC
The Shang developed around the Hwang Ho river valley.
Famous for their bronze artifacts, oracle bones, and writing system.
Defeated by the Zhou in 1100 BC

Quiz #1Quiz #1
1.Groups of early humans were nomadic., this means?A. frequently moving from place to placeB. no written languageC. are farmers.
2.Human ancestors developed into homo sapiens approximatelyA. 1-4 million years ago
B. 100,000 to 400,000 yearsC. 1,000 to 4,000 years ago

Quiz #1 continuedQuiz #1 continued
3. Hieroglyphics are associated withA. Egypt, B Mesopotamia, C Indus Valley
4. The first alphabet was developed by:A. Egyptians, B. Babylonians, C. Phoenicians
5. Cuneiform was a:A. Egyptian burial, B. B. Sumerian writing,C. Religious practice of the Hebrews

Ancient Greece Ancient Greece

GreeceGreeceCradle of western civilization, located on a peninsula between the Aegean and Mediterranean seas.Early influences were the Egyptians
and the Minoans (isle of Crete)Mild climate promoted outdoor activity, leading to a lot of social contact. End result conscientious civil life, seen both in their political and social philosophies.Three periods of history; Heroic, Hellenic, and Hellenistic eras. (Mycenaean & Ionians first wave of Indo-European invaders Heroic Age), After the Dorians invade, the Hellenic Age will emerge.


Greece continuedGreece continued
Geography; lots of mountains. Most Greeks lived in the fertile valleys between the mountains. As a result of limited water supply: (no major rivers and most of the rain came in the winter)there were few places to grow fruits and vegetables and insufficient grass for grazing large herds of animals.With the limits on food production, Greece could only sustain small populations. (never more then 2 million people in Ancient Greece.)

There was no river system to unify. Lots of natural harbors added to a mild climate saw the Greeks make their living by fishing, trading, and piracy.Greeks were also great colonizers, they needed the resources from outside of Greece to supplement what little they grew in Greece.The Greeks utilized the resources they had, long coast lines and excellent harbors to build their cities around the Aegean, the Ionian, and the Black Seas, the seas united them!
Greece continuedGreece continued


The Greek PolisThe Greek Polis
When the Warrior Kingdoms of the Hellenic Ages fell to the Dorian Invasions, Greece entered into the “Dark Age”
As trade recovered, and coins replaced barter, powerful city-states emerged. (Athens, Sparta, Thebes…)
Greece’s geographical barriers made it difficult for Polis’s to unite under one government, instead they competed for the limited resources of the mainland, and established colonies abroad

The two most famous Greek City States were Athens (Democracy) and Sparta. (Oligarchy)In Athens, all free males eventually were accorded citizenship giving them access to all avenues of political power. Citizens only made up 20% of the population, foreigners, slaves, and women were not allowed to participate in the government.Sparta used it’s military to control all aspects of life. The Spartans were afraid of their Helots (hereditary slaves) and used a militaristic system of government to keep them under control. Spartans did have an assembly, but it was controlled by a few elders, thus making it an oligarchy.
The Greek Polis-ContinuedThe Greek Polis-Continued

Each Polis had three groups; citizens (adult males), free people,Metics (no rights, foreigners who sometimes lived for several generations in this classification.), and slaves. (Sparta’s were called helots). Important areas in each Polis were the ; Acropolis (location of the temples) and the Agora (marketplace) where all public business was transacted, including politics.Key people in developing Athenian Democracy are Draco, Solon, and Cleisthenes.Hoplites (soldiers), Phalanx (military formation)
The Greek Polis-ContinuedThe Greek Polis-Continued


Persian and Peloponnesian WarsPersian and Peloponnesian Wars
Persian Wars began when the Athenians aided their “cousins” in Asia Minor in their rebellion against the Persians.Greek Persian Wars, Athens and Sparta lead the fight. Great battles are; Marathon, Thermopylae, SalamisAt Marathon, the Athenians surprise Darius’s force and win in an upset!Thermopylae is where the Spartans win fame for their heroic three day stand

