Microgallbladder: Self-Remitting Acute Cholecystitis-Like ...
Acute Cholecystitis 1
-
Upload
randy-musashi -
Category
Documents
-
view
253 -
download
6
description
Transcript of Acute Cholecystitis 1

ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS
Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of gall-bladder.

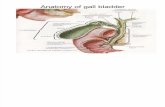
BILIARY ANATOMYBILIARY ANATOMY

Anatomy: vascular supplyAnatomy: vascular supply

ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
• infection• discoordination passage of bile • metabolic disturbance

CLASSIFICATION
I. Acute calculous cholecystitis II. Acute non-calculous cholecystitis 1. Catarrhal. 2. Phlegmonous. 3. Gangrenous. 4. Perforated. 5. Complicated:
a) Hydropsy;b) Empyema;c) Pancreatitis;d) Jaundice;e) Hepatitis;f) Cholangitis; g) Infiltrate;h) Abscess;i) hepato-renal insufficiency;j) Peritonitis.

Classifying the Biliary Stone Classifying the Biliary Stone PatientPatient
Asymptomatic Cholelithiasis Incidental Finding on Sonogram
Acute Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis on Sonogram, clinical Cholecystitis diagnosis or Positive Pipida Scan
Symptomatic Cholelithiasis Positive Sonogram, normal Liver Function Tests
Cholelithiasis with Suspected Choledocholithiasis
Abnormal Liver Function Tests (Serum Transaminases elevation or Bilirubin >3.0, gallstone pancreatitis)
Cholelithiasis with Choledocholithiasis
CBD Stone on Sonogram, MR Cholangiography or Jaundice
Cholelithiasis with Resolving Gallstone Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis on Sonogram, CT or MER Cholangiography or clinically, Documented High Serum Amylase and Lipase - WITH - Decreasing Serum Pancreatic Enzymes after initial attack

Identifying Biliary Stone PatientsIdentifying Biliary Stone Patients
1) History and Physical Examination, 1) History and Physical Examination, 2) Liver Function Studies, 2) Liver Function Studies, 3) Sonographic Findings.3) Sonographic Findings.

BILE STONES

BILE STONES

The pathological sequences during
a bout of uncomplicated cholecystitis

Sequence of pathological
processes with local inflammation
around a gallbladder

Sequence of pathological processes.
Formation of an empyema or
mucocele of the gallbladder

Sequence of pathological
processes leading to perforation of the gallbladder

Sequence of pathological processes localising a
perforation of the gallbladder

Symptoms and clinical signs
Pain syndrome. Characteristic for it is great acute pain in right hypochondrium and epigastric area with an irradiation in right supraclavicular area and right shoulder. If pain syndrome has the strongly expressed character, it is named hepatic colic.
Dyspepsic syndrome. Frequent symptoms which disturb a patient, are nausea, frequent vomitting, at first by gastric maintenance, and later — with bile. Afterwards feelings of swelling of stomach, delay of emptying and gases.

Symptoms and clinical signsMurphy's symptoms is a delay of breathing during
palpation of gall-bladder on inhalation. Kehr's symptom is strengthening of pain at
pressure on the area of gall-bladder, especially on deep inhalation.
Ortner's symptom — painfulness at the easy pushing on right costal arc by the edge of palm.
Mussy's symptom — painfulness at palpation between the legs (above a collar-bone) of right nodding muscle.
Blumberg's signs are the increases of painfulness at the rapid taking away of fingers by which a front abdominal wall is pressed on. This symptom is not pathognomic for cholecystitis but matters very much in diagnostics of peritonitis.

