Ancient Civilizations
description
Transcript of Ancient Civilizations

Ancient CivilizationsAncient Civilizations

Paleolithic EraPaleolithic Era Paleolithic Paleolithic Era (Old Stone Age)Era (Old Stone Age)
• When - When - 2 million BCE to 10,000 BCE2 million BCE to 10,000 BCE• First people lived in East Africa First people lived in East Africa
Hunters and Gatherers Hunters and Gatherers • NomadsNomads –– moved to find foodmoved to find food• Men would hunt game animals and fishMen would hunt game animals and fish• Women would collect fruits, berries Women would collect fruits, berries and other ediblesand other edibles
Tools Tools Simple tools Simple tools - - spears and axes made of stone, bone or spears and axes made of stone, bone or
wood. wood. ClothingClothing - skins of animals - skins of animals ShelterShelter – caves – caves FireFire – – used for warmth and cookingused for warmth and cooking..

Paleolithic EraPaleolithic Era

Paleolithic EraPaleolithic Era Paleolithic SocietiesPaleolithic Societies
• Small groups Small groups - 20-30 people- 20-30 people• Spoken languages to communicate Spoken languages to communicate
Early belief systemsEarly belief systems• Polytheistic Polytheistic – – animismanimism• BuryingBurying the deadthe dead
AfterlifeAfterlife – Showing care for the dead – Showing care for the dead Buried with their tools and weaponsBuried with their tools and weapons

Paleolithic EraPaleolithic Era Out of Africa TheoryOut of Africa Theory
• PeoplePeople migrated from Africa migrated from Africa to the rest of the to the rest of the world world
Scarce resourcesScarce resources• Hunting and gatheringHunting and gathering sustainedsustained life life BUT BUT
people people barelybarely survived. survived.• People were nomadic because People were nomadic because foodfood waswas
scarcescarce

Paleolithic EraPaleolithic Era

Neolithic RevolutionNeolithic Revolution Neolithic Revolution Neolithic Revolution (New Stone Age)(New Stone Age) When - When - 10,000 BCE10,000 BCE
Important discoveries Important discoveries • Farming Farming
People People learned to plant seeds to grow foodlearned to plant seeds to grow food
• Domesticate animalsDomesticate animals Tamed animals Tamed animals they had been huntingthey had been hunting Herded and penned Herded and penned the animalsthe animals Sources of Sources of food, clothing, labor and transportationfood, clothing, labor and transportation

Neolithic RevolutionNeolithic Revolution

Neolithic RevolutionNeolithic Revolution ImpactImpact of Neolithic Revolutionof Neolithic Revolution
Reliable source of foodReliable source of food AsAs food supply increases, food supply increases, so did the population so did the population Villages of hundredsVillages of hundreds andand cities of thousands emergecities of thousands emerge
Permanent communities formedPermanent communities formed• Sedentary Agriculture Sedentary Agriculture – – farming in one placefarming in one place
New Technologies New Technologies – to meet their new needs– to meet their new needs• CalendarsCalendars – – know when to plant and harvest cropsknow when to plant and harvest crops• Metal tools Metal tools – – bronze and then iron bronze and then iron ((plows, sicklesplows, sickles))• Irrigation systems Irrigation systems – – brought water to farmsbrought water to farms• Metal weapons Metal weapons – – defend their resources defend their resources and villages and villages

Neolithic RevolutionNeolithic Revolution

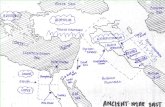
River Valley CivilizationsRiver Valley Civilizations Rise of Civilizations Rise of Civilizations
Rivers valleys Rivers valleys - - home to the first home to the first civilizations civilizations
• Fertile LandFertile Land – the yearly – the yearly floods provided floods provided arable landarable land
• Fresh Water Fresh Water – gave people – gave people water water sourcesource• TransportationTransportation – Used the river as a – Used the river as a means of means of
transportation transportation• TradeTrade ––civilizations exchanged goods and civilizations exchanged goods and
ideasideas when people came into contact with when people came into contact with one anotherone another

River Valley CivilizationsRiver Valley Civilizations

Rise of CivilizationsRise of Civilizations Characteristics Characteristics of a Civilizationof a Civilization
• CitiesCities – – populations of thousands populations of thousands • Governments Governments – – provide order, organization provide order, organization
and protection and protection • Traditional economy Traditional economy – – based on farming and based on farming and
other skilled crafts other skilled crafts such as pottery, clothing such as pottery, clothing and other goodsand other goods
• Organized religion Organized religion – – priests would perform priests would perform ceremoniesceremonies to ensure plentiful crops and to ensure plentiful crops and protection from the Gods (protection from the Gods (PolytheisticPolytheistic))

