7.1 – Basic Trigonometric Identities and Equations
-
Upload
vladimir-holman -
Category
Documents
-
view
36 -
download
6
description
Transcript of 7.1 – Basic Trigonometric Identities and Equations

7.1 – Basic Trigonometric Identities and
Equations

5.4.3
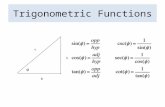
Trigonometric Identities
Quotient Identities
tanθ=sinθcosθ cotθ=cosθ
sinθReciprocal Identities
sinθ= 1cscθ
cosθ= 1secθ
tanθ= 1cotθ
Pythagorean Identities
sin2+ cos2 = 1 tan2+ 1 = sec2 cot2+ 1 = csc2
sin2= 1 - cos2
cos2 = 1 - sin2
tan2= sec2- 1 cot2= csc2- 1

Do you remember the Unit Circle?
• What is the equation for the unit circle?x2 + y2 = 1
• What does x = ? What does y = ? (in terms of trig functions)
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
Pythagorean Identity!
Where did our pythagorean identities come from??

Take the Pythagorean Identity and discover a new one!
Hint: Try dividing everything by cos2θ
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1 .cos2θ cos2θ cos2θ tan2θ + 1 = sec2θ
Quotient Identity
ReciprocalIdentityanother
Pythagorean Identity

Take the Pythagorean Identity and discover a new one!
Hint: Try dividing everything by sin2θ
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1 .sin2θ sin2θ sin2θ 1 + cot2θ = csc2θ
Quotient Identity
ReciprocalIdentitya third
Pythagorean Identity

Using the identities you now know, find the trig value.
1.) If cosθ = 3/4, find secθ 2.) If cosθ = 3/5, find cscθ.
€
secθ =1
cosθ=
13
4=
43
€
sin2θ + cos2θ =1
sin2θ +35 ⎛ ⎝ ⎜
⎞ ⎠ ⎟2
=1
sin2θ =2525
−9
25
sin2θ =1625
sinθ = ±45
cscθ =1
sinθ=
1± 4
5= ±
54

3.) sinθ = -1/3, find tanθ
4.) secθ = -7/5, find sinθ€
tan2θ +1 = sec2θ
tan2θ +1 = (−3)2
tan2θ = 8
tan2θ = 8
€
tanθ = 2 2

Identities can be used to simplify trigonometric expressions.
Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
cosθ+sinθ tanθ
=cosθ +sinθ sinθ
cosθ
=cosθ + sin2θ
cosθ
=cos2θ + sin2θ
cosθ= 1
cosθ=secθ
a)
Simplify.
b)cot2θ
1−sin2θ
=cos2θsin2θcos2θ
1
= 1sin2θ
=csc2θ
5.4.5
=cos2θsin2θ× 1
cos2θ

Simplifing Trigonometric Expressions
c) (1 + tan x)2 - 2 sin x sec x
=1+2tanx+tan2x−2sinxcosx
=1+tan2x+2tanx−2tanx=sec2x
d)cscx
tanx+cotx= 1
sinxsinxcosx
+cosxsinx
= 1sinx
sin2x+cos2xsinxcosx
= 1sinx×sinxcosx
1=cosx
= 1sinx1
sinxcosx
=(1+tanx)2 −2sinx 1cosx

Simplify each expression.
€
1sinθ
cossinθ
1sinθ
•sinθcosθ
1cosθ
= secθ€
=cos x1
sin x ⎛ ⎝ ⎜
⎞ ⎠ ⎟ sin xcos x ⎛ ⎝ ⎜
⎞ ⎠ ⎟
=1
€
cos xcos xsin x ⎛ ⎝ ⎜
⎞ ⎠ ⎟+ sin x
cos2 xsin x
+sin2 xsin x
cos2 x + sin2 xsin x
1sin x
= csc x

Simplifying trig Identity
Example1: simplify tanxcosx
tanx cosxsin xcos x
tanxcosx = sin x

Example2: simplifysec xcsc x
sec xcsc x1sin x
1cos x 1
cos xsinx
1= x
=sin xcos x
= tan x
Simplifying trig Identity

Simplifying trig Identity
Example2: simplify cos2x - sin2x
cos xcos2x - sin2x
cos xcos2x - sin2x 1 = sec x

ExampleSimplify:
= cot x (csc2 x - 1)
= cot x (cot2 x)
= cot3 x
Factor out cot x
Use pythagorean identity
Simplify

ExampleSimplify:
Use quotient identitySimplify fraction with LCD
Simplify numerator
= sin x (sin x) + cos xcos x= sin2 x + (cos x)
cos x cos xcos x
= sin2 x + cos2x
cos x = 1
cos x
= sec x
Use pythagorean identity
Use reciprocal identity

Your Turn!Combine fractionSimplify the numeratorUse pythagorean identityUse Reciprocal Identity

Practice

One way to use identities is to simplify expressions involving trigonometric functions. Often a good strategy for doing this is to write all trig functions in terms of sines and cosines and then simplify. Let’s see an example of this:
sintancosxxx
=
1seccos
xx
=
1cscsin
xx
=
tan cscSimplify: secx xx
sin 1cos sin
1cos
xx x
x
=
substitute using each identity
simplify
1cos
1cos
x
x
= 1=

Another way to use identities is to write one function in terms of another function. Let’s see an example of this:
2
Write the following expression in terms of only one trig function:
cos sin 1x x This expression involves both sine and cosine. The Fundamental Identity makes a connection between sine and cosine so we can use that and solve for cosine squared and substitute.
2 2sin cos 1x x = 2 2cos 1 sinx x=
2= 1 sin sin 1x x
2= sin sin 2x x

20
(E) Examples• Prove tan(x) cos(x) = sin(x)
RSLSxLS
xxxLS
xxLS
==
=
=
sin
coscossin
costan

21
(E) Examples • Prove tan2(x) = sin2(x) cos-2(x)
LSRSxRSxxRS
xxRS
xxRS
xxRS
xxRS
==
=
=
=
=
=
2
2
2
2
22
22
22
tancossin
cossin
cos1sin
cos1sin
cossin

22
(E) Examples
• Prove tan
tan sin cosx
x x x =
1 1
LS xx
LS xx x
x
LS xx
xx
LSx x x x
x x
LS x xx x
LSx x
LS RS
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
tantan
sincos sin
cossincos
cossin
sin sin cos coscos sin
sin coscos sin
cos sin
1
1
1
2 2

23
(E) Examples
• Prove sin
coscos
2
11x
xx
=
LS xx
LS xx
LS x xx
LS xLS RS
=
=
=
=
=
sincoscoscos
( cos )( cos )( cos )
cos
2
2
1111 1
11