The Athenians win fame again when they defeat Xerxes forces in a naval battle, effectively ending the Wars.There are many long term effects of the wars, but one very significant one is that Athens emerges as a major power (Delian League) and Sparta is embittered over their efforts not being more greatly appreciated. End result…The Peloponnesian War; the 20 year struggle between Athens and Sparta, along with their allies to control Greece. This war ends the “Golden Age” of Greece as well as the Golden Age of Athens.
Persian and Peloponnesian WarsPersian and Peloponnesian Wars

Greece VIP’sGreece VIP’s
mythology, Zeus, Athena, Poseidon…
Homer’s epic poems; the Iliad & the Odyssey.Heroes included; Achilles, Hector, and Odysseus. These stories and heroes will be referenced in all forms of western literature, even up to the 21st century.

Alexander the GreatAlexander the Great
Father – Philip of MacedonTutor – AristotleBefore dying at 33, he defeated the mighty PersiansHe is responsible for the Hellenistic (fusion of Greek with near Eastern cultures) philosophy which will dominate the Mediterranean region for centuries.Great Philosophies of the time were; Stoicism, Cynicism, Epicureanism.

RomeRome
Geography, snug in the middle of the Italian peninsula, the Alps to the north protected them from invasion by the land. ( with a notable exception). The seas protected as well, and helped to put the Romans at the crossroads of Mediterranean trade. (Look at map)Roman mythology very similar to Greeks, from whom the Romans borrow much.Socially and politically, the Patricians and the Plebeians were the major players.

RomeRome

RomeRome
Government, after getting rid of the monarchy, they devised a representative republic, made up of two groups. (the Senate and the Assembly) The Twelve Tables was their legal code, and posted in the Forum.Important officials were the;consuls, tribunes, and the senators. Octavian Caesar, after a series of civil wars, ends the Republic and creates the Empire.Mark Antony, Octavian Caesar, Marcus Aurelius, Diocletian, and Constantine, all great Romans (Know them for the SOL)

Roman-Punic WarsRoman-Punic Wars

Rome fights three of them. Most famous adversary is Hannibal of the Alps. War initiated over Sicily and control of trade. When over, after three conflicts, Rome controls the Western Mediterranean in 146 BC
First Punic War ends with Rome developing a fleet of ships and negating that Carthaginian advantage.
2nd Punic War is fought when Hannibal attempts to avenge the earlier Carthaginian defeat. Eventually, he is outmaneuvered and defeated at the battle of Zama
Famous Romans in this war are; Scipio Africanus (Zama), Cato the Elder, the catalyst for the 3rd Punic War. (“Carthage must be destroyed!”)
Punic WarsPunic Wars

Roman expansion problemsRoman expansion problems
After the wars, Roman society is fundamentally changed. Roman soldiers lost their farms, Latifundias (Large estates worked by slaves) are created. Landless citizens go to Rome and become the proletariat (the “mob”).
Eventually, the population of Rome consisted of up to one third slaves as well as the landless citizens.
The Roman Republic is not equipped to rule foreign lands, they end up exploiting the people they govern. This also contributes to political corruption at home.

Rome -Wars of Expansion and Rome -Wars of Expansion and ResultsResults
. Notable reformers are the Gracchi brothers, Tiberius and Gaius. They attempted to reform land holdings in Roman society and for their efforts received death.Cicero is a great writer and politician, who fails to end the “slide “ of the Roman Republic.Later civil wars come, Sulla vs Marius. The 1st Triumvirate; Julius Caesar, Marcus Crassus, PompeyCaesar, as a result of the Gallic wars, will become the most powerful of the three, a struggle for supremacy will ensue.

Creation of the EmpireCreation of the Empire
Caesar wins the Civil War, but later assassinated by Marcus Brutus, 2nd Triumvirate formed.Key men are Octavian Caesar, Caesars nephew and heir, and Marc Antony. After Antony and Caesar split the Roman world, a final war will be fought with Octavian defeating the forces of Antony and Cleopatra.Octavian is granted the title of Augustus, organizes the empire and the Pax Romana begins.

