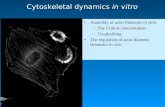
actin filaments
description
Transcript of actin filaments

These filaments These filaments contract or contract or
lengthen to give lengthen to give cells the flexibility cells the flexibility
to move and to move and change shape. change shape. Together with Together with myosin, these myosin, these filaments are filaments are
responsible for responsible for muscle muscle
contraction. contraction.

actin filamentsactin filaments

A small, A small, membrane-membrane-
bounded sac that bounded sac that transports transports substances substances
between organelles between organelles as well as to and as well as to and
from the cell from the cell membrane. membrane.

vesiclevesicle

A group of tissues A group of tissues that perform a that perform a particular job.particular job.

organorgan

A fatty, waxy, or A fatty, waxy, or oily compound that oily compound that will not dissolve in will not dissolve in water. These are a water. These are a
major part of major part of biological biological
membranes. membranes.

lipidslipids

A protein that A protein that speeds up a speeds up a
specific chemical specific chemical reaction without reaction without
being permanently being permanently altered or altered or consumed consumed

enzymeenzyme

The substance of The substance of heredity. A long, heredity. A long, helical, double-helical, double-
stranded molecule stranded molecule that carries the that carries the cell's genetic cell's genetic information. information.

DNADNAdeoxyribonucleic deoxyribonucleic
acidacid

The semi-fluid The semi-fluid portion of the portion of the
cytoplasm, cytoplasm, excluding the excluding the
organelles. This is organelles. This is a concentrated a concentrated
solution of solution of proteins, salts, and proteins, salts, and other molecules other molecules

cytosolcytosol

The basic subunit The basic subunit of any living of any living
organism; the organism; the simplest unit simplest unit
capable of capable of independent life.independent life.

cellcell

A cell that lacks a A cell that lacks a nucleus. nucleus.
An example is An example is bacteria or blue bacteria or blue green alage. A green alage. A
small cell.small cell.

prokaryotic cellprokaryotic cell

A cell that has a A cell that has a nucleus and other nucleus and other
organelles not organelles not found in found in
prokaryotes; prokaryotes; includes all animal includes all animal
and most plant and most plant cells. These are big cells. These are big
cells.cells.

eukaryotic celleukaryotic cell

The process of The process of making proteins making proteins based on genetic based on genetic
information information encoded in encoded in
messenger RNA. messenger RNA. It occurs in It occurs in ribosomes. ribosomes.

translationtranslation

The process of The process of copying copying
information from information from genes (made of genes (made of
DNA) into DNA) into messenger RNA. messenger RNA. This happens in This happens in
the nucleusthe nucleus

transcriptiontranscription

A molecule very A molecule very similar to DNA that similar to DNA that plays a key role in plays a key role in making proteins. making proteins. There are three There are three
main types.main types.

RNARNAribonucleic acidribonucleic acid

The material found The material found between the cell between the cell
membrane and the membrane and the nuclear envelope. nuclear envelope.
It includes the It includes the cytosol and all cytosol and all
organelles except organelles except the nucleus. the nucleus.

cytoplasmcytoplasm

A semi-fluid layer of A semi-fluid layer of lipids and proteins. lipids and proteins. This encloses cells This encloses cells and organelles and and organelles and control the passage control the passage
of materials into and of materials into and out of them.out of them.

membranemembrane

The cell's power The cell's power plant; the organelle plant; the organelle that converts energy that converts energy from food into ATP, from food into ATP,
fueling the cell. fueling the cell. These contain their These contain their own small genome own small genome
and appears to have and appears to have descended from free-descended from free-
living bacteria. living bacteria.

mitochondriamitochondria

A barrier that A barrier that encloses the encloses the
nucleus and is nucleus and is made up of two made up of two
membranes membranes perforated by perforated by nuclear pores nuclear pores

nuclear envelopenuclear envelope

An opening in the An opening in the nuclear envelope nuclear envelope that allows the that allows the
passage of small passage of small molecules such as molecules such as
salts, small salts, small proteins, and RNA proteins, and RNA
molecules.molecules.

nuclear porenuclear pore

A chemical A chemical building block of building block of
proteins. There are proteins. There are twenty.twenty.

amino acidamino acid

A hollow or pore-A hollow or pore-containing containing
structure that structure that spans a cell spans a cell
membrane and acts membrane and acts as a conduit for as a conduit for small molecules, small molecules, such as charged such as charged particles (ions). particles (ions).

channel proteinchannel protein

The major source The major source of energy for of energy for biochemical biochemical
reactions in all reactions in all organisms. organisms.