Hydropsy (mucocele) of gall-bladder is its aseptic inflammation, that arises up as a result of blockade of cystic duct by concrement or mucus. The bile from a bubble is sucked in, and on replacement transparent exudation accumulates in its formation. During palpation increased and unpainfully gall-bladder is marked in patients.
Empyema of gall-bladder is unliquidated in time hydropsy, that at repeated infection is transformed in a new form. Gall-bladder in such patients is palpated as a dense, moderately painful formation, however, the symptoms of irritation of peritoneum, as a rule, are absent. The high temperature of body is periodically observed. In blood high leucocytosis with the shift of formula of blood to the left is present.
Complications

Biliary pancreatitis. Worsening of the patient’s condition, appearance of pain, frequent vomitting, signs of cardio-vascular insufficiency, high amylasuria, presence of infiltrate in epigastric area and positive Voskresensky's and Mayo-Robson's symptoms are its basic signs.An icterus arises up at violation of passage of bile in duodenum as a result of obturation of choledochus by concrement, by putty or through the edema of head of pancreas. Thus icterus sclera, bilirubinemia, dark urine and light unpainted excrement arise.
Cholangitis. The Sharko triad is characteristic for the patient with this pathology. Next to pain syndrome and icterus, the temperature of body rises to 38–39 0С, there is a fever, high leucocytosis and decline of sizes of functional tests of liver is observed.
Complications

DIAGNOSTIC PROGRAM
1. Anamnesis and physical methods of inspection.2. Survey sciagraphy of organs of abdominal cavity.3. Sonography.4. General analysis of blood and urine.5. Diastase urines.6. Biochemical blood test (bilirubin, amylase, alanine aminotransferase, asparaginase, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine).7. Coagulogram.

Tactics and choice of treatment method
1. Bed rest. 2. Hunger of 1–3 days, than diet № 5 by Peuzner. 3. Desintoxication therapy (neohemodes, reopolyglucine).4. Spasmolytics ( platyphyllin, no-shparum, baralgin).5. Antibacterial therapy:6. Inhibitors of protease (contrical, trasilol, gordox). 7. Desensitizing preparation (dimedrole, pipolphen, tavegile). 8. Vitamins (С, В1, В6, В12 vitamins).

Indication To Surgical Treatment
• All forms of acute calculous cholecystitis• Destructive and complicated forms of noncalculous cholecystitis • Acute catarrhal cholecystitis, conservative treatment of which was uneffective

Methods of Operative Treatment
• Cholecystectomy from the neck (retrograde) • Cholecystectomy from the bottom (antegrade) • Laparoscopic cholecystectomy

CHOLECYSTECTOMY

OPERATING ROOM SET-UPOPERATING ROOM SET-UP

OPERATING ROOM SET-UPOPERATING ROOM SET-UP

EquipmentEquipment

STEP 1: Exposing the Cystic STEP 1: Exposing the Cystic Duct and ArteryDuct and Artery

STEP 2: Dissecting the Cystic STEP 2: Dissecting the Cystic Duct and ArteryDuct and Artery

STEP 3: Routine Intra-operative STEP 3: Routine Intra-operative CholangiogramCholangiogram

STEP 4: Transecting the Cystic STEP 4: Transecting the Cystic Duct and ArteryDuct and Artery

STEP 5: Dissecting the Body of STEP 5: Dissecting the Body of the Gallbladderthe Gallbladder

CHOLECYSTECTOMY

Complications

Complications


INTRA-OPERATIVE EXAMINATION
• Sonography Cholangiography Cholangioscopy

INTRA-OPERATIVE SONOGRAPHY

INTRA-OPERATIVE SONOGRAPHY

The Intra-operative The Intra-operative CholangiographyCholangiography

The Intra-operative The Intra-operative CholangiogramCholangiogram

The Intra-operative The Intra-operative CholangiogramCholangiogram

The Intra-operative CholangiogramThe Intra-operative Cholangiogram

The Intra-operative The Intra-operative CholangiogramCholangiogram

The Intra-operative The Intra-operative CholedochoscopyCholedochoscopy

The CholedochoscopyThe Choledochoscopy

Retrieving the CBD StonesRetrieving the CBD Stones

CBD StonesCBD Stones