An inflammatory response of pulpal CT. to an periapical.pdf · pulp is characterized by overgrowth...
Transcript of An inflammatory response of pulpal CT. to an periapical.pdf · pulp is characterized by overgrowth...


An inflammatory response of pulpal CT. to an
irritant that stimulate granulation tissue
formation
( tendency for healing )
4) Chronic pulpitis:

A) Chronic pulpitis is asymptomatic, as there is
outlet for exudate through:
- Carious cavity
- Venous or lymphatic circulation.
So the pressure did not reach the pain threshold.
B) The low grade irritation stimulates formation
of granulation tissue:
- Young fibroblasts
- Young blood vessels.
- Young nerve endings.
N.B.. Granulomatous tissue (fibrous tissue + chronic
inflammatory cells).

It is a chronic
inflammation of a
cariously exposed pulp.
by the formation of an
abscess at a point of
leading to ulceration.
A) Chronic ulcerative pulpitis:

The pulp is formed of 3 zoncs:
1) Zone of necrosis: Inner most zone formed of necrotic tissue
releasing exudate and necrotic by-products.
2) Zone of contamination: Middle zone. that consists of exudate
+ chronic inflammatory cells.
3) Zone III: Outermost zone. that consists of granulation tissue.

- This chronic inflammation of cariously exposed
pulp is
characterized by overgrowth of granulomatous
tissue into the carious cavity.
forming a polyp which is usually lined by stratified
squamous epithelium of mucosa.
- It occurs in young patients or adolescents.
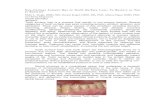
B) Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis
(pulp polyp):

Polyp is
- pinkish in
colour
- easily
bleeding
- not sensitive

Visual
examination:
History of a long standing carious cavity.
Visually: ulcerated
lesion and large carious cavity in chronic
ulcerative cases. Pinkish polyp which bleeds
easily in chronic hyperplastic.
Signs and
Symptoms:
No or slight pain so called asymptomatic
because produet of
exudative zones is drained away through:
1) Carious cavity.
2) Venous or lymphatic circulation.
Percussion: -ve
Radiographically:
normal
Vitality tests:
Themal test no response or may be delayed
response with heat.
Electric pulp test responds at high current -

Treatment:
Cauterization of the
polyp.
followed by root canal treatment.

Additional Pulp Diseases

Def.:
Death of pulp tissue in
sequel of :
a) Acute and chronic
inflammation.
b) Immediate arrest of
circulation due to
traumatic injury.
1) Necrosis:

Necrosis
Liquifactive
Coagulative

*Occurs when there is good blood supply i.e. acute
or chronic inflammation.
**Characterized by the presence of pus.
***Proteolytic enzymes -> proteolysis.
Cells die and autolytic enzymes produce autolysis.
Anaerobic bacteria -> putrifiying enzymes -
>putrifaction pus.
I) Liquifactive necrosis

*Occurs, when there is poor blood supply e.g.
trauma.
**Characterized by a soft solid cheesy-like
mass (caseation)
*** this mass is formed of coagulated protein,
fat and little amount of water.
II) Coagulative necrosis

visual examination: 1)carious tooth
2)trauma.
The tooth is dark in color (due to affection
of dentin by necrotic tissue or extravasated
R.B.Cs).
Signs and Symptoms: painless
Percussion: -ve
Radiographically: normal or slight widening of the lamina
dura.
Vitality tests: -ve, except for
a) Partial necrosis (if only one root is
totally necrotic and other roots are not ).
b) Liquifactive necrosis ( fluild will
transmit current to P.L ) FALSE POSITIVE

Treatment:
Root canal treatment must not be done in
one visit,
the clinician cleans and shapes the canal
using crown down technique.

2) Retrogressive pulp changes
( Irritation of tooth induce aging of pulp )

Def.:
decrease in the size of an organ due to faulty
nutrition.
( 1 ) fibrosis:

Histopathology and pathogenesis:
a. Decreased no. of cells.
b. Decreased ground substance.
c. Increase mature collagen fibers
these bundles cause anoxia or hypoxia of
cells
The cells shrink and their nuclei become
pyknotic

visual examination: caries,attrition,erosion or trauma.
Signs and symptoms: painless
Percussion: -ve
Radiographically: normal
Vitality tests: -ve or shows a slight response to a
very high current.

Treatment:
May be left untreated.
unless the patient
complains.

Def.:
Calcium deposits in the pulp Chamber or
root canal.
II) Calcification (Chalky Tooth):

A) Pulp stone (denticles):
More common in the pulp
Chamber.
a) According to location:
Free (lying free in the pulp
Chamber)
Attached (due to further
calcium deposition)
Embedded (more dentin laid
around them)

b) According to structure:
1) True denticles:
composed of dentin formed by:
Detached odontoblasts
Proliferation of fragment of
epithelial sheath of Hertwig.
2) False denticles:
deposition of calcium salts in dead or
degenerated tissue occurs, due to the
alkalinity of the destroyed tissue,
which acts as central nidus for
deposition of concentric layers of
calcified tissues .

More common in the
root canal alongside
walls of blood vessels
and nerves.
B) Diffuse calcification:

visual examination: history of trauma, or caries.
The tooth looks lifeless,(chalky tooth)
Signs and symptoms: Painless
Percussion: -ve
Radiographically: Calcific changes
Vitality tests: Response at a very high current or no
response, depending on the degree of
calcification.

Treatment:
No need for treatment unless
patient is complaining

III) Internal resorption (pink
spot):
Etiology:
-Trauma
-Inflammation
-Idiopathic

Trauma
Intra-pulpal hemorrhage.
Extravasation of blood, which changes into granulation
tissue.
When in contact with dentin Stimulation of
dentino-clasts.
*This process can go on until:
1- (pink spot)
2- (pathologic perforation)
Pathogenesis:

Pinkish discoloration of right deciduous mandibular molar


visual
examination:
History of chronic inflammation or
trauma.
Pink spot can be seen.
Signs and
Symptoms:
No pain
Percussion: -ve
Radiographically Area of internal resorption .
Vitality tests: Response at low current , when dentin
removed from resorbed area .

Root canal treatment done
immediately
Treatment: