ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS
-
Upload
maxine-quinn -
Category
Documents
-
view
26 -
download
0
description
Transcript of ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS

ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS
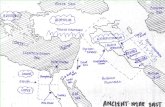
The Fertile Crescent

Land Between Two Rivers
Students will:Students will:
•Find out how geography Find out how geography made the rise of civilization in made the rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent possible.the Fertile Crescent possible.
•Learn about Sumer‘s first Learn about Sumer‘s first cities.cities.
•Learn about the two most Learn about the two most important empires in important empires in Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia.

Land Between Two RiversEssential Essential Question: Question:
• What were What were the the beginnings beginnings of human of human society?society?
• How has How has geography geography shaped the shaped the patterns of patterns of history?history?

Farming in Mesopotamia
You’re going to create a Mesopotamian Farming manual
• You will have a total of 6 steps, describe the steps in order and next to each description draw a picture that represents the step.
• Take 15 minutes to find steps and draw an illustration

Steps to Farming in Mesopotamia
1. Local officials decided when to open flood gates
2. Animals grazed in soil to trample ground and eat weeds

Steps
1. Local officials decide when to let water flow onto crops
2. Farmers let animals graze in soil to trample and eat weeds.
3. Farmers break up the soil using hand tools4. Spread seeds and plow5. Plant seeds6. Harvest the plants

VocabularyMesopotamia: The Development of Written Language
city-state Definition: A self-governing state consisting of a city and
surrounding territory Context: Nippur was the most important city-state in Sumer.
demon Definition: An evil spirit Context: According to Sumerian legend, Gilgamesh killed the
demon Huwawa with the help of the sun god.

VocabularyMesopotamia: The Development of Written Language
epic Definition: A long poem telling the deeds of a hero and often centering
on the ideals of a nation or culture Context: The Epic of Gilgamesh teaches us to enjoy the time we have
on Earth.
immortality Definition: The quality or state of having an endless life Context: Gilgamesh was unable to achieve immortality, but he was able
to leave behind a legacy through the work he had done during his lifetime.
Mesopotamia Definition: An ancient land located where we find the modern country
of Iraq Context: Mesopotamia means, “land between the rivers” and got its
name because it was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.

VocabularyMesopotamia: The Development of Written Language
scribe Definition: A person paid to write, especially in ancient times Context: Mesopotamian scribes worked closely with the priests
and kings.
stylus Definition: A hard, pointed writing tool cut from a reed Context: Sumerian scribe wrote with styluses they made from
reeds.
Sumerians Definition: Residents of Sumer, a region of the ancient land of
Mesopotamia Context: The Sumerians developed many inventions, such as the
wheel and the plow.

VocabularyMesopotamia: The Development of Written Language
Nippur Definition: A major city-state in the ancient Sumerian region of
Mesopotamia Context: Nippur was a busy trading center in Sumer and its most
important religious city.
tablet Definition: A flat slab – often of clay or stone – suitable for an
inscription Context: The Sumerians etched symbols into wet clay tablets to
create a permanent document of their activities.

Ancient MesopotamiaWriting
• The Sumerians developed the first form of writing.• As Sumerian towns grew into cities, the people needed a way
to keep track of business transactions, ownership rights, and government records.
• Around 3300 BC the Sumerians began to use picture symbols marked into clay tablets to keep their records

• Clay Tablets • Writing was inscribed on clay tablets. • Scribes would take a stylus (a stick made from a reed) and
press the lines and symbols into soft, moist clay. • Once they were done, they would let the clay harden and they
had a permanent record.
Ancient MesopotamiaWriting

• Cuneiform
The initial writing of the Sumerians utilized simple pictures or pictograms.
• The writing of the Sumerians further developed to include sounds and meanings.
• Scribes would use the stylus to make wedge shaped marks in the clay.
• This type of writing is called cuneiform writing, which means "wedge-shaped".
Ancient MesopotamiaWriting

Write Like a Babylonian

QuestionsMesopotamia: The Development of Written Language
1. What was the importance of scribes in Mesopotamia?
2. Why did the scribes have greater access to the priests and kings than other people in the city-states?
3. How long did it take to train a scribe?
4. What is the name of the training school where scribes learn how to write?

VocabularyMesopotamia: From Nomads to Farmers
. ancestors Definition: People in one’s family, from whom one is descended Context: Your ancestors include your grandparents, great grandparents, and great-great grandparents.
domestication Definition: The taming of wild animals to use for farming or to be kept as pets Context: The domestication of sheep and goats helped the Mesopotamians become farmers.

VocabularyMesopotamia: From Nomads to Farmers
. journal Definition: A record of personal experiences and thoughts kept on a regular basis Context: Writing a journal can help you understand yourself.
levee Definition: Earthen dams constructed to hold back floodwaters Context: A levee system helped the Mesopotamians farm their most fertile land.
Mesopotamia Definition: An ancient land located where we find the modern country of Iraq Context: Mesopotamia means, “land between the rivers” and got its name because it was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.

