7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
-
Upload
nur-sabrina-rosli -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
1/40
FST 307 BASIC
NUTRITION
CHAPTER 7
MAJOR
NUTRITIONAL DISEASE
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
2/40
CHAPTER OUTCOMES
At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:-
a) Explain briefly about obesity and fat cell development
b) Describe briefly factors contributing to obesity and ways to overcome
obesity.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
3/40
NEWS PAPER & TV REPORT
http://localhost/var/www/apps/conversion/tmp/scratch_5/1st%20in%20asean.wmv -
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
4/40
a) Definition: Excessive accumulation of body fat that can lead
us to substantially increase in height to weight
ratio than normal accepted standard.
b) The amount of fat in our diet may effect the risk of
becoming obese.
OBESITY
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
5/40
a) Body mass index (BMI), is a simple and widely used
method for estimating body fat
A BMI less than 18.5 (underweight)A BMI of 18.522.9 (Desirable weight)
A BMI of 23.027.4 (Overweight)
A BMI of 27.5 or higher (Obese)
ASSESSING OBESITY
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
6/40
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
7/40
TYPES OF OBESITY
a) Hypercellular obesity
Obesity due to an above-average
number of fat cells.
b) Hypertrophic obesity
obesity due an increase in the
size of fat cells.
c) Hyperplastic obesity
Obesity due to increase in both
the size and number of fat cells.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
8/40
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
9/40
a) Fat cell increase rapidly when:
I. Late childhood and early puberty
II. Excessive Positive Energy Balance
b) If Positive Energy Balance continues, the fat cellincrease in size first than increase in number.
c) If Positive Energy Balance stop, the fat cell willreduce in size but not in number.
FAT CELL DEVELOPEMENT
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
10/40
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
11/40
1. Lifestyle - Sedentary lifestyles
2. Genetics - Inheritance
3. Gender - Women
4. Sociocultural InfluencesCulture & education
MAIN FACTORS THAT CONTRIBUTE
TO OBESITY
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
12/40
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
13/40
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
14/40
PAUSE TO PONDER
a) Please explain briefly about obesity and fat celldevelopment .
b) Can you describe briefly factors contributing to
obesity and ways to overcome obesity?
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
15/40
CHAPTER OUTCOMES
At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:-
a) Explain briefly about heart disease and atherosclerosis.
b) Describe briefly factors that will increase and decrease the risk of
atherosclerosis.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
16/40
HEART DISEASE
a) Heart disease is the leading cause of death in US andsecond in Malaysia
b) Fat intake is a key factor in its development.
c) High saturated and trans fat intake raises blood
cholesterol level (LDL).
d) High blood cholesterolmajor risk factors foratherosclerosis.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
17/40
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
a) A type of heart disease where arteries
become progressively clogged with
deposits of fatty material.
b) Definition:Atherosclerosis is a disease affecting
arterial blood vessels and it is a chronic
inflammatory response in the walls of
arteries, in large part to the deposition
of lipoprotein (plasma proteins that
carry cholesterol and triglycerides).
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
18/40
c) It is commonly referred to as a "hardening" or
"furring" of the arteries. It is caused by the
formation of multiple plaques within the arteries.
d) Atherosclerosis plaque is formed by a buildup of
fatty material in the wall of artery. An artery
narrowed by plaque is vulnerable to blockage by ablood clot, causing a heart attack or stroke.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
19/40
RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS
a) Risk factor that are under our control include:-
i. High blood pressure
ii. High blood cholesterol
iii. Cigarette smoking
iv. Diabetes
v. Overweight
vi. Physical inactivity
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
20/40
b) Risk factor beyond our control include:-
i. Age (45 or older for men; 55 or older forwomen)
ii. Family history of early heart disease (mother/
sister before age 65, father/ brother before 55)
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
21/40
FACTORS FOR REDUCING
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
a) Regular exercise
b) Linoleic acid
c) Fish and fish oils (EPA, DHA)d) Vegetables
e) Potassium
f) Low to moderate alcohol intake (for CHD)
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
22/40
ADULT BLOOD CHOLESTEROL
& TG LEVELS
a) Total cholesterol < 200mg/dL (1dL=100ml blood)
b) LDL Cholesterol < 100mg/dL
c) HDL Cholesterol < 40mg/dL
d) Triglyceride < 150mg/dL
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
23/40
PAUSE TO PONDER
a) Ask your friend to explain briefly about heartdisease and atherosclerosis.
b) Can you describe briefly factors that will increase
and decrease the risk of atherosclerosis?
