Unit II Introduction to 8086 Microprocessor 8086 Architecture
8086 System Connection and Timing
Transcript of 8086 System Connection and Timing
Microcomputer
A microcomputer system is one which uses a microprocessor as its cpu
In addition the microcomputer also has a memory unit,input/output
devices and system buses.
The system buses are of three types:
1.Address bus
2.Data bus
3.Control bus
Physically buses are group of wires
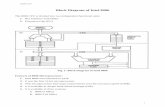
Basic 8086 Microcomputer System
Fig: Block Diagram of 8086 Microcomputer
CLK
ESET
8284ACLOCKGENE-RATOR
WAIT STATEGENERATOR
MN/MX
READYRM/IO
INTA
RD
WR
DT/R
DEN
ALE
AD0-AD15
A16-A19
8282
LATCH
8286
TRANS-CEIVER
RAM 21422716
PROM
PERI-
PHERAL
DATAADDR/DATA
ADDR
Basic 8086 Microcomputer System
A closer look at the generalized microcomputer in fig. we find
The 8086 CPU, the ROM and the RAM
The ports, represented by the block labeled MCS.80 PERIPHERALS.
The BUSES
The 8286 Transceiver
The 8284A clock generator
The PORTSThere is a wide variety of port devices are available in 8086
i. Parallel port devices- 8255A
ii. Serial Port devices- DB9
iii. Special port devices- Interface with CRTs.
iv. Port devices which interface with keyboards and
v. Port devices which interface with floppy disks.
The BUSES
Next we find in the figure1.Control Bus - The basic control bus consists M/lO, RD, and WR.
2.Address Bus -The 8086 has 20 Address lines.
3.Data Bus - The 8086 has 16 Data lines.
In any operation the 8086 sends out the lower 16 bits of the
address on the data bus. External latches “grab" this address and
hold it during the rest of the operation.
The 8286 Transceiver
This block represents bidirectional three-state buffers.
For a vely small system these buffers are not needed, but as more
devices are added to a system,they become necessary.
The Data Transmit / Receive signal, DT/R. from the 8086 sets thedirection In which data will pass through the buffers.
8284A clock Generator
This device usesa crystal to produce the stable-frequency clock
signal which steps the 8086 through execution of its iñstructions
In an orderly manner.
The 8284A also synchronizes the RESET ilgnal and the READY
signal with the clock.
When the RESET input Is asserted, the 8086 goes to address FFFFOH to get Its next Instruction.
Introduction
Pin diagram is shows all the signal pins used by themicroprocessor and the sequence of the signals and theirconnections.
8086 microprocessor is a 40 pin IC which operateon 5volt power supply.
Pin Description
The 8086 signals can be categorized in three groups
The first are the signal having common functions in minimum as
well as maximum mode.
The second are the signals which have special functions for
minimum mode
The third are the signals having special functions for maximum mode.
Pin Description
AD15-AD0:
These are the time multiplexed memory I/O address and data lines
Address remains on the lines during T1 state, while the data isavailable on the data bus during T2, T3, Tw and T4. These lines areactive high and float to a tristate during interrupt acknowledge andlocal bus hold acknowledge cycles.
A19-A16:A19/S6,A18/S5,A17/S4,A16/S3
These are the time multiplexed address and status lines. During T1these are the most significantaddress lines for memory operations.
Pin Description(Cont..)
BHE/S7:
The bus high enable is used to indicate the transfer
of data over the higher order ( D15-D8 ) data bus.
RD, READY:
RD-READ signal indicates that the processor is performing memory or
I/O read operation
READY This is the acknowledgement from the memory that they have
completed the data transfer.
Pin Description(Cont..)
INTR(Interrupt Request)
This is a triggered input. If any interrupt request is pending, the processor enters the interrupt acknowledge cycle.
TEST,CLK
TEST input is examined by a ‘WAIT’instruction. If the TEST pin goes low, execution will continue, else the processor remains in an idle state.
CLK- Clock Input : The clock input provides the basic timing for processor operation and bus control activity.