Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545...
Transcript of Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545...

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !1 12
Attendance Problems
Desmos: Polygraph: Parabolas (bwcn)
For each quadratic function, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, and state whether the function opens upward or downward.
1. y = x2 + 3 2. y = 2x2
3. y = –0.5x2 – 4

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !2 12
I can graph and transform quadratic functions.
Common Core CC.9-12.F.BF.3 Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, k f(x), f(kx), and f(x + k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative); find the value of k given the graphs. Experiment with cases and illustrate an explanation of the effects on the graph using technology. CC.9-12.F.IF.7 Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated cases.*
a. Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maxima, and minima. b. Graph square root, cube root, and piecewise-defined functions, including step functions and absolute value functions. c. Graph polynomial functions, identifying zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing end behavior. d. (+) Graph rational functions, identifying zeros and asymptotes when suitable factorizations are available, and showing end behavior. e. Graph exponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric functions, showing period, midline, and amplitude.
CC.9-12.F.IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes.*
!
4. What is the parent function of a quadratic equation?
Desmos: Quadratic Graphing lab: SFAN
You saw in Lesson 5-10 that the graphs of all linear functions are transformations of the linear parent function y = x.
Remember!

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !3 12
!
5. How does the leading coefficient effect the parabola?
!
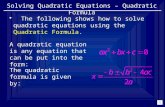
Transforming Quadratic Functions
ObjectiveGraph and transform quadratic functions.
The quadratic parent function is f (x) = x 2 . The graph of all other quadratic functions are transformations of the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
For the parent function f (x) = x 2 : • The axis of symmetry is x = 0,
or the y-axis.
• The vertex is (0, 0) .• The function has only one zero, 0.
Compare the coefficients in Compare the graphs of the following functions. the same functions.
f (x) = x 2 g (x) = 1 _ 2
x 2
h (x) = -3 x 2
f (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 0
g (x) = 1 _ 2
x 2 + 0x + 0
h (x) = -3 x 2 + 0x + 0
Same Different
• b = 0• c = 0
• Value of a
Same Different
• Axis of symmetry is x = 0.
• Vertex is (0, 0) .
• Widths of parabolas
The value of a in a quadratic function determines not only the direction a parabola opens, but also the width of the parabola.
WORDS EXAMPLES
The graph of f (x) = a x 2 is narrower than the graph of f (x) = x 2 if ⎪a⎥ > 1 and wider if ⎪a⎥ < 1.
Compare the graphs of g (x) and h (x) with the graph of f (x) .
⎪-2⎥ ? 1 ⎪ 1 __ 4 ⎥ ? 1
2 > 1 1 __ 4 < 1 narrower wider
Width of a Parabola
Why learn this?You can compare how long it takes raindrops to reach the ground from different heights. (See Exercise 18.)
Recall that the graphs of all linear functions are transformations of the linear parent function, f(x) = x.
© C
raig
Tut
tle/C
OR
BIS
© C
raig
Tut
tle/C
OR
BIS
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions 545
8-4CC.9-12.F.BF.3 Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, kf(x), f(kx), and f(x + k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative); …. Also CC.9-12.F.IF.7*, CC.9-12.F.IF.5*
CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 545CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 545 5/2/11 1:53:07 PM5/2/11 1:53:07 PM
Transforming Quadratic Functions
ObjectiveGraph and transform quadratic functions.
The quadratic parent function is f (x) = x 2 . The graph of all other quadratic functions are transformations of the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
For the parent function f (x) = x 2 : • The axis of symmetry is x = 0,
or the y-axis.
• The vertex is (0, 0) .• The function has only one zero, 0.
Compare the coefficients in Compare the graphs of the following functions. the same functions.
f (x) = x 2 g (x) = 1 _ 2
x 2
h (x) = -3 x 2
f (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 0
g (x) = 1 _ 2
x 2 + 0x + 0
h (x) = -3 x 2 + 0x + 0
Same Different
• b = 0• c = 0
• Value of a
Same Different
• Axis of symmetry is x = 0.
• Vertex is (0, 0) .
• Widths of parabolas
The value of a in a quadratic function determines not only the direction a parabola opens, but also the width of the parabola.
WORDS EXAMPLES
The graph of f (x) = a x 2 is narrower than the graph of f (x) = x 2 if ⎪a⎥ > 1 and wider if ⎪a⎥ < 1.
Compare the graphs of g (x) and h (x) with the graph of f (x) .
⎪-2⎥ ? 1 ⎪ 1 __ 4 ⎥ ? 1
2 > 1 1 __ 4 < 1 narrower wider
Width of a Parabola
Why learn this?You can compare how long it takes raindrops to reach the ground from different heights. (See Exercise 18.)
Recall that the graphs of all linear functions are transformations of the linear parent function, f(x) = x.
© C
raig
Tut
tle/C
OR
BIS
© C
raig
Tut
tle/C
OR
BIS
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions 545
8-4CC.9-12.F.BF.3 Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, kf(x), f(kx), and f(x + k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative); …. Also CC.9-12.F.IF.7*, CC.9-12.F.IF.5*
CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 545CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 545 5/2/11 1:53:07 PM5/2/11 1:53:07 PM