Rise of CivilizationsRise of Civilizations

Rise of CivilizationsRise of Civilizations Specialization of labor Specialization of labor
• people to people to perform different jobsperform different jobs/functions in society /functions in society Social classes emerge Social classes emerge – – based on one’s based on one’s occupationoccupation
• Ruler - Ruler - Leader of the armyLeader of the army• Priests – Priests – led religious ritualsled religious rituals• Warriors - Warriors - protected resources and citiesprotected resources and cities• Merchants Merchants and and artisanartisan• Peasant FarmerPeasant Farmer• Women’sWomen’s - status declined - status declined as men took lead roles as as men took lead roles as
warriorswarriors Systems of writing Systems of writing – – Used for Used for record keepingrecord keeping. . Early Early
writing writing used pictures used pictures and and then developed into symbolsthen developed into symbols Art and architecture Art and architecture – – Built temples and palaces to Built temples and palaces to
honor religious and political leaders.honor religious and political leaders. Public works Public works – – built infrastructurebuilt infrastructure such as such as roads, roads,
bridges and walls for protectionbridges and walls for protection

Nile Valley CivilizationsNile Valley Civilizations River Valley Civilizations (4000 BCE–1650 BCERiver Valley Civilizations (4000 BCE–1650 BCE)) Nile River Valley – Egypt Nile River Valley – Egypt ((North AfricaNorth Africa) ) Geographic SettingGeographic Setting
Region Region – – North Africa, Middle EastNorth Africa, Middle East Topography - Topography - Mostly Desert – Mostly Desert – land with little land with little
rainfall and sparse vegetationrainfall and sparse vegetation• Natural barrier Natural barrier – – provided protection provided protection from invasionfrom invasion
Nile River Nile River - River flows from South to North- River flows from South to North• Fertile Soil – Fertile Soil – Silt Silt from floods leaves a rich deposit of from floods leaves a rich deposit of
soilsoil• TransportationTransportation - - highway for travel and tradehighway for travel and trade• CitiesCities - - Villages merge Villages merge to form cities to form cities • Nile Delta Nile Delta - - where the where the Nile emptied into the Nile emptied into the
Mediterranean SeaMediterranean Sea

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley GovernmentGovernment
PharaohsPharaohs – – ruler of Egypt ruler of Egypt Divine Right Divine Right -- worshipped as a worshipped as a living Godliving God Absolute power Absolute power Centralized Government Centralized Government
BureaucracyBureaucracy – – government agencies government agencies ((collecting collecting taxestaxes))
DynastyDynasty – – Ruling family of EgyptRuling family of Egypt; When the ; When the pharaoh died, power was passed onto the another pharaoh died, power was passed onto the another family memberfamily member
MenesMenes – – PharaohPharaoh (3100 BCE) - (3100 BCE) - United Upper and United Upper and Lower Egypt Lower Egypt to create the first dynastyto create the first dynasty
Used the Nile to link Upper and Lower EgyptUsed the Nile to link Upper and Lower Egypt

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley
ReligionReligion PolytheisticPolytheistic – – Worshipped many gods Worshipped many gods
• Amon-ReAmon-Re – The – The Sun GodSun God and the and the Chief GodChief God• Osirus Osirus – – God of the NileGod of the Nile, controlled the Nile’s , controlled the Nile’s
annual floodannual flood Afterlife Afterlife – prepared the dead for – prepared the dead for life after life after
deathdeath Pyramids Pyramids – Tombs and – Tombs and monuments used monuments used
to store the remains of dead pharaohs to store the remains of dead pharaohs as as they await the afterlifethey await the afterlife

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley SocietySociety
Social ClassesSocial Classes UpperUpper ClassClass – – Pharaoh, Priests, NoblesPharaoh, Priests, Nobles MiddleMiddle Class – Class – Merchants and artisansMerchants and artisans Lower Lower Class – Class – PeasantsPeasants ((FarmersFarmers)) SlavesSlaves
Role of WomenRole of Women:: LegallyLegally own propertyown property Run businessRun business DivorceDivorce

Nile River ValleyNile River Valley ContributionsContributions
PapyrusPapyrus – – Egyptian PaperEgyptian Paper HieroglyphicsHieroglyphics – – Writing system that used Writing system that used
pictures pictures to represent words and ideasto represent words and ideas Rosetta Stone Rosetta Stone - - translated Hieroglyphicstranslated Hieroglyphics
LiteratureLiterature - - poetry, songs, hymns poetry, songs, hymns and fictionand fiction Surgery and MedicineSurgery and Medicine
Mummification helped them diagnose Mummification helped them diagnose illnesses and perform surgeryillnesses and perform surgery
CalendarCalendar – – 365 days 365 days (solar)(solar) Math - Math - Number systemNumber system based on 10 based on 10 (10, 100, (10, 100,
1000, etc.)1000, etc.)