The Roman EmpireThe Roman Empire

Roman accomplishmentsRoman accomplishments
Writers like Ovid, Vergil (Aeneid), the historian LivyScientists like Ptolemy and doctors like GalenThe advantages of Roman citizenship brought the Empire together. Roman law developed a standard of justice that applied to all people, which carried over after the fall of the empire.the Pax Romana (27 BC – 192 AD), roads, aqueducts, the Coliseum…During the empire a major religion is born, Christianity, and another scattered in the Jewish Diaspora.

Rome continuedRome continuedThe apostles, Peter and Paul(Epistles) spread the faith. Paul is the apostle to the Gentiles. (non- Jews)Nero begins the persecutions of Christians(64 AD). Constantine ends the persecution with the Edict of Milan(312 AD), and Theodosius makes Christianity the official religion of the empire. Decline of Rome occurs slowly; political instability (the Barrack Emperors), coupled with plagues, and finally barbarian invasions. (Huns, Vandals, Visigoths..)Diocletian divides the empire in half, to no avail. Constantine will move the seat of power to Byzantium. (Constantinople)The Western Empire ends in 476, while the Byzantine Empire continues till 1453 AD

Greece and Rome Questions.Greece and Rome Questions.
Greek polis’s had three groups of inhabitants, which group was comprised of adult males, who engaged in commerce?A) citizens B) free people, C) non-citizen
Who were the Metics and Helots, and where did they live? Which great leader died during the Peloponnesian War? A) Herodotus, B) Zeno, C) Pericles, D)Aristotle?
This philosopher ended his life by drinking poison rather then accept ostracism. A) Zeno, B) Plato, C)Sophist, D) Socrates

Quiz on Greece and Quiz on Greece and RomeRomeThe Roman Senate and Assembly were
associated with: A) the Republic, B) Empire
The codified Roman laws were called:A) 10 Commandments, B) Twelve Tables
The Punic Wars were fought between Rome andA) Athens, B) Gauls, C) Carthage
This man reorganized the Republic into an Empire: A) Antony, B) Julius Caesar, C) Octavian

Greece and Rome QuizGreece and Rome Quiz• Famous Christian missionary, who wrote many
of the Epistles: A) Peter, B) John, C) Paul
*The Pax Romana ended with his death: A) Julius Caesar, B) Marcus Aurelius, C) Diocletian
• This emperor ended the persecution of Chrisitians: A) Constantine, B) Nero, C) Herod
• This Roman city’s harbor was known as the “Golden Horn”: A) Rome, B) Byzantium, C) Venice


Middle East, Russia, and Medieval EuropeMiddle East, Russia, and Medieval Europe
“There is only one God, Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet” The profession of faith is central to the religion, born in the Arabian desert during the 7th century.AD 622-Hijrah to Madinah, 624-Madinah Compact.Important points to remember; the Qur’an and the Hadith are books of scripture. The Shar’iah is the body of law. The Muslims live their lives by the 5 Pillars of Islam. (Know them)Muhammad is succeeded by the Caliphs, Abu Bakr being the first. Later after Ali is killed major split in Islam

Islam continuedIslam continued
After the death of Ali and Husayn, the split in Islam is between the Sunni (followers of the way) and the Shia (Shiites), who believe the Caliphate should only be held by a descendent of Muhammad.Two dynasties after the 4 Caliphs are the ; Umayyad(whose founder overthrew Ali and placed his capital in Damascus) and the Abbasid(moved the capital to Baghdad). Later the Seljuk Turks take power from the Abbasids and govern as Sultans. (they allow the Abbasids to rule as figureheads) Islam will spread as far west as Spain, and east to China. Two primary ways in which the message of Allah are carried is through the Jihad and Trade.

Golden Age of IslamGolden Age of Islam
Golden Age occurs during the Abbasids reign.Moving the capital from Damascus to Baghdad they established the House of Wisdom (Ma’mun). Arabic numerals were introduced, Maimonides writes, ibn Sina, and al Rhazes develop their theories. Omar Khayyam composes his quatrains.Europeans will be introduced to much of this culture during the Christian crusades.


The Byzantine Empire ends in 1453 ADThe Byzantine Empire ends in 1453 AD
As the western Empire weakens and falls, the eastern portion of the empire remains strong as a result of the leadership by the capital that Constantine founded, Constantinople. It’s harbor the “Golden Horn” allows it to control trade from east to west. After a few short years it’s culture becomes Hellenistic as opposed to Roman.