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !4 12
Video Example 1: Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest: f(x) = -3x2, g(x) = , h(x) = 3x2, p(x) = -5x2 and
!
14x2 q(x) = 7
2x2
1E X A M P L E Comparing Widths of Parabolas
Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest.
A f (x) = -2 x 2 , g (x) = 1 _ 3
x 2 , h (x) = 4 x 2
Step 1 Find ⎪a⎥ for each function.
⎪-2⎥ = 2 ⎪ 1 _ 3
⎥ = 1 _ 3
⎪4⎥ = 4
Step 2 Order the functions.
h (x) = 4 x 2 The function with the narrowest graph has the greatest value for |a|.f (x) = -2 x 2
g (x) = 1 _ 3
x 2
Check Use a graphing calculator to compare the graphs.
h (x) = 4x2 has the narrowest graph, and g (x) = 1 __ 3 x 2 has the widest graph. ✓
B f (x) = 2 x 2 , g (x) = -2 x 2
Step 1 Find ⎪a⎥ for each function. ⎪2⎥ = 2 ⎪-2⎥ = 2
Step 2 Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest. Since the absolute values are equal, the graphs are the same width.
Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest.
1a. f (x) = - x 2 , g (x) = 2 _ 3
x 2
1b. f (x) = -4 x 2 , g (x) = 6 x 2 , h (x) = 0.2 x 2
Compare the coefficients in Compare the graphs of the following functions. the same functions.
f (x) = x 2 g (x) = x 2 - 4
h (x) = x 2 + 3
f (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 0
g (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + (-4)
h (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 3
Same Different
• a = 1• b = 0
• Value of c
Same Different
• Axis of symmetry is x = 0.
• Width of parabola
• Vertex of parabola
The value of c makes these graphs look different. The value of c in a quadratic function determines not only the value of the y-intercept but also a vertical translation of the graph of f (x) = a x 2 up or down the y-axis.
546 Chapter 8 Quadratic Functions and Equations
CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 546CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 546 2/9/11 10:23:16 PM2/9/11 10:23:16 PM