Nile river ValleyNile river Valley

MesopotamiaMesopotamia Tigris & Euphrates Rivers Tigris & Euphrates Rivers – – Mesopotamia Mesopotamia Geographic SettingGeographic Setting
Region – Region – Middle EastMiddle East
• MesopotamiaMesopotamia – The – The land between the riversland between the rivers• The Fertile Crescent The Fertile Crescent – – Fertile land that Fertile land that
stretches from the Persian Gulf to the stretches from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean SeaMediterranean Sea Few natural barriers Few natural barriers
• Cultural diffusion Cultural diffusion – exchange of goods – exchange of goods and ideasand ideas
• InvasionInvasion – – allowed for several invasionsallowed for several invasions

MesopotamiaMesopotamia

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer Sumerian Civilization Sumerian Civilization – (3000 BCE)– (3000 BCE)
Government Government • City- StatesCity- States – – independent areas but shared a independent areas but shared a
common culturecommon culture• RulersRulers – seen as the – seen as the chief servant to the godschief servant to the gods
Role of Government Role of Government – – Enforced laws, collected Enforced laws, collected taxes, led armies, kept records, maintained city taxes, led armies, kept records, maintained city walls and irrigation systemswalls and irrigation systems
Religion Religion • PolytheisticPolytheistic – – Gods had human qualities Gods had human qualities and were and were
tied to the forces of naturetied to the forces of nature Each city-state had their own God or GoddessEach city-state had their own God or Goddess
• ZigguratsZiggurats - - Stone temples made out of sun-dried Stone temples made out of sun-dried bricks bricks Used to show the power of the government and Used to show the power of the government and
religionreligion

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer Social ClassesSocial Classes
Upper Class – Upper Class – Ruling family, Gov’t Ruling family, Gov’t officials and high priestsofficials and high priests
Middle Class –Middle Class –Merchants and artisansMerchants and artisans Lower Class – Lower Class – Peasants (Farmers)Peasants (Farmers)

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer ContributionsContributions
InventionsInventions• SailboatSailboat• WheelWheel• PlowPlow• Walled citiesWalled cities• Irrigation Systems Irrigation Systems – – brought water to farms; expand brought water to farms; expand
farmingfarming ArchitectureArchitecture
• ZigguratsZiggurats WritingWriting
• CuneiformCuneiform – – Writing systems to keep records Writing systems to keep records LiteratureLiterature
• The Epic of GilgameshThe Epic of Gilgamesh MathMath
• Basic algebraBasic algebra• GeometryGeometry• Number system based on 6 Number system based on 6 (60 minute in an hour, 360 (60 minute in an hour, 360
degrees in a circle)degrees in a circle)

Mesopotamia - SumerMesopotamia - Sumer

Mesopotamia - BabylonMesopotamia - Babylon Babylonian Babylonian Civilization Civilization
Government Government • Centralized government Centralized government – – strong strong central governmentcentral government
Hammurabi Hammurabi – (1792-1750 BCE) – (1792-1750 BCE) God-like kingGod-like king Code of Hammurabi Code of Hammurabi – – 300 codified laws carved 300 codified laws carved
in stone in stone • Criminal Law Criminal Law – – robbery, assault, murderrobbery, assault, murder• Civil law Civil law – – business contracts, property, taxes, business contracts, property, taxes,
marriage and divorcemarriage and divorce• SpecificSpecific punishmentspunishments for specific lawsfor specific laws• Harsh punishments Harsh punishments – “– “Eye for an EyeEye for an Eye””• Social inequality Social inequality – laws were – laws were harsher for lower harsher for lower
classes, women and childrenclasses, women and children

Mesopotamia - BabylonMesopotamia - Babylon

Mesopotamia - BabylonMesopotamia - Babylon Contributions Contributions
• ContractContract - written agreement- written agreement• AstronomyAstronomy – Study of universe – Study of universe• Lunar calendar Lunar calendar ((12 months, 7 day week, 24 hr 12 months, 7 day week, 24 hr
dayday))• Map makers Map makers – – cartographercartographer

Indus River ValleyIndus River Valley Indus River Valley Indus River Valley – – Indian SubcontinentIndian Subcontinent
Geographic SettingGeographic Setting Region - Region - South AsiaSouth Asia Mountain rangesMountain ranges
• Hindu Kush Hindu Kush • Himalayan Himalayan
MonsoonsMonsoons – – seasonal winds seasonal winds that brought that brought rainfall to rainfall to the Indian Subcontinentthe Indian Subcontinent
UnpredictableUnpredictable – – Drought or FloodsDrought or Floods Indus River Indus River – – Rich, fertile soil Rich, fertile soil

Indus River ValleyIndus River Valley

Indus River ValleyIndus River Valley Mystery Mystery
• Little is known about the Indus river valley Little is known about the Indus river valley because because historians and archaeologists have historians and archaeologists have not been able to not been able to decipher the writing systemdecipher the writing system..
• All that is known comes from archaeological findsAll that is known comes from archaeological finds Centralized GovernmentCentralized Government
• Well-Planned Cities Well-Planned Cities – – HarappaHarappa and and Mohenjo-DaroMohenjo-Daro • StreetsStreets – set up in a – set up in a grid patterngrid pattern• StandardizedStandardized - - weights and measuresweights and measures• Religious TemplesReligious Temples• Granaries Granaries – buildings used to – buildings used to store grainstore grain
ContributionsContributions• Plumbing systems Plumbing systems – – baths, drains, sewersbaths, drains, sewers• Irrigation ditchesIrrigation ditches and and flood barriersflood barriers• WheelWheel