Notes on ByzantiumNotes on Byzantium
Most famous of the Emperors is Justinian. Accomplishments are; Justinians Code, the building of the Hagia Sophia, and the reconquest of the old empire (Belisarius)The city was famous for its mosaics, its silk trade, (stolen by Missionaries from the Chinese) and their Icons.Its religious tradition; the icon controversy, and the split from Rome to form the Greek Orthodox Church.

Medieval Europe up to 1000 ADMedieval Europe up to 1000 AD
Feudalism is the political structure, and manorialism is the economic engine for the times.Feudalism is a decentralized form of government consisting of lords and vassals, each owing to the other certain obligations.Below the vassals were the serfs, workers bound to the land.Lands granted to the vassals were called fiefs (manors), many of which were self sufficient.

Feudalism and the ChurchFeudalism and the ChurchThe practice of primogeniture begins, where the eldest son gets all.Chivalry was a code of behavior for the knights of the realm (fighting men)The Christian Church is the only central authority to be found in Europe, the Pope being the single most powerful figure.Many noblemen’s sons went into the church, because an elder sibling received all the land. Many Church Bishops, served both a spiritual lord as well as a temporal one.

Middle Ages: Important EuropeansMiddle Ages: Important EuropeansCharlemagne-Holy Roman Emperor, crowned in 800 AD. (displeasing the Byzantines) Viking invasions began at the end of his reign.Pepin the Short(Charlemagne’s Dad)- gained the title of King for his family, by helping the Pope with the Lombards (Gift of Pepin)Charles Martel(Pepin’s dad)- Mayor of the Place, defeated the Muslims at
Tours (732 AD). Probably began the European military tradition of Knights, with the lands that went with it.

Palace schools-called for by Charlemagne, promoting education. Helped to fuel the Carolingian renaissance. Charlemagne’s school employed Alcuin, a great Saxon scholar.Treaty of Verdun-divided Charlemagne's empire into three parts.Vikings,Norseman, warriors and raiders who terrorized Europe till 1000 AD. They settled everywhere from England-Ireland-Normandy-Sicily-Eastern and Central Europe. Most famous, Leif EricksonOtto the Great, rebuilt the Empire and competed with the Papacy for control of Europe.
Middle Ages: Important EuropeansMiddle Ages: Important Europeans

Russia – Heir to RomeRussia – Heir to Rome
Rus, Vikings, who settled in Kiev and adopted the Eastern Orthodox Church (Vladimir)Boyars, Slavic nobles, the Steppes (plains)Golden Horde, Mongols who dominated Eastern Europe for 200 years, also known as the TatarsIvan III, married the niece of the last Byzantine Emperor. Through this marriage claimed the power of Byzantium.Moscow, the third Rome. The Eastern Church locates here and Ivan takes the title of Tsar.

Quiz on Islam, Byzantium, Europe, and Russia.*Capital of the Umayyads:A) Madinah, B)
Mecca,C)Damascus, D) Baghdad*The Golden Age of the Islamic
world:A)AbbasidsB) Ummayads, C)Samanids*The revealed word of Allah is found in the:
A)Torah, B)Hadith, C) Qur’an,*The Islamic Shar’iah is comparable to the?*What does Muhammad mean in talking about
“People of the Book”?

*Roman Catholic is to Eastern Orthodox as Sunni is to?
*In Feudalism, who just was beneath the King? A)Serf, B) peasants, C) vassals, D)citizens
*Code of conduct for Christian knights was called? A) Bushido, B) Chivalry
*Crowned the Holy Roman Emperor in 800 AD:A) Charlemagne, B)Otto the Great, C) Justinian
*The practice of giving the whole inheritance to the eldest son is called? A) selfish, B)primogeniture

Quiz continuedQuiz continued
*The Vikings were called by all of the following titles except; A) Norsemen, B)Danes, C)Rus, D) the Huns
*Byzantium was transformed into the city of Constantinople by? A) Constantine, B) Diocletian, C) Theodosius, D) Nero
*Justinian’s Code was a legal system for the ? A) Muslims, B) Byzantines, C) the Rus.
* This battle and defeat by the Byzantines directly led to the Crusades; A) Bulge, B)Verdun, C) Manzikert, D) Omaha Beach

