K - 1 & K - 2 Formatio Reticularis & Sistem Limbik (Anatomi)
Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Limbik
-
Upload
janice-chiquita-bella -
Category
Documents
-
view
132 -
download
14
description
Transcript of Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Limbik
-
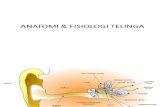
Anatomi Sistem LimbikStruktur seluler otak manusia terdiri atas :terdiri dari enam lapisan (isocortex/neocortex)pengaturan sensoris, motoris, dan fungsi luhur terdiri dari tiga lapisan (allocortex/archicortex/paleocortex)emosi, ingatan, dan sifat/behaviour seseorang Sistem limbik allocortex
-
Sistem limbik terdiri atas :Formatio hippocampi : hippocampus (gyrus hippocampalis), gyrus dentatus, subiculum, dan cortex entorhinal (area entorhinal) yang terletak di lobus temporal pada dasar cornu inferior ventriculus lateralis.FornixCorpus amygdaloideumCorpus mamillarisThalamus (nucleus anterior)Lobus limbicus : gyrus cinguli, gyrus parahippocampalis, gyrus dentatus, fimbria hippocampi, bagian lain telencephalon medial sekitar corpus callosum.Cortex prefronta
-
Amygdala Almond YunaniUkuran 2.5 cm Letak ujung anterior hipocampus, medial lobus temporalBersama dengan hipocampus sistem limbik ( cerebrum )Berkontribusi dengan emosi ( marah, senang, kuatir, takut )Mempunyai pengaruh input dan output (bilateral) dengan berbagai sistem korteks sensoris (umum&khusus)Hipocampus & cortex etorhinalKorteks prefrontal untuk regulasi Sensoris yang berasal dari batang otak (gustatorius, nyeri, viscera)Hipotalamus (simpatetik pengaturan hormon)
-
Input : menerima impuls dari sensoris thalamus (somatosensoris, visual, auditorius)Output : menghantarkan impuls Nucleus dorsalis vagi (parasimpatis)Sistem modulasi : norepinefrin, asetilkolin, serotonin, dopaminHipocampusBagian sistem limbikBentuk kuda laut Letak medial temporal & ventrikel lateralFungsi proses memori jangka panjang & mengingat kembali
-
Thalamus Letak di diencephalon ; dorsal terhadap hipotalamus, lateral terhadap ventrikel III Menerima sensai korteks cerebriPeran mengarahkan fungsi-fungsi luhur (kognitif, afektif, perilaku) yang juga diatur oleh korteks prefrontal
-
Fisiologi Sistem Limbik
-
Limbic system ring of forebrain surround brain stem & interconnected by intricate neuron pathwaysCerebral cortex ( limbic association cortex ) Basal nuclei ThalamusHypothalamus This complex associated with emotions, basic survival, sociosexual behavioral patterns, motivation, learning
-
Limbic system key role in emotion feelings, moods physical responses associated with the feelingsResponses include specific behavioral patterns ( defense when attack )Stimulating specific region produce subjective sensations Amygdala fears Higher levels of the cortex crucial for conscious awareness of emotional feelings
-
The limbic system and higher cortex participate in controlling basic behavioral patterns Basic inborn behavioral patterns limbic system include individual survival (attack, searching food), perpetuating the species ( sociosexual behavior )The relationship among the hypothalamus, limbic system and higher cortical regions regarding emotions & behavior are still not well understood
-
Hypothalamus involuntary internal responses in preparation for appropriate action to accompany a particular emotional state (heart rate, blood pressure,skeletal muscle) No conscious control In executing complex behavioral activities (attack) interact with external environment Higher cortical mechanism are called to connect the limbic system & hypothalamus with the outter world appropriate behaviors are manifested
-
Higher cortical levels also can reinforce, modify, or suppress basic behavioral responses can be guided by planning, strategy, judgment based on the situation Higher level of the cortex (prefrontal & limbic association area) important to conscious learned control innate behavioral pattern
-
fear as an example,emotional stimulus: a fast track in which the lower-level amygdala plays a key role permits a rapid, rather crude, instinctive response (gut reaction) and is essential for the feeling of being afraida slower track mediated primarily by the higher-level prefrontal cortex.permits a more refined response to the aversive stimulus based on a rational analysis of the current situation compared to stored past experiences.prefrontal cortex formulates plans and guides behavior, suppressing amygdala-induced responses that may be inappropriate for the situation at hand.
-
Reward & PunishmentReward centers are found most abundantly in regions involved in mediating the highly motivated behavioral activities of eating, drinking, and sexual activity.Motivation ability to direct behavior toward specific goalssome goal-directed behaviors are aimed at satisfying specific identifiable physical needs related to homeostasisHomeostatic drives represent the subjective urges associated with specific bodily needs that motivate appropriate behavior to satisfy those needs
-
Example :sensation of thirst accompanying a water deficit in the body drives an individual to drink to satisfy the homeostatic need for waterhowever, whether water, a soft drink, or another beverage is chosen as the thirst quencher is unrelated to homeostasis