Indus River ValleyIndus River Valley

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley Yellow River Valley Yellow River Valley (3000-2500 BCE) (3000-2500 BCE)
Geographic SettingGeographic Setting
• Region – Region – East AsiaEast Asia• Natural barriers Natural barriers – – mountains, deserts, rainforest, oceanmountains, deserts, rainforest, ocean
Isolation - Isolation - cut off from others (cut off from others (early historyearly history)) River ValleysRiver Valleys
• Huang He Huang He – – Yellow RiverYellow River LoessLoess - - yellow matter in riveryellow matter in river that brings nutrients that brings nutrients
to soilto soil FloodsFloods – given the nickname, “ – given the nickname, “River of SorrowsRiver of Sorrows””
• Yangzi River Yangzi River

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley GovernmentGovernment
Shang Dynasty Shang Dynasty – – 1650 BCE – 1027 BCE1650 BCE – 1027 BCE• DynastyDynasty – – Ruling family of ChinaRuling family of China; when the ; when the
emperor died, another family member took emperor died, another family member took overover
• Decentralized government Decentralized government – – land and power land and power was delegated to noble families was delegated to noble families (military (military leaders) to governleaders) to govern
Kings led nobles into battleKings led nobles into battle Owned small areas of landOwned small areas of land

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley ReligionReligion
PolytheisticPolytheistic – – worshipped many gods and worshipped many gods and nature spiritsnature spirits
Early DaoismEarly Daoism• Yin and yang Yin and yang – – opposing forces that held opposing forces that held
nature in balancenature in balance• Ancestor Worship Ancestor Worship – – honored ancestors honored ancestors with with
sacrifices and shrinessacrifices and shrines

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley SocietySociety
Social ClassesSocial Classes Upper Upper Class - Class - Royals family and noblesRoyals family and nobles Middle Middle Class - Class - Merchants and artisansMerchants and artisans Lower Lower Class - Class - Peasants farmersPeasants farmers
““Middle KingdomMiddle Kingdom” ” - - Due to isolation, Due to isolation, early Chinese were cut off from other early Chinese were cut off from other cultures andcultures and thought of themselves as thought of themselves as the center of the universethe center of the universe

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley
ContributionsContributions Writing systemWriting system
Thousands of characters made it hard to learnThousands of characters made it hard to learn Pictographs Pictographs – Drawings of objects– Drawings of objects IdeographsIdeographs – Drawings of thoughts and ideas – Drawings of thoughts and ideas

Yellow River ValleyYellow River Valley

Classical Civilizations - ChinaClassical Civilizations - China Zhou Dynasty Zhou Dynasty – – ChinaChina ( (1027 BCE-221 1027 BCE-221
BCEBCE)) GovernmentGovernment
• OverthrowOverthrow – the Shang Dynasty – the Shang Dynasty• Mandate of heaven Mandate of heaven – – Right to rule comes Right to rule comes
from heavenfrom heaven; used to explain the dynastic ; used to explain the dynastic cyclecycle
• Dynastic Cycle Dynastic Cycle – cycle that – cycle that explained the explained the rise and fall of dynastiesrise and fall of dynasties, based on the , based on the mandate of heavenmandate of heaven
• Feudal government Feudal government – Zhou emperors – Zhou emperors granted control of large areas of land granted control of large areas of land to to local lords, but local lords, but owed military service owed military service to the to the emperoremperor

Zhou DynastyZhou Dynasty

Zhou DynastyZhou Dynasty
Economy Economy TradeTrade – – increased increased as a result of as a result of new new
roads and canalsroads and canals ( (infrastructureinfrastructure)) MoneyMoney – Chinese – Chinese copper coinscopper coins as a form as a form
of currencyof currency AgricultureAgriculture expands expands – development – development of of
iron tools iron tools

Zhou Dynasty Zhou Dynasty

Zhou Dynasty Zhou Dynasty
Contributions Contributions ConfucianismConfucianism – – Belief system that Belief system that provided provided
order and stability in China by creating rules of order and stability in China by creating rules of behaviors behaviors for individuals for individuals based on filial pietybased on filial piety
DaoismDaoism – – Belief system that Belief system that stressed harmony stressed harmony in naturein nature, , based on the Dao based on the Dao and concepts of the and concepts of the yin and yangyin and yang