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
24/40
CHAPTER OUTCOMES
At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:-
a) Explain briefly about diabetes and its types.
b) Describe briefly ways that will overcome diabetes
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
25/40
DIABETES
Definition:a) A metabolic disorder characterized by:-
i. Elevated blood glucose
ii. Altered energy metabolism
b) It is caused by:-
i. Defective insulin action
ii. Defective insulin secretion
iii. Both combination
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
26/40
Types of diabetes
a) Type 1
i. Failure of insulin production
ii. Dependent on insulin injection because insulinnot produce by pancreas
iii. Usually happen to children and adolescent
b) Type 2
i. Not dependent on insulin injection
ii. Insufficient/inactivate insulin produced by the
pancreasiii. Usually happens to people 40 years and above,
heredity and obese is the main contributor
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
27/40
1. Type I diabetes
a) Almost impossible to overcome
b) It occured naturally
c) People die without insulin injections.
2. Type II diabetes
a) Can be overcome (if not severe)
b) Carefully managing diet intake
c) Regular physical exercise.
WAYS TO OVERCOME DIABETES
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
28/40
PAUSE TO PONDER
a) Please explain briefly about diabetes and its types.
b) Please describe briefly ways that will overcomediabetes.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
29/40
CHAPTER OUTCOMES
At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:-
a) Explain briefly about nutritional status.
b) Describe briefly about nutritional assessments that can be done.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
30/40
MALNUTRITION
http://rds.yahoo.com/_ylt=A0Je5mXNIrtE54cAiMuJzbkF;_ylu=X3oDMTBwaG5sZzluBHBvcwMxBHNlYwNzcgR2dGlkA0kwMDFfNzA-/SIG=1edl4s92r/EXP=1153201229/**http:/images.search.yahoo.com/search/images/view?back=http://images.search.yahoo.com/search/images?p=kwashiorkor&fr=FP-tab-img-t&toggle=1&cop=&ei=UTF-8&w=229&h=291&imgurl=barry-b.tripod.com/kwashiorkor2.JPG&rurl=http://barry-b.tripod.com/childnutrition.html&size=12.8kB&name=kwashiorkor2.JPG&p=kwashiorkor&type=jpeg&no=1&tt=231&ei=UTF-8 -
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
31/40
Malnutritiona) Any condition caused by excess or deficient food
energy or nutrient intake or by an imbalance of
nutrient
b) Classification:
i. Undernutrition
ii. Overnutrition
NUTRITIONAL STATUS
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
32/40
a) The nutritional health of a person as determined by:
i. Anthropometric measurement
ii. Biochemical analysis (measurements of nutrients
or by their by-products in blood and urine)iii. Clinical examination
iv. Dietary analysis
NUTRITION ASSESSMENT
i) ANTHROPOMETRIC
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
33/40
a) Physical measurements reflect bodycomposition and development
b) Evaluate the growth progress, detect underor over nutrition, measure changes in body
compositionc) Types of measurement:
i. Height and weight indices of growth forchildren and adults, relationship of height
and weight = BMI (Obesity Index)ii. skinfold thickness measure the thickness of
subcutaneous fat
iii. body circumference (head and chest) foryoung children, index of brain development
i) ANTHROPOMETRIC
MEASUREMENT
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
34/40
a) Determine what is happening in our body
b) Common test based on blood and urine samples whichcontain nutrients / enzymes / metabolite
c) Detection of abnormal metabolites in the blood / urine :-
i. normal cholesterol level = 11g/Dl
d) Interpretation of biochemical data requires skill
e) No single test can reveal nutritional status
f) But it help to create a picture and becomes clear withcareful interpretation
ii) BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
35/40
a) Complete physical examination and medical history
b) Search for signs of nutrient deficiency or toxicity
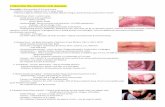
c) Close of observation of skin, hair, teeth, lips,tongue, eyes
d) nail
spoon shaped, pale, brittle = iron status
e) glandswollen at front neck = iodine status
iii) CLINICAL EXAMINATION
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
36/40
a) Measurement of diet intake (excessive / deficient)
b) Documenting previous few days diet intake 24hour diet recall, food frequency intake, food
record
c) Health history diseases (chronic / acute), eatingdisorder problem, infections
d) Socioeconomic history age, ethnic, educationlevel, income level, occupation, no. of household
iv) DIET AND HEALTH HISTORY
METHOD USED FOR GATHERING
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
37/40
a) 24 hour diet recall
i. provide data for one day only
ii. to obtain information on the typical food intakes
for a population
iii. subjects were asked to recount everything eatenor drunk in the past 24 hours or the previous day
METHOD USED FOR GATHERING
FOOD INTAKE DATA
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
38/40
b) Dietary record
i. can be used to determine factor associated
with eating that may affect dietary balanceand adequacy
ii. subjects record food eaten including thequantity and method of preparation
c) Food frequency questionnaire
i. all types of food were listed and subjects willanswer how frequent, how many servings of
each food they ate in a typical day.ii. This will measure help to pinpoint food
groups that may excessive or deficient in thediet
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
39/40
PAUSE TO PONDER
a) Can you explain briefly about nutritional status?
b) Ask your friend to describe briefly about nutritionalassessments that can be done.
-
7/21/2019 7 - Major Nutritional Diseases New
40/40
END OF CHAPTER 7
MAJOR NUTRITIONAL DISEASE