VocabularyMesopotamia: From Nomads to Farmers
. Sumerians Definition: Residents of Sumer, a region of the ancient land of Mesopotamia Context: Sumerians developed a culture whose members farmed and traded instead of hunting and gathering to make a living.
Tigris River Definition: One of the rivers that borders what was the land of Mesopotamia Context: The Tigris River bordered Mesopotamia to the east.
Euphrates River Definition: One of the rivers that borders what was the land of Mesopotamia. Context: The Euphrates River bordered Mesopotamia to the west.

Questions Mesopotamia: From Nomads to Farmers
1. Why did the ancient Sumerians look for new ways to produce their food?
2. How did growing crops and domesticating animals like sheep and goats allow the Sumerians to build cities and live in one place all year long?
3. What does the word “Mesopotamia” mean? 4. Between which rivers did Mesopotamia lie? 5. Why did the soil of the Mesopotamian region of
Sumer grow such good crops? 6. What problem at first made farming difficult
there and how did the Sumerians solve it?

Questions Mesopotamia: From Nomads to Farmers
7. In what other way did the Sumerians control the rivers? 8. What important farming tool did the Sumerians invent? 9. What else did the Mesopotamians invent? 10. What do we call their system of writing? 11. What tools did the Mesopotamians use for writing? 12. What did the Sumerians put into writing before any
other society? 13. What was the name of the temple where Sumerians
believed their gods lived? 14. Of what material were the houses in Sumerian cities
made?

Babylonia and Assyria
Students will:Students will:
•Find out how geography made the Find out how geography made the rise of civilization in the Fertile rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent possible.Crescent possible.
•Learn about Sumer‘s first cities.Learn about Sumer‘s first cities.
•Learn about the two most Learn about the two most important empires in Mesopotamia. important empires in Mesopotamia.

Babylonia and AssyriaHave the students create a Venn Diagram
• List appropriate details in the “Babylonia” circle.
• List appropriate details in the “Assyrians” circle.

Babylonia and AssyriaIn your own words define the following
words –
Empire, Caravan, Bazaar
• Have the students create a Venn Diagram • List appropriate details in the “Babylonia” circle.• List appropriate details in the “Assyrians” circle.

Babylonia v. Assyria Venn DiagramMesopotamia Empires
Babylonia Assyria

The Legacy of Mesopotamia
Essential Question: Essential Question:
• What were the beginnings of human What were the beginnings of human society?society?
• How has geography shaped the How has geography shaped the patterns of history?patterns of history?

The Legacy of Mesopotamia
In this section you will learn of the advances made by the
Mesopotamians, including the art of writing.
Think about how your lives would different without writing.

Mediterranean Civilizations
Essential Question: Essential Question: • What were the beginnings of What were the beginnings of
human society?human society?• How has geography shaped the How has geography shaped the
patterns of history?patterns of history?

Mediterranean Civilizations
What happens to a story as it is retold over a long period of time?
What important development changed the way stories were told?

The Fertile Crescent Summary
• Stretching from the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in present day Israel to the Persian Gulf, the Fertile Crescent was the birthplace of many early civilizations.
• The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers provided ideal conditions for human settlement, with the first civilizations rising in Mesopotamia, or the land between the rivers.

Land Between Two Rivers• Mesopotamia lay between the Tigris and
Euphrates rivers. These two rivers and the rich, fertile soil drew people to the region.
• The early people of Mesopotamia became farmers and then builders of cities. The most successful and advanced cities were the city-states of Sumer.

Babylonia and Assyria• After the fall of Sumer, the biggest and most
important civilizations were the empires of Babylonia and Assyria.
• These civilizations built grand cities where culture and learning were highly valued.

The Legacy of Mesopotamia• The Mesopotamians were probably the first to
develop two of the key components of almost all civilizations—a system of writing and a set of written laws.

Mediterranean Civilizations• Phoenicia developed into a great sea power
with trade routes throughout the Mediterranean region.
• These trade routes brought great wealth and knowledge to the Phoenicians.
• The Phoenicians developed a system of writing with an alphabet of 22 letters. This alphabet formed the basis of the alphabets that many nations use today.

ReviewThe Fertile Crescent
Students will:Students will:
•Found out how geography made the Found out how geography made the rise of civilization in the Fertile rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent possible.Crescent possible.
•Learn about Sumer‘s first cities.Learn about Sumer‘s first cities.
•Learn about the two most important Learn about the two most important empires in Mesopotamia. empires in Mesopotamia.

ReviewThe Fertile Crescent
Essential Question: Essential Question: • What were the beginnings of What were the beginnings of
human society?human society?• How has geography shaped How has geography shaped
the patterns of history?the patterns of history?