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !5 12
Example 1. Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest. A. f(x) = 3x2, g(x) = 0.5x2 B. f(x) = x2, g(x) = x2, h(x) = –2x2
Guided Practice 6) Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest: f(x) = –x2, g(x) = x2
7) Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest: f(x) = –4x2, g(x) = 6x2, h(x) = 0.2x2
!
8. How does the constant (c) effect the parabola?
1E X A M P L E Comparing Widths of Parabolas
Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest.
A f (x) = -2 x 2 , g (x) = 1 _ 3
x 2 , h (x) = 4 x 2
Step 1 Find ⎪a⎥ for each function.
⎪-2⎥ = 2 ⎪ 1 _ 3
⎥ = 1 _ 3
⎪4⎥ = 4
Step 2 Order the functions.
h (x) = 4 x 2 The function with the narrowest graph has the greatest value for |a|.f (x) = -2 x 2
g (x) = 1 _ 3
x 2
Check Use a graphing calculator to compare the graphs.
h (x) = 4x2 has the narrowest graph, and g (x) = 1 __ 3 x 2 has the widest graph. ✓
B f (x) = 2 x 2 , g (x) = -2 x 2
Step 1 Find ⎪a⎥ for each function. ⎪2⎥ = 2 ⎪-2⎥ = 2
Step 2 Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest. Since the absolute values are equal, the graphs are the same width.
Order the functions from narrowest graph to widest.
1a. f (x) = - x 2 , g (x) = 2 _ 3
x 2
1b. f (x) = -4 x 2 , g (x) = 6 x 2 , h (x) = 0.2 x 2
Compare the coefficients in Compare the graphs of the following functions. the same functions.
f (x) = x 2 g (x) = x 2 - 4
h (x) = x 2 + 3
f (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 0
g (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + (-4)
h (x) = 1 x 2 + 0x + 3
Same Different
• a = 1• b = 0
• Value of c
Same Different
• Axis of symmetry is x = 0.
• Width of parabola
• Vertex of parabola
The value of c makes these graphs look different. The value of c in a quadratic function determines not only the value of the y-intercept but also a vertical translation of the graph of f (x) = a x 2 up or down the y-axis.
546 Chapter 8 Quadratic Functions and Equations
CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 546CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 546 2/9/11 10:23:16 PM2/9/11 10:23:16 PM

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !6 12
Video Example 2
A. Compare the graph of g(x) ! with the graph of
f(x) = x2.
B) Compare the graph of g(x) = 5x2 + 3 with the graph of f(x) = x2.
−14x2 − 2
When comparing graphs, it is helpful to draw them on the same coordinate plane.
Helpful Hint

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !7 12
2E X A M P L E Comparing Graphs of Quadratic Functions
Compare the graph of each function with the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
A g (x) = - 1 _ 3
x 2 + 2
Method 1 Compare the graphs.
• The graph of g (x) = - 1 __ 3 x 2 + 2 is wider than the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
• The graph of g (x) = - 1 __ 3 x 2 + 2 opens downward, and the graph of f (x) = x 2 opens upward.
• The axis of symmetry is the same.
• The vertex of f (x) = x 2 is (0, 0) .
The vertex of g (x) = - 1 __ 3 x 2 + 2 is translated 2 units up to (0, 2) .
B g (x) = 2 x 2 - 3
Method 2 Use the functions.
• Since ⎪2⎥ > ⎪1⎥ , the graph of g (x) = 2 x 2 - 3 is narrower than the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
• Since - b __ 2a = 0 for both functions, the axis of symmetry is the same.
• The vertex of f (x) = x 2 is (0, 0) . The vertex of g (x) = 2 x 2 - 3 is translated 3 units down to (0, -3) .
Check Use a graph to verify all comparisons.
y = x2
y = 2x2 - 3
y = x2
y = 2x2 - 3
y = x2
y = 2x2 - 3
yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy ================ xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx222222222222222222222222222222222
================ 22 2 2222222222222xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2 2 2 2222222222222 - - - ------------- 3333333333333333
y = x2
y = 2x2 - 3
y = x2
y = 2x2 - 3
Compare the graph of each function with the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
2a. g (x) = - x 2 - 4 2b. g (x) = 3 x 2 + 9 2c. g (x) = 1 _ 2
x 2 + 2
The quadratic function h (t) = -16 t 2 + c can be used to approximate the height h in feet above the ground of a falling object t seconds after it is dropped from a height of c feet. This model is used only to approximate the height of falling objects because it does not account for air resistance, wind, and other real-world factors.
When comparing graphs, it is helpful to draw them on the same coordinate plane.
The graph of the function f (x) = x 2 + c is the graph of f (x) = x 2 translated vertically.
• If c > 0, the graph of f (x) = x 2 is translated c units up.
• If c < 0, the graph of f (x) = x 2 is translated c units down.
Vertical Translations of a Parabola
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions 547
CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 547CS10_A1_MESE612225_C08L04.indd 547 2/9/11 10:23:18 PM2/9/11 10:23:18 PM

