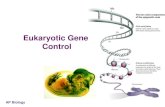
a. DNA is a double helix molecule. b. DNA coils around proteins called histones (similar to spools...
-
Upload
phebe-tracey-martin -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of a. DNA is a double helix molecule. b. DNA coils around proteins called histones (similar to spools...


a. DNA is a double helix molecule.b. DNA coils around proteins called histones (similar to spools of thread).c. DNA supercoils itself (like a telephone cord).d. DNA is then organized into 2 sister chromatids connected together at the centromere.


From 1990 to 2003, scientists from the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Department of Energy worked together to…
determine the sequence of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA
identify all of the 20,000 to 25,000 genes in human DNA
store this information in databases address the ethical, legal and social issues
that arise from this project

to compare human sequences with other species to provide insight into human embryonic development and genetic relationships
to identify genes associated with diseases
to develop of treatments and preventions for genetic disorders

The human genome contains about 3 billion chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G).
The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases.
Chromosome 1 has the most genes (2968), and the Y chromosome has the fewest (231).
The total number of genes is estimated at 20,000 to 25, 000 Almost all (99.9%) nucleotide bases are exactly the same in all people.
The functions are unknown for over 50% of discovered genes. Chromosome Poster

Can you make a relationship between the number of chromosomes and the complexity of an organism? Why or why not?

How do you think this individual inherited an extra chromosome? HINT: Think about meiosis!

Nondisjunction – a pair of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis. i.e. Downs syndrome
Duplication- part of a chromosome is repeated.
Deletion- part of a chromosome is lost Inversion- part of chromosome is reversed Translocation- part of chromosome attaches
to a non homologous chromosome

A pedigree is a family tree that records and traces the occurrence of a trait in a family.
It can determine whether a trait is inherited.
It shows how a trait is passed from one generation to the next.
It can determine if an allele is dominant or not.

What is the inheritance pattern for hemophilia? How does a pedigree enable you to determine it?

An individual with one copy of a recessive allele is called a carrier.
Since most genetic disorders are recessive, they are self limiting.
Males more commonly exhibit sex linked traits because they only need one recessive allele located on the X chromosome.