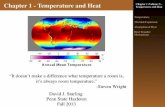
7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
Transcript of 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
1/66
Topics
1. Introduction
2.Energy and thermodynamics
3.Feeding and digestion
4. Ionic gradient, electrical potential
5.Electrical signals and neurons
6.Cytoskeletons, motor proteins and muscle
7.Heat production and body temperature
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
2/66
Heat production and
body tempeature
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
3/66
Homeostasis
http://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-
our-bodies-274183.html
Feedback mechanisms
http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Feedback_mechanism
Regulation of blood pressure
http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-
hypertension/
http://www.interactivephysiology.com/demo/systems/buildframes.html?ca
rdio/mainbp/01
http://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-
pressure.html
http://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Feedback_mechanismhttp://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.interactivephysiology.com/demo/systems/buildframes.html?cardio/mainbp/01http://www.interactivephysiology.com/demo/systems/buildframes.html?cardio/mainbp/01http://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.ehow.com/about_5565094_homeostatic-regulation-blood-pressure.htmlhttp://www.interactivephysiology.com/demo/systems/buildframes.html?cardio/mainbp/01http://www.interactivephysiology.com/demo/systems/buildframes.html?cardio/mainbp/01http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.metabolism.com/2008/08/23/blood-pressure-regulation-hypertension/http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Feedback_mechanismhttp://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Feedback_mechanismhttp://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Feedback_mechanismhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.htmlhttp://www.articlesbase.com/health-articles/homeostasis-regulation-of-our-bodies-274183.html -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
4/66
Regulation of body temperature
http://www.biologymad.com/resources/A2%20Homeostasis.pdf
http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-
regulation-in-humans.html
Fever
http://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node46.html#SECTION00520000000000000000
http://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node47.html#SECTION00530000000
000000000
http://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node48.html#SECTION00540000000000000000
http://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node49.html#SECTION00550000000
000000000
http://www.biologymad.com/resources/A2%20Homeostasis.pdfhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node46.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node46.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node47.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node47.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node48.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node48.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node49.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node49.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node49.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node49.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node48.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node48.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node47.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node47.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node46.htmlhttp://nic.sav.sk/logos/books/scientific/node46.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/homeostasis-and-temperature-regulation-in-humans.htmlhttp://www.biologymad.com/resources/A2%20Homeostasis.pdf -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
5/66
Todays question:
How muchsugar(glucose) do
you need to eat inONE day?
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
6/66
sugar
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
7/66
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
H = 673 kcal / mole
MW = 180 g / mole
154 lb (70 kg)
BMR1500 kcal
Activities
2000 kcal
3500 kcal
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
8/66
How much do you eat / day?
180 : 673 = x : 3500
x =(180) (3500)673
=936g
0.94kg
5.2mole2.06lb
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
9/66
Glucose Glycolysis
Krebs cycle(TCA)
38 moles ATP
CO2 + H2O
ETSO2
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
10/66
You eat 3times a day
ATPproduced = 38 x 5.2
= 197.6 moles
M.W. (ATP) = 507 g / mole
.
. .
197.6 x 507 = 100,183 g100 kg
After each meal:
1003 = 33 kg of ATP
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
11/66
What is our ATP pool?
10 mol / g body
10 x 10-6 x 70,000 x 507 = 354 g of ATP
We produce (or need) 100,183 g / day= 100,183 = 70 g / min
354 gcan sustain 5 minif we are notproducing ATP anymore.
60 x 24
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
12/66
We have made 5.2 x 38 = 197.6 moles ATP
ATP ADP + Pi H = 5.1 kg
197.6 x 5.1 = 1008 kcal
Efficiency = (1008 / 3500) x 100Glucose ATP 3500
= 28.8 %
Efficiency = 30% of 28.8 %
ATP Work
= 302 kcal
Or, 3198 kcal Heat
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
13/66
We are not heat engines!!
Efficiency= (T2-T1)