ANATOMY OF TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREE
description
Transcript of ANATOMY OF TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREE
ANATOMY OF TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREE
ANATOMY OF TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREEPRESENTED BY- Dr. CHITRAMODERATOR-Dr.AJAY SOOD
Respiratory System
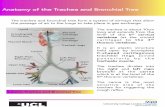
TRACHEAIt is a cartilaginous and membranous tubeEXTENT - from 6th cervical vertebra till the body of 5th thoracic vertebraDuring expiration the bifurcation rises by one vertebral level and during inspiration may be lowered as far as 6th thoracic vertebraLENGTH - 11cmDIAMETER - 2 to 2.5cmCHILDREN - smaller, deeper, more moveable
STRUCTURECARTILAGES-16to20 in no.,each forms an incomplete ring,which occupies anterior two third of circumference of tracheaAre placed horizontally above each other,separated by narrow intervals4mm deep and 1mm thickOuter surface is flattened in vertical direction and convex from inner sideHighly elastic,but may calcify in later stagesFIRST TRACHEAL CARTILAGE-broader,divided connected to lower end of cricoid by cricotracheal ligamentLAST TRACHEAL CARTILAGE-thick and broad in midlle, lower border is prolonged to a triangular hook shaped process which curves downward and backward between two bronchi
FIBROUS MEMBRANE-cartilages are enclosed in an elastic fibrous membrane which consists of two layers,one passes over the outer surface the other one over the inner surfaceAt upper and lower margins they blend together to form a single membraneMUSCULAR TISSUES-two layers of non striated muscles longitudinal and transeverseLongitudinal fibres are external,consist of few scattered bundles onlyTranseverse fibers(trachealis muscle) are internal,extends between the end of cartilages
MUCUS MEMBRANE-continous above with larynx and below with bronchusConsist of areolar and lymphoid tissue,basement membrane,supporting stratified epithelium ,surface layer of which is columnar and ciliatedBeneath basement membrane there is a layer of longitudinal elastic fibreSubmucus layer,composed of loose meshwork of connective tissueVESSELS AND NERVES-ARTERIAL SUPPLY-Inferior thyroid arteriesNERVE SUPPLY-vagus nerve,recurrent nerve,sympathetic nerves
RIGHT BRONCHUS2.5cm longWider,shorter,more verticalDivides into EPARTERIAL and HYPARTERIAL BRONCHUS based on right pulmonary artery
RIGHT UPPER LOBE BRONCHUSIt divides into three segmental bronchi which supply apical,anterior and posterior segments of upper lobeAPICAL SEGMENTAL BRONCHUS-divides into apical and anterior subsegmental branchesPOSTERIOR SEGMENTAL BRONCHUS-divides into lateral and anterior subsegmental branches. It serves the posteroinferior part of superior lobe of lungANTERIOR SEGMENTAL BRONCHUS-runs anteroinferiorly to supply rest of the part of upper bronchus. Divides into lateral and anterior subsegmental branchesRIGHT MIDDLE LOBE BRONCHUSDivides into lateral and medial subsegmentsRIGHT LOWER LOBE BRONCHUSContinuation of principal stem beyond the origin of middle lobe bronchusSupplies 5 segments of the lungApical segmental bronchusMedial basal segmental bronchusAnterior basal segmental bronchusLateral and posterior basal segmental bronchus
LEFT BRONCHUS5cm in lengthSmaller in caliberEnters the lung opposite 6th thoracic vertebraRELATIONS-passes beneath the aortic arch,crosses in front of oesophagus,thoracic duct,descending aorta,has left pulmonary artery at first above and then in frontLEFT UPPER LOBE BRONCHUSCranially it divides into anterior ,apical and posterior segmental branchesCaudally into superior and inferior lingual branchesLEFT LOWER LOBE BRONCHUSDivides into apical segmental bronchus,medial basal,anterior basal,lateral and posterior basal branches
-BRONCHIRight bronchusWiderMore verticalshorterSupported by C shaped cartilages20-30 degree angleFirst generationLeft bronchusNarrowerMore angularLongerSupported by C shaped cartilages40-60 degree angleFirst generation
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE Right main bronchus is more in line with tracheaInhaled foreign bodies and gastric contents enter right bronchial treeIf patient is lying on his side,lateral subsegments of anterior and posterior segments are more likely to get such materialIf patient is supine,then apical segmental bronchus which arise from right or left lower lobe bronchus is the most common part of lung for the aspirated material to collect
BRONCHOPULMONARY SEGMENTSAnatomic,functional and surgical units of lung23 divisons or generations are involved in dichotomous division,starting from trachea till alveolar sacsEach lobar bronchus(secondary bronchus) gives off branches called segmental bronchus(tertiary bronchus)
As bronchi become smaller, cartilages also become smaller and fewer in noBronchioles are formed which are less then 1mm in dia,no cartilages and lined by ciliated columnar epitheliumDivide to form terminal bronchioles,which show delicate outpouchings from their wallThese are respiratory bronchioles,dia is 0.5mm,they end by branching into alveolar ducts
Each alveolar sac consist of around 17 alveoliEach alveolus surrounded by rich network of blood capillariesGas exchange primarily occurs on thin side of alveolocapillary membrane,thick side provides structural support
ALVEOLIType I pneumocytes-large flattened cells, present a very thin diffusion barrier for gasesType II pneumocytes-secretes surfactant,which decreases the surface tension between thin alveolar wallsmacrophages
Subdivision of lung lobePyramid shaped,apex towards lung rootSurrounded by connective tissueSegmental bronchus,segmental artery,lymph vessels and autonomic nervesSegmental vein lies between adjacent segments
BLOOD SUPPLY OF LUNGSBy bronchial arteries which are branches of descending aortaNERVE SUPPLY OF LUNGSPulmonary plexus-efferent and afferent autonomic nerve fibresSympathetic efferent fibres produce bronchodilation and vasoconstrictionParasympathetic efferent produces bronchoconstriction,vasodilation,increase glandular secretions