Zhou DynastyZhou Dynasty

Zhou DynastyZhou Dynasty
Contributions continued…Contributions continued… LiteratureLiterature – – ““Book of SongsBook of Songs” – ” – poems poems that that
describe farming, government, ceremonies and describe farming, government, ceremonies and lovelove
AstronomyAstronomy – – Studied planet movements Studied planet movements and and ellipses to ellipses to create a 365 day calendarcreate a 365 day calendar
SilkSilk – – Expensive material used for clothing Expensive material used for clothing that that was China’s mostwas China’s most valuable export valuable export
IronIron – – used for weapons and toolsused for weapons and tools

Zhou Dynasty Zhou Dynasty

Qin Dynasty Qin Dynasty QinQin Dynasty – China (221 BCE – 206 BCE) Dynasty – China (221 BCE – 206 BCE)
GovernmentGovernment• Overthrew the Overthrew the ZhouZhou dynasty dynasty • Shi Huangdi Shi Huangdi claims to be claims to be China’s “First Emperor”China’s “First Emperor”
Centralized government Centralized government • Abolished feudal statesAbolished feudal states• Created military districts Created military districts - official heading each area- official heading each area
LegalismLegalism - - strict set of laws that imposed harsh strict set of laws that imposed harsh penalties. Used to jail, torture and kill those who imposed penalties. Used to jail, torture and kill those who imposed the emperor. Would target nobles and Confucian the emperor. Would target nobles and Confucian scholarsscholars..
• Burned books Burned books – destruction of all books of literature – destruction of all books of literature and philosophyand philosophy

Qin Dynasty Qin Dynasty
EconomyEconomy StandardizedStandardized weights and measures weights and measures Created national Created national coinscoins RepairedRepaired infrastructure (infrastructure (roads and canalsroads and canals))

Qin DynastyQin Dynasty
ContributionsContributions Great Wall of China Great Wall of China – – Built to keep China’s Built to keep China’s
civilized world separated from nomadic invaders civilized world separated from nomadic invaders from the north (Mongols)from the north (Mongols)• Thousands of workers died building the wall Thousands of workers died building the wall
due to harsh conditions.due to harsh conditions.

Qin DynastyQin Dynasty

Han DynastyHan Dynasty
Han Dynasty Han Dynasty – – ChinaChina (206 BCE - 220 CE) (206 BCE - 220 CE) GovernmentGovernment
• Dynastic Cycle Dynastic Cycle - - People despised the Qin’s People despised the Qin’s dynasty’s harsh laws and heavy taxesdynasty’s harsh laws and heavy taxes; Led by ; Led by peasants, the Han Dynasty would take control of Chinapeasants, the Han Dynasty would take control of China
• Han Dynasty Han Dynasty – – Reduced taxes and repealed Reduced taxes and repealed LegalismLegalism
• Civil Service Exams Civil Service Exams – Emperor Wudi improved – Emperor Wudi improved China’s government by setting up China’s government by setting up exams based on exams based on Confucian principlesConfucian principles; this would ; this would assure Chinese assure Chinese officials were given jobs based on meritofficials were given jobs based on merit, not their , not their family influencefamily influence

Han DynastyHan Dynasty
Economy Economy • InfrastructureInfrastructure – – new roads and canals improved new roads and canals improved
tradetrade
• MonopolyMonopoly – – set up an set up an monopoly on iron and saltmonopoly on iron and salt; ; this gave the government another source of income this gave the government another source of income other than the taxes on peasants other than the taxes on peasants
• Silk Road Silk Road – – Wudi opened a Wudi opened a trade route to the west trade route to the west that expanded from china to the Middle East that expanded from china to the Middle East and and Eastern Europe. Eastern Europe.

Han DynastyHan Dynasty

Han Dynasty Han Dynasty
SocietySociety Scholar gentry Scholar gentry – – Wealthy educated class Wealthy educated class
emerged from the Civil Service Examsemerged from the Civil Service Exams WomenWomen – – Confucian principles had women Confucian principles had women
subordinate to mensubordinate to men; ; women were not allowed to women were not allowed to take the exams take the exams and could not take a government and could not take a government jobjob

Han Dynasty Han Dynasty
ContributionsContributions Technology Technology
• Paper making Paper making from wood pulpfrom wood pulp• Wheel barrowWheel barrow• Fishing reelFishing reel• RudderRudder – device to help – device to help steer shipssteer ships• Suspension bridgesSuspension bridges• Iron stirrupsIron stirrups

Han DynastyHan Dynasty

Han DynastyHan Dynasty Science Science
AcupunctureAcupuncture – needles are inserted – needles are inserted under the skin to under the skin to relieve pain and to treat relieve pain and to treat illnessesillnesses

Han DynastyHan Dynasty
Arts Arts Temples Temples and and palacespalaces Jade and Ivory Jade and Ivory carvingscarvings BronzeBronze artworks artworks SilkSilk Literature – “Literature – “Lessons for a WomanLessons for a Woman” – ” –
Roles for men and womenRoles for men and women