Indian Sub-ContinentIndian Sub-Continent
Hinduism and reincarnation, concepts that developed after the invasion of the Aryans, (through the Khyber Pass), around AD 1500.
Development of the caste system, to provide social order and keep the indigenous people enslaved.(Sparta’s helot system similar to the pariahs)Concepts of dharma, and karma to provide order and hope.Scripture; Vedas, Mahabarata (Arjuna & Vishnu)

India continuedIndia continuedImportant political dynasties; Mauryan (Asoka, the Buddhist King) & the Gupta (India’s Golden Age)During the “Golden Age); arabic numerals, concept of pi, decimal system, medical advances, literature.Buddhism-Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha, the Enlightened One)
Concepts; the Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path, Nirvana (state of nothingness), life as a cycle of misery) rejection of Hindu gods and the caste system.Theravada and Mahayana sects, where?

India and ChinaIndia and China
Gupta India, after 720 AD, invaded by Muslims. Islamic influence greater in the Northern subcontinent, Hinduism remained dominant through the rest of continent.
Today, three major countries; India (Hindu), Pakistan (Islamic), and Bangladesh (Islamic)

China and the Silk RoadChina and the Silk Road

China, the Great Wall and the Silk Road.
Confucius and Lao-Tzu; later part of Zhou Dynasty, two great philosophies.Confucianism, a life philosophy focused upon familial and public responsibilities.Confucius based his philosophy upon his Five Primary Relationships; Ruler/Ruled, Father/Son, Husband/Wife, Old/Young,
and Friend/Friend.
China and the Silk RoadChina and the Silk Road

Confucianism & TaoismConfucianism & Taoism
Han Dynasty first to implement teachings in government, with their Civil service exams and Mandarins (title for people who passed the exams). Confucianism becomes the foundation for public life for centuries.Lao-Tzu and Taoism, preach inner harmony (getting in touch with the Tao (universal life force)Lao-Tzu rejects public responsibility
(tune in and drop out)

Confucianism & TaoismConfucianism & Taoism
Concept of Yin and Yang allows the Chinese to be both Confucian in public and Daoist in private.Innovations developing from Taoism; magnetic compass, gunpowder,acupuncture.Taoism heavily influences the arts; music, poetry, painting. (focusing on nature)Other Chinese concepts; Mandate of Heaven (political), three classes of people (Nobles land owners, peasant, and merchants)

China and JapanChina and Japan
China experiences a “Golden Age” during the T’ang Dynasty (7th to 9th century AD)Skilled in all of the human arts, it excels in poetry, which reveals the “soul” of China at this time.The printing process is inaugurated during this period, spreading all of China’s innovations throughout Southeastern Asia. (Korea and Japan).Japan, four main islands off of the coast of Asia

JapanJapan
Because of physical location, Japanese develops their own unique culture.Japanese religion-Shintoism. Important concept is Kami, life force that includes; “spirits”, ancestors, parts of nature. Shintoism focuses upon obedience and proper behavior. Buddhism and Confucianism introduced to Japan, Japanese both Buddhist (Zen) and Shinto.

JapanJapan
Zen Buddhism emphasized meditation and physical discipline, over book learning.Japan’s political structure is feudal; Daimyos and Samurai (similar to Lords and Knights in Europe. Shogun is the military dictator.Bushido is the code of behavior for the Samurai, “honor’ is the most important concern for all. When honor lost, ritual suicide (seppuku) is encouraged, both for men and women.


Kush , Ghana, and MaliKush , Ghana, and Mali
There were several Sub-Saharan countries, Nubia, Axum, Nok, and Bantu cultures. The focus for the SOL’s is in Kush and Ghana because of trade!Kush is in East Africa, most significant trade partner is Egypt. The capital is in Meroe, major trade item is iron. Brief period of time, Kush controls Egypt. Kush is located in modern day Sudan.Ghana and Mali’s wealth is based upon the Gold and Salt trade.

