A Prokaryotic Cell
description
Transcript of A Prokaryotic Cell

A Prokaryotic Cell
of

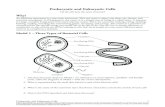
Directions: Match the structure with the correct function.
___Most unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, that do not have membrane bound organelles.
___Site for protein synthesis.
___Supports and protects the cell
___Maintains homeostasis by its selective permeability.
___Coaled up DNA into a circular loop.
___The region of the cell that contains genetic information.
___Gelatinous-like fluid mostly composed of water.
___Long projections that move with a whip-like motion.
a) Prokaryoticb) Ribosomec) Cell Wall
d) Plasma Membranee) Plasmidf) Nucleoidg) Flagella
h) Cytoplasm

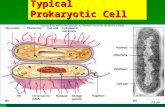
Prokaryotic Cells
• oldest single-celled organisms• most common cell• found almost everywhere• no true nucleus• bacteria

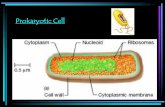
Cell Wall• rigid and inflexible wall
• thick, tough, fibrous barrier• very porous
• Supports and protects the cell

Plasma Membrane• flexible boundary • lipid bilayer• maintains homeostasis• selectively permeable• allows nutrients, ions, and other
substances across the membrane through protein channels

Cytoplasm• clear, gelatinous fluid• contains all the
necessary parts of a prokaryotic cell
• composed mostly of water

Ribosomes• floats freely in the cytoplasm• receive and translate genetic information• site for protein synthesis
Actual structure of a ribosome

Nucleoid• region of DNA• DNA is condensed into a circular loop PLASMID• How is this different from a nucleus?

Flagella
• long projections• produce whip-like motions• major means of
locomotion/movement for cell

Site of protein synthesis
Contained in the nucleoid, condensed into circular loop called PLASMID
Major means of locomotion
Supports and protects the cell
Selectively permeable to maintain homeostasis
Gel-like fluid in cell, mostly composed of water

Quick Review___ Most unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, that
do not have membrane bound organelles. PROKARYOTE
___ Site for protein synthesis. RIBOSOME
___ Supports and protects the cell CELL WALL
___ Maintains homeostasis by its selective permeability.
PLASMA MEMBRANE
___ Coaled up DNA into a circular loop. PLASMID
___The region of the cell that contains genetic information.
NUCLEIOD
___Gelatinous-like fluid mostly composed of water. CYTOPLASM
___ Long projections that move with a whip-like motion.
FLAGELLA

Eukaryotic Cell
Animal Cell• http://www.youtube.com/w
atch?v=PXbv95P3uhI
Plant Cell• http://www.youtube.com/w
atch?v=LMVQ-INMSVw&feature=related