Han DynastyHan Dynasty

Han DynastyHan Dynasty
Fall of the Han DynastyFall of the Han Dynasty PoliticalPolitical Causes – Causes – Weak rulers Weak rulers after the death of after the death of
Wudi; unable to control powerful warlordsWudi; unable to control powerful warlords EconomicEconomic Causes – Causes – Did not maintain canals and Did not maintain canals and
roadsroads which were vital for trade to prosper; which were vital for trade to prosper; Increased taxes on the peasants, led to a revoltIncreased taxes on the peasants, led to a revolt
MilitaryMilitary Causes – Causes – Warlords overthrew the last Warlords overthrew the last Han emperor in 22 CEHan emperor in 22 CE, the empire was split into , the empire was split into several kingdoms; several kingdoms; invaders overran the Great invaders overran the Great Wall Wall and set up their own kingdomsand set up their own kingdoms

GreeceGreece
GreeceGreece (1750 BCE – 133 BC) (1750 BCE – 133 BC) Geographic settingGeographic setting
• Region - Region - Southeast EuropeSoutheast Europe• Topography - manyTopography - many mountainsmountains, isolated , isolated
valleysvalleys and small and small islandsislands• The The MediterraneanMediterranean and and Aegean Seas Aegean Seas --
important link to the outside worldimportant link to the outside world The Greeks became The Greeks became skilled sea traders skilled sea traders allowed for allowed for
cultural diffusion cultural diffusion where they exchanged goods where they exchanged goods and ideas (technology) and ideas (technology)
They adopted the They adopted the PhoenicianPhoenician alphabet alphabet for their for their own use.own use.

GreeceGreece

GreeceGreece
Early civilizationsEarly civilizations MinoansMinoans (1750 BCE) - (1750 BCE) - first Greek first Greek
civilizationcivilization was established. was established. • The Minoans traded with Egypt and The Minoans traded with Egypt and
MesopotamiaMesopotamia

GreeceGreece
GovernmentGovernment City-States - City-States - Due to the rugged mountains Due to the rugged mountains
and isolated valleysand isolated valleys, Greek civilizations , Greek civilizations revolved around the small city-state or revolved around the small city-state or polispolis..
This This geography prevented the Greeks from geography prevented the Greeks from building a large empirebuilding a large empire like the Egyptians like the Egyptians or Mesopotamiansor Mesopotamians

GreeceGreece
The Rise of City StatesThe Rise of City States Greek culture Greek culture – – Greek Greek city-states had city-states had
independent governmentindependent government but shared many but shared many cultural characteristics such as: language, cultural characteristics such as: language, religion, and sports.religion, and sports.
Between 750 BCE and 500BCE the city states Between 750 BCE and 500BCE the city states had several different types of governmenthad several different types of government• MonarchyMonarchy – first form of government – first form of government• AristocracyAristocracy – ruled by – ruled by landowning nobleslandowning nobles

GreeceGreece SpartaSparta – A – A Totalitarian, Military Dictatorship Totalitarian, Military Dictatorship
At the age of At the age of sevenseven boys moved into the military boys moved into the military
barracksbarracks They They trained hardtrained hard and faced rigid discipline and faced rigid discipline GirlsGirls also trained hard also trained hard to strengthen their bodiesto strengthen their bodies Healthy women produce healthy babiesHealthy women produce healthy babies Sparta was an Sparta was an totalitariantotalitarian statestate that produced an that produced an
excellentexcellent militarymilitary But they did not trade, create products, nor were But they did not trade, create products, nor were
they scholarly they scholarly so they left no cultural achievements so they left no cultural achievements Spartan inability to change, would lead to its declineSpartan inability to change, would lead to its decline

GreeceGreece

GreeceGreece AthensAthens – A – A Limited DemocracyLimited Democracy
Golden Age Golden Age - - Under the leadership of Under the leadership of Pericles Pericles (460BCE – 429 BCE)(460BCE – 429 BCE)
Direct-DemocracyDirect-Democracy - - all “citizens” all “citizens” participated in governmentparticipated in government by debating by debating all political actions.all political actions.• MalesMales - - over 30, who owns land could voteover 30, who owns land could vote• WomenWomen - were seen as needing male guidance - were seen as needing male guidance
and were and were not allowed to participatenot allowed to participate..• SlavesSlaves and and foreignersforeigners - also - also did not did not
participateparticipate

GreeceGreece

Hellenistic CivilizationHellenistic Civilization Alexander the Great Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic ageand the Hellenistic age
MacedoniaMacedonia - a mountainous region in the - a mountainous region in the kingdom of northern Greece.kingdom of northern Greece.
EmpireEmpire – – Conquered Greece, Egypt, Persia and Conquered Greece, Egypt, Persia and parts of Indiaparts of India
Hellenistic culture Hellenistic culture - - blended aspects of Greek, blended aspects of Greek, Persian, Egyptian and Indian life Persian, Egyptian and Indian life
• This culture gave more rights and This culture gave more rights and opportunities to women.opportunities to women.
• Although the empire fell soon after his death, Although the empire fell soon after his death, Hellenistic culture had a Hellenistic culture had a lasting impact in the lasting impact in the regions he had ruled.regions he had ruled.