ATPATP
adenosine triphosphateadenosine triphosphate

A specialized, A specialized, membrane-bounded membrane-bounded structure that has a structure that has a specific function in a specific function in a
cell. Examples cell. Examples include the nucleus, include the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi, mitochondria, Golgi, ER, and lysosomes. ER, and lysosomes.

organelleorganelle

A process cells use A process cells use to send substances to send substances
outside their outside their surface membrane surface membrane
via vesicles via vesicles

exocytosisexocytosis

An enzyme that An enzyme that makes RNA using makes RNA using DNA as a template DNA as a template in a process called in a process called
transcription.transcription.

RNA polymeraseRNA polymerase

A process cells use to A process cells use to engulf particles or engulf particles or liquid from their liquid from their surroundings. It surroundings. It
occurs when the cell occurs when the cell surface membrane surface membrane
puckers inward, puckers inward, encircling the encircling the
material, then pinches material, then pinches off, producing a off, producing a
vesicle inside the cell.vesicle inside the cell.

endocytosisendocytosis

A waxy lipid A waxy lipid produced by produced by
animal cells that is animal cells that is a major component a major component of cell membranes. of cell membranes. It is also used as a It is also used as a building block for building block for some hormones. some hormones.

cholesterolcholesterol

A molecule made A molecule made up of one or up of one or more sugars.more sugars.

carbohydratecarbohydrate

A molecular A molecular complex in which complex in which
proteins are made. proteins are made. In eukaryotic cells, In eukaryotic cells, it is either free in it is either free in
the cytoplasm or is the cytoplasm or is attached to the attached to the
rough endoplasmic rough endoplasmic reticulum.reticulum.

ribosomeribosome

One millionth of a One millionth of a meter or one meter or one
thousandth of a thousandth of a millimeter. This is millimeter. This is frequently used to frequently used to measure cells and measure cells and
organelles. organelles.

micrometermicrometer

An organelle An organelle composed of composed of
membranous sacs membranous sacs in which many in which many
newly made newly made proteins mature proteins mature
and become and become functional. functional.

golgi golgi

Part of the Part of the cytoskeleton that cytoskeleton that provides strength. provides strength. Some form nails, Some form nails,
hair, and the outer hair, and the outer layer of skin. layer of skin.
Others are found in Others are found in nerves or other nerves or other
organs. organs.

intermediate intermediate filamentfilament

A powerful A powerful microscope that microscope that
uses beams of fast-uses beams of fast-moving electrons moving electrons instead of light to instead of light to magnify samples. magnify samples. Powerful magnets Powerful magnets focus the electrons focus the electrons
into an image. into an image.

electron electron microscopemicroscope

A molecule A molecule composed of amino composed of amino acids lined up in a acids lined up in a
precise order precise order determined by a determined by a
gene, then folded gene, then folded into a specific into a specific
three-dimensional three-dimensional shape. shape.

proteinprotein

A group of cells that act A group of cells that act together to carry out a together to carry out a specific function in the specific function in the body. Examples include body. Examples include muscle, nervous system muscle, nervous system
(including the brain, (including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves), spinal cord, and nerves),
and connective (including and connective (including ligaments, tendons, bones, ligaments, tendons, bones,
and fat)and fat)

tissuetissue

The process of using The process of using small pieces of small pieces of
double-stranded RNA double-stranded RNA to reduce the activity to reduce the activity of specific genes. The of specific genes. The
process occurs process occurs naturally in many naturally in many
organisms and is now organisms and is now commonly used in commonly used in basic research.basic research.

RNAiRNAi
RNA interferenceRNA interference

A bubble-like A bubble-like organelle that organelle that
contains powerful contains powerful enzymes that can enzymes that can digest a variety of digest a variety of
biological biological materials. materials.

lysosomelysosome

The organelle in The organelle in eukaryotic cells eukaryotic cells
that contains that contains genetic material.genetic material.

nucleusnucleus

An organelle made up of An organelle made up of interconnected tubes and interconnected tubes and
flattened sacs.flattened sacs. There are two kinds: There are two kinds:
rough, which processes rough, which processes newly made proteins, and newly made proteins, and smooth, which helps make smooth, which helps make
lipids and neutralizes lipids and neutralizes toxins.toxins.

endoplasmic endoplasmic reticulumreticulum

A collection of fibers that A collection of fibers that gives a cell shape and gives a cell shape and
support and allows support and allows movement within the cell. movement within the cell.
The three main types of The three main types of fibers are microtubules, fibers are microtubules,
actin filaments, and actin filaments, and intermediate filaments.intermediate filaments.

cytoskeletoncytoskeleton

The process of The process of adding specialized adding specialized
chains of sugar chains of sugar molecules to molecules to
proteins or lipids; proteins or lipids; occurs in the ER occurs in the ER
and Golgi. and Golgi.

glycosylationglycosylation