Ghana, Mali, and MayansGhana, Mali, and Mayans
Mali capital of Timbuktu, famed for wealth and scholarship. Mansa Musa on his pilgrimage to Makkah displays incredible wealth.Mayan civilization flourished from approximately 900 BC– AD 900 (Yucatan peninsula).Politically a collection of city-states, found in present day southern Mexico and parts of Central America.The Mayans are famed for their pyramids, hieroglyphs, mathematics, calendars..

History Skills- Three Categories
Generalizations; You might be asked to determine whether a quote you had just read was a primary or secondary source. An example might be a quote from Julius Caesar;”All of Gaul is divided into three parts.” If this is a quote directly attributed to Caesar it is a “Usually, the test will ask you to read a quote and make a generalization.

Generalization & Population DistributionAn excerpt from the Code of Hammurabi: if a noble has knocked out the tooth of a noble of his own rank, then that noble shall have a tooth of his own knocked out.But if he has knocked out a commoner’s tooth, he shall pay one-third mina of silver.You might be asked something like: Based on the passage above, what generalization can you make about Babylonian society? You would pick an answer that stated that there were divisions in Babylonian society.

Population DistributionPopulation Distribution (Movement), main facts to keep in mind:Before the rise of early civilizations, populations were nomadic.Early civilizations were located in river valleys, populations clusteredIn the ancient world, the highest concentrations of people were in the Mediterranean region, Indus Valley, Hwang Ho Valley in China, and increasingly in Central America.As empires grew, so did wealth, thus cities grew. Cities such as ; Thebes, Babylon, Athens, Rome, Carthage, and later Constantinople and Baghdad are excellent examples of this type of urban growth.During the European Middle Ages, the vast majority of the population was agrarian, living on fiefs as;serfs, knights, Lords.As trade increased between civilizations, populations distributed themselves along ports(Constantinople) and trade routes. (Silk Road)

Generalizations & Political BoundariesIn general, the arts and sciences were advanced in civilizations which consist of large populations, that generate the wealth to support the advances (arts and sciences)Populations go toward arable land (often river valleys) and jobs (which often mean cities at the center of trade in major sea harbors or along major land trade routes.The SOL’s will test your knowledge of history with respect to what contemporary nations exist in the areas which we studied. For example; Mesopotamia is now part of Irag. The Mayans occupied territory that is currently part of Mexico. Ancient Gaul is now France. The city of Constantinople is now known as Istanbul. Mecca and Medina are located in present day Saudi Arabia.

Quick QuizWhat is the difference between a primary and secondary source?During the European Middles Ages the vast majority of the population was involved in what type of work?Describe the difference between Feudalism and Manorialism.Which two religions did most people in traditional Japan identify with?What did the ancient Egyptians and Mayans have in common with each other?Christian Knights behavior was regulated by the code of Chivalry, what similar code regulated the Samurai’s behavior?List the following Chinese Dynasties in chronological order, from earliest to last. Also, place an important accomplishment next to each of the Dynasties. Han, Qin, T’ang, Shang, and Zhou.Describe the difference between Taoism and Confucianism, and what concept allowed the Chinese to practice both?

Geography Knowledge and ConceptsHuman/Environment InteractionCharacteristics of a geographical regionCultural characteristics of the landscape.Movement (migration and cultural interaction)Patterns of urban development.Human Environment Interaction: looking at how people adapt themselves to the environment they live in. An example of this is when ancient people settled in river valleys, they had to deal with floods. The test might look at the Nile and or the Euphrates. Floods brought silt, but also death so people learned how to predict and control floods*People also learned how to build canals and aqueducts to bring water to the crops and cities.(The Romans were the best example of this technology)

Human/Environment Interaction• Effects on landscape: How does the building of a city impact
on the environment of a once pristine river valley? Examples; pollution, importing of materials not available at the site, impact on animal population. Most importantly, what happened to the earth in the areas affected by the Agriculture Revolution?* farmers changed the land, irrigation etc.
• Managing time; hours, days, minutes. Calendars based upon religious events (Birth of Christ, Muhammad’s flight, Chinese calendar based upon the first recording of Chinese civilization)

Characteristics of a geographic regionRegion is a name we give to a place that has something distinctive about it, when compared to other places.(usually no definitive borders, but general patterns that dominate. Chesapeake Bay, the Washington Metropolitan Region.On this test we will probably have to distinguish between land (physical) or cultural characteristics.Physical Regions like the Mesopotamian Region and the Mediterranean world, these locations are identified with two rivers, Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean Sea, thus physical regions.Cultural Regions share a common cultural identity without regard to the characteristics of the physical landscape.Examples of a few historical cultural regions would be; the Roman world, the Islamic world, the Silk Road. All of these regions have different physical features within their boundaries, but shared common a cultural feature. In the Roman world Londonium (London) was part of the same cultural region as Jerusalem.