Hellenistic CivilizationHellenistic Civilization

Greek and Hellenic ContributionsGreek and Hellenic Contributions GreekGreek and and HellenisticHellenistic Contributions Contributions
PhilosophyPhilosophy• Greek thinkers usedGreek thinkers used observationobservation andand reasonreason
to understand why things happenedto understand why things happened• The word philosopher means “The word philosopher means “lover of wisdomlover of wisdom””• SocratesSocrates - Developed the - Developed the Socratic method: learning Socratic method: learning
about beliefs and ideas by asking questionsabout beliefs and ideas by asking questions; ; Government put him to death Government put him to death
• PlatoPlato - Believed - Believed government should control the lives of government should control the lives of the peoplethe people; Divided society into three classes; ; Divided society into three classes; workers, philosophers and soldiersworkers, philosophers and soldiers
• AristotleAristotle - - Believed strong and good leaders ruled Believed strong and good leaders ruled through reasonthrough reason

Greek and Hellenic Contributions Greek and Hellenic Contributions

Greek and Hellenic Contributions Greek and Hellenic Contributions
LiteratureLiterature TheatreTheatre – – dramas, tragedies and comediesdramas, tragedies and comedies Homer Homer – Famous poet– Famous poet• IliadIliad - - Set in the Trojan War Set in the Trojan War - the ten-year siege of - the ten-year siege of
Ilium by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the Ilium by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles
• OdysseyOdyssey – a – a sequel to the Iliadsequel to the Iliad, The poem mainly , The poem mainly centers on the centers on the Greek hero Ulysses and his long Greek hero Ulysses and his long journey home following the fall of Troyjourney home following the fall of Troy. It takes . It takes Odysseus ten years to reach homeOdysseus ten years to reach home
HerodotusHerodotus – First true historian – First true historian• Considered the “Considered the “father of historyfather of history” for his careful ” for his careful
historical writinghistorical writing

Greek and Hellenic ContributionsGreek and Hellenic Contributions

Greek and Hellenic ContributionsGreek and Hellenic Contributions
Art and ArchitectureArt and Architecture Greek Statues Greek Statues - - were life-like, and showed the were life-like, and showed the
human body in the perfect formhuman body in the perfect form ParthenonParthenon - - The most famous The most famous Greek building Greek building
• Columns – Columns – structures that structures that provided support provided support to a buildingto a building
• Symmetry - Symmetry - equal angles, lengths and sidesequal angles, lengths and sides

Greek and Hellenic ContributionsGreek and Hellenic Contributions

Greek and Hellenic ContributionsGreek and Hellenic Contributions Science Science
• AstronomyAstronomy - Aristarchus - Aristarchus discovered that the discovered that the earth rotated on its axisearth rotated on its axis and and moves around the moves around the sunsun
• Archimedes -Archimedes - explored the explored the principals of the principals of the lever and pulleylever and pulley
• HippocratesHippocrates - a - a Greek physician Greek physician studies the studies the causes of illness and looked for curescauses of illness and looked for cures Hippocratic Hippocratic Oath – Oath – Oath doctors swore to do no harm Oath doctors swore to do no harm
and to keep their patient’s information confidentialand to keep their patient’s information confidential
MathematicsMathematics• PythagorasPythagoras - the - the formula of a right triangleformula of a right triangle• EuclidEuclid – his – his book is the basis for modern book is the basis for modern
geometry geometry

RomeRome (509 BCE – 476 CE)(509 BCE – 476 CE)
GeographyGeography Region – Region – South Western EuropeSouth Western Europe Rome Rome – – located in the located in the center of the Italian center of the Italian
peninsulapeninsula Mediterranean SeaMediterranean Sea – – helped the Romans helped the Romans
trade and expand into an empire trade and expand into an empire that spanned that spanned three continents (Europe, North Africa and the three continents (Europe, North Africa and the Middle East)Middle East)

RomeRome

RomeRome
GovernmentGovernment Roman Republic Roman Republic – established a government where – established a government where
people had the power to elect representativespeople had the power to elect representatives
• SenateSenate – most – most powerful governing body powerful governing body of the of the republicrepublic
Roman Law Roman Law – – Rome’sRome’s greatest achievementgreatest achievement Twelve Tables Twelve Tables – – codified laws of Rome codified laws of Rome that that
guaranteed the right to all Roman citizensguaranteed the right to all Roman citizens
• Basic principles Basic principles – – equality under the lawequality under the law, right of , right of the accused to the accused to face the accuser face the accuser and defend one’s and defend one’s self, idea of being self, idea of being innocent until proven guiltyinnocent until proven guilty
• Males had authority over his wife and familyMales had authority over his wife and family

