Anatomy of orbital cavity
-
Upload
othman-al-abbadi -
Category
Education
-
view
475 -
download
12
description
Transcript of Anatomy of orbital cavity

Anatomy of orbital cavity
Dr. Othman Al-Abbadi, M.D

Introduction
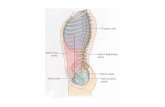
The orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull, that contain the eye ball and muscles ,nerve, vessels, fat and lacrimal apparatus.
Each cavity is pear shaped ,and its apex is directed posteriorly ,medially ,and slightly upward.
The medial wall runs antero-posterior parallel to sagittal plane ,lateral wall diverges at angle 45degrees.
Seven individual bones form the orbit (maxilla ,palatine ,zygomatic , sphenoid ,frontal ,ethmoid ,and lacrimal ).
.

O

Orbital dimensions Depth 42 mm along medial wall Depth 50 mm along lat wall
Base : Width 40 mm Ht 35 mm Orbital index : (ht/width)X100 Racial variations
Intraorbital width 25 mm Exrtraorbital width 100 mm Vol: 30 ml

Orbital margin
Quadrilateral in shape with rounded corner. In adult : wider than it is high . supraorbital margin is formed by frontal bone .
(lat 2/3 sharp , med 1/3 rounded at the junction of two area supraorbital notch or foramen for passage of supraorbital vessels and nerve).
infraorbital margin is formed (lat by zygomatic ,med by maxilla). Lateral margin is the strongest part is formed (above by
frontal , below by zygomatic ). Medial margin is formed ( above by frontal , below by lacrimal
crest of maxilla),

Orbital margin


Walls of orbital cavity
Walls are lined with periosteum ,and consist of roof ,floor ,medial, lateral wall.
Apex is at medial end of superior orbital fissure.
Roof
formed by orbital plate of frontal bone and small extent of lesser
wing of sphenoid posteriorly. anterolaterally there is slight depression ( lacrimal fossa )for orbital
part of lacrimal gland .
Roof is thin and fragile ,in old age portion of roof may be absorbed.
Roof separates orbital cavity from anterior crainal fossa and frontal lobe.

Lateral wall is the thickest wall.
anterior 1/3 is formed by zygomatic bone, separate orbit from temporal fossa.
posterior 2/3 is formed by greater wing of sphenoid ,separate orbit from temperal lobe of brain.
it is continuous with roof anteriorly but seperated posteriorly by superior orbital fissure .
marginal tubercle : a small prominence just posterior to orbital margin on frontal process of zygoma , give attachment to aponeurosis of levator palpebrae superioris ,lateral palpebral ligament ,lateral check ligament .

Floor Formed largely by orbital plate of maxilla ,
orbital surface of zygomatic ,small orbital process of palatine.
separate cavity from maxillary sinus. Floor is continuous with lateral wall anteriorly, but seperated posteriorly by inferior orbital fissure .

Medial wall very thin wall, Formed by four bone from anterior to posterior :
frontal process of maxilla,
lacrimal bone,
Orbital plate of ethmoid (largest part, very thin separate cavity from ethmoid sinus),
Small part of body of sphenoid.
Lacrimal groove: on anterior part of medial wall ,for lacrimal sac , formed by lacrimal bone posterior ,frontal process of maxilla anterior,bounded by lacrimal crests, continuous below with
nasolacrimal canal.

Opening in the cavity

Openings

Openings Optic canal: lies in the lesser wing of sphenoid.
related medially to body of sphenoid.
connect orbital cavity to middle cranial fossa .
transmit optic nerve, ophthalamic artery with surrounding sympathetic plexus .
Superior orbital fissure: Lying between lesser and greater wing of sphenoid.
connect orbital cavity to middle crainal fossa .
widest part at its medial end.
midway on the lower edge of fissure is a small sharp spine give attachment to common tendinous ring of origin for four rectus muscle.
transmit from lateral to medial (lacrimal nerve ,frontal nerve, trochlear nerve, upper and lower division of oculmotor nerve , nasociliary nerve, abducent nerve ,superior ophthalamic vein) .

Inferior orbital fissure :
lies between greater wing of sphenoid and maxilla.
Connect pterygiopalatine and infratemperal fossa to orbital cavity . transmit maxillary nerve, zygomatic nerve ,branches of pterygiopalatine ganglion,
inferior ophthalamic vein .
Ethamoidal foramina: lies in frontoethmoidal suture or in frontal bone.
anterior foramen open in anterior cranial fossa at lateral edge of cribriform plate transmit anterior ethamoidal artery and nerve.
posterior foramen traverse ethamoidal bone transmit posterior ethamiodal artery and nerve.
Zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemperal foramen:
lies on the lateral wall of orbit. zygomaticofacial foramen transmit zygomaticofacial nerve. zygomaticotemperal foramen transmit zygomaticotemperal nerve.


Relation
Superior anteromedially : frontal air sinus. anterior cranial fossa . inferior maxillary air sinus Lateral anteriorly : temperal fossa. posteriorly :middle cranial fossa. Medially nasal cavity ,ethmoidal sinus , sphenoid sinus.

Orbital periosteum( orbital fascia)Periorbita: is the periosteum of the bone that form the wall of
orbit, loosely attached to bone .
At orbital margin, the periorbita is continuous with periosteum on external surface of skull, ive attachment to the orbital
septum .At lacrimal groove it splits to enclose lacrimal sac and continue inferior to form periosteum of nasolacrimal canal.
Posteriorly, around optic canal and medial end of superior palpebral fissure, it thickens to form a fibrous ring (common tendinous ring).
periorbita receive its sensory innervations from branch of trigeminal nerve.

Orbital muscle
Muscle of Müller (Orbitalis muscle)
Thin layer of smooth muscle that bridge the inferior orbital fissure .(vestigeal muscle)
Nerve supply : sympathetic
Function : unknown

Effect of age on orbital cavity
At birth : Relatively large and ossified margins Young children : Look more lat than adult Superior & inferior orbital fissure are wider become
narrowed by growth of greater wing of sphenoid . Distance between the orbit are small and increases by
growth of frontal& ethamoidal sinuses Old age : Bony absorption >>> holes in roof , med & lat walls

Surface Anatomy Superciliary ridges: prominent ridge above upper margin, deep to
ridge frontal sinus.
Eyebrows
Orbital margins ( frontal ,maxillary, zygomatic ) Frontozygomatic suture Supraorbital notch trochlea Lat and med palpebral ligament Ant lacrimal crest Lac groove Post lacrimal crest Infraorbital foramen (5mmbelow lower margin)

Trauma to the orbit: the orbit margin is very strong and not easily fractured .Sever injury may cause fracture eg: automobile accident. fracture of superior margin give symptom of superior oblique paralysis. fracture of lateral margin >>>>depression & prominence of cheek. comminuted fracture lower margin >>>blow out fracture. Penetrating wound surgical instrument, pointed metal object pierce thin roof of orbit
enter crainal cavity and frontal lobe .Air sinuses infection of sinus is commonest causes of orbital cellulitis