Cultural Characteristics of a LandscapeWhen looking at a location or a city one can easily observe the cultural characteristics of the place. Examples would be the colonial architecture of Williamsburg, or the domes, minarets, and arabesque of a Mosque, which identifies it as an artifact of the Islamic religion.Other examples of a cultural landscape would be buildings like the Coliseum of Rome, the Great Wall of China. From the Coliseum we learn about the Roman emphasis on large scale entertainment, from the Great Wall we learn of the Chinese’s vulnerability, and the direction from which they feared attack.Statues and monuments reveal to us what the people of that region felt was significant and what the people should aspire to achieve

Migration and Cultural InteractionMigration is a permanent move to a new location. Thus a visit a two week visit to Disney World does not constitute a migration. In other words, leaving your present home to establish a new residence is considered a migration, even if you do not know where you are going, even if you don’t stay long!Two broad categories cause the human population to migrate; push and pull factors.Push factors drive people out, with no obvious place to go, often times different groups are thrown together creating diversity.Push factors up to 1,000 AD: 1)overpopulation,2) religious persecution, 3) agriculture decline or famine, 4) war & conflict, 5) slavery, 6) natural disasters, like floods and earthquakes.Some of the Push factors that might be on the test would be the; Jewish Diaspora, the Bantu migration, the Viking raids, the Germanic invasions of Rome.

Migration: Pull Factors & the legacy of migrationPull Factors, people migrate because they have heard or know that a location is attractive to their needs.Great examples of pull factors are arable lands and religious acceptance.Often push and pull factors are working simultaneously.Legacy of Migration:expansion of cultural regions (Islamic culture), the fall of other regions (the Roman world),the spread of architectural styles, .. The movement of people has resulted ina tremendous amount of cultural diffusion in the world.

Patterns of Urban DevelopmentRegardless of which early river system we looked at, all developed the same pattern of urban development, the building of similar towns and villages. Proof of aliens? No, simply that people are smart, river valleys provide arable land, water for irrigation, and transportation.Two categories best explain patterns of Urban Development; Site Factors, and Situation Factors.Site factors; Athens and Constantinople develop as they did because of the access to excellent natural harbors. People who are looking to settle down search for such physical features. because it is easily defended, again Constantinople, centrally located, Baghdad, or along trade routesSituational features; the choice to settle down in a spot might be because it is easily defended, again Constantinople, centrally located, Baghdad, or along trade routes like Damascus.

Geography SkillsMap projection and distortion:Cartographers (map makers)have struggled with the act of transforming information from the earth’s surface onto a flat map is know as a projection. The Mercator projection is the most popular of these projections, because it keeps the land masses relatively undistorted.The problem with the Mercator projection is that the land masses near the Poles appear much larger then they really are.Scale: the relation between the distance on a map and the distance in the real world.The smaller the map, the more detail and individual locations that can be identified.Latitude and Longitude:Longitude lines (meridians) run from the North to the South Pole, with the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England being the Prime Meridian. ( the starting point) Latitude lines run east and west around the globe and the one exactly halfway from the poles is the Equator.

Geography SkillsWith the latitude and longitude lines in place, every location in the world can be precisely charted.Points of View: Often times maps would reflect cultural bias, which cities should be included, spelling of locations,…Maps often were designed to support the view of an emperor, religious leader, or merchant.(sometimes the maps were intentionally lopsided to project a cultural superiority)Thematic Maps:Maps not only show physical features, political boundaries, the contour (lay of the land), they can also show all types of information; population density (most common), economic activity, distribution of resources, languages or religions. These types of maps are called Thematic Maps.The test might show you a thematic map and ask you to make a conclusion based upon a map.