RomeRome

Rome Rome
SocietySociety PatriciansPatricians – – Upper class, landowning Roman Upper class, landowning Roman
citizenscitizens• EligibleEligible to take to take part in the Senatepart in the Senate
PlebeiansPlebeians – – Social class made up Social class made up of farmers, of farmers, merchants, artisans and traders; merchants, artisans and traders;
• Limited Power Limited Power - because they - because they relied on the Patricians to relied on the Patricians to make changesmake changes in the government in the government
WomenWomen – – were were subordinate to mensubordinate to men, but gained , but gained right to right to hold a prominent public role hold a prominent public role and and own own businessesbusinesses

RomeRome
Roman EmpireRoman Empire ConquestConquest – – By By 270 BCE, Rome had conquered 270 BCE, Rome had conquered
the Italian peninsula the Italian peninsula and thenand then used the used the Mediterranean Sea to conquer an empire Mediterranean Sea to conquer an empire that that spanned three continents: spanned three continents:
EuropeEurope (including present day (including present day England, France, England, France, Germany, and GreeceGermany, and Greece))
North Africa North Africa – – Mediterranean CoastMediterranean Coast Middle EastMiddle East (SW Asia) – (SW Asia) – Asia Minor Asia Minor and areas and areas
surrounding thesurrounding the Mediterranean Sea Mediterranean Sea

RomeRome

Rome Rome
Caesar’s Caesar’s AssassinationAssassination – – Killed Killed because because he declared himself dictator for lifehe declared himself dictator for life
• Civil War Civil War – – Rome erupted into Rome erupted into civil war as ambitious civil war as ambitious generalsgenerals tried to conquer Rome for themselvestried to conquer Rome for themselves. .
• OctavianOctavian (Caesar’s Grandnephew) (Caesar’s Grandnephew) emerged the victoremerged the victor and changed his name to and changed his name to AugustusAugustus
EmpireEmpire – Rome was an empire led by a – Rome was an empire led by a monarch. The monarch. The Roman Senate was still kept Roman Senate was still kept but but absolute power was in the hands of the emperor absolute power was in the hands of the emperor
and the and the age of the Roman Empire had begunage of the Roman Empire had begun..

RomeRome
AugustusAugustus ruled Rome with ruled Rome with absolute absolute powerpower
Strong Central Strong Central GovernmentGovernment Civil Service Exams Civil Service Exams – – ensured a well educated ensured a well educated
government officialsgovernment officials Reformed Reformed tax systemtax system Uniform coins Uniform coins – – made trade easiermade trade easier Strong military Strong military – – expanded and protected the expanded and protected the
empireempire

RomeRome
Pax Romana Pax Romana – – ““Roman PeaceRoman Peace” was a time of ” was a time of peace and prosperity (peace and prosperity (golden agegolden age)). .
TradeTrade - - Through Through vast road networks vast road networks and the and the Mediterranean Sea. People freely traded Mediterranean Sea. People freely traded with others in with others in the empire and with other parts of the world,the empire and with other parts of the world,
GoodsGoods – – grain from Nile Rivergrain from Nile River Valley, ivory and gold Valley, ivory and gold from Africa, spices and gems from India and silk from from Africa, spices and gems from India and silk from ChinaChina

RomeRome
Religion - Religion - 313 CE Emperor Constantine 313 CE Emperor Constantine legalizes legalizes Christianity Christianity - Edict of Milan- Edict of Milan

RomeRome EngineeringEngineering
RoadsRoads – allowed for – allowed for trade and military trade and military expansionexpansion
ArchesArches – engineering technique that allowed – engineering technique that allowed Rome to Rome to create large buildingscreate large buildings
ConcreteConcrete – material – material used for constructing used for constructing large large buildingsbuildings
AqueductsAqueducts – bridge-like structures that used the – bridge-like structures that used the Roman arch to Roman arch to carry water from the hills to the carry water from the hills to the citiescities
DomeDome – a half, – a half, sphere-like roofsphere-like roof ColiseumColiseum – – Stadium built in Rome that was used Stadium built in Rome that was used
for Gladiator fights, chariot races and for Gladiator fights, chariot races and executions executions (Bread and circuses)(Bread and circuses)

RomeRome

RomeRome Fall of the Roman Empire Fall of the Roman Empire
PoliticalPolitical Causes Causes• People stop supporting the governmentPeople stop supporting the government• CorruptCorrupt officials officials• DividedDivided empire becomes too weak empire becomes too weak
EconomicEconomic Causes Causes • Heavy Heavy taxestaxes
MilitaryMilitary Causes Causes• Constant Constant invasionsinvasions• BordersBorders are are too big too big to defendto defend• HireHire foreignforeign soldiers soldiers
SocialSocial Causes Causes• Gap between Gap between thethe rich rich and the and the poor poor widenswidens