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !8 12
Example 2. Compare the graph of the function with the graph of f(x) = x2. A. B. g(x) = 3x2
Guided Practice 9. Compare the graph of g(x) = -x2 - 4 with the graph of f(x) = x2.
10. Compare the graph of g(x) = 3x2 + 9 with the graph of f(x) = x2.
11) Compare the graph of g(x) = x2 + 2 with the graph of f(x) = x2.
g(x) = − 14x2 + 3

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !9 12
Video Example 3:
!
The quadratic function h(t) = –16t2 + c can be used to approximate the height h in feet above the ground of a falling object t seconds after it is dropped from a height of c feet. This model is used only to approximate the height of falling objects because it does not account for air resistance, wind, and other real-world factors.

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !10 12
!
!
144 ft
64 ft
3E X A M P L E Physics Application
Two identical water balloons are dropped from different heights as shown in the diagram.
a. Write the two height functions and compare their graphs.
Step 1 Write the height functions. The y-intercept c represents the original height.
h 1 (t) = -16 t 2 + 64 Dropped from 64 feet
Dropped from 144 feeth 2 (t) = -16 t 2 + 144
Step 2 Use a graphing calculator. Since time and height cannot be negative, set the window for nonnegative values.
The graph of h 2 is a vertical translation of the graph of h 1 . Since the balloon in h 2 is dropped from 80 feet higher than the one in h 1 , the y-intercept of h 2 is 80 units higher.
b. Use the graphs to tell when each water balloon reaches the ground.
The zeros of each function are when the water balloons reach the ground.
The water balloon dropped from 64 feet reaches the ground in 2 seconds. The water balloon dropped from 144 feet reaches the ground in 3 seconds.
Check These answers seem reasonable because the water balloon dropped from a greater height should take longer to reach the ground.
3. Two tennis balls are dropped, one from a height of 16 feet and the other from a height of 100 feet.
a. Write the two height functions and compare their graphs.
b. Use the graphs to tell when each tennis ball reaches the ground.
THINK AND DISCUSS 1. Describe how the graph of f (x) = x 2 + c differs from the graph of
f (x) = x 2 when the value of c is positive and when the value of c is negative.
2. Tell how to determine whether a graph of a function is wider or narrower than the graph of f (x) = x 2 .
3. GET ORGANIZED Copy and complete the graphic organizer by explaining how each change affects the graph f (x) = a x 2 + c.
c is decreased?
!a! is decreased?
!a! is increased?
c is increased?
How does the graph off(x) = ax2 + c change when…
Remember that the graphs shown here represent the height of the objects over time, not the paths of the objects.
548 Chapter 8 Quadratic Functions and Equations
CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 548CC13_A1_MESE647036_C08L04.indd 548 4/30/11 7:05:32 AM4/30/11 7:05:32 AM
Remember that the graphs shown here represent the height of the objects over time, not the paths of the objects.
Caution!

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !11 12
Example 3. Two identical softballs are dropped. The first is dropped from a height of 400 feet and the second is dropped from a height of 324 feet. Write the two height functions and compare their graphs. Graph the functions and state when the tennis balls will hit the ground.
12. Guided Practice: Two tennis balls are dropped, one from a height of 16 feet and the other from a height of 100 feet. Write the two height functions and compare their graphs. Graph the functions and state when the tennis balls will hit the ground.
8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions • Desmos: Polygraph: Parabolas (bwcn) • Desmos: Quadratic Graphing lab: SFAN • Desmos: Marbleslide Parabolas: P8W3 • 8A Are You Ready pretest & posttests.

Algebra 8-4 Transforming Quadratic Functions (pp 545-551) Page ! of !12 12
Server: May I help you? Student: Yes, I would like to order ! & ! Server: What are you talking about? Student: My teacher told me to order my quadratic functions.
"If you are patient in one moment of anger, you will escape a hundred days of sorrow.”—Chinese Epigram
f x( )= x2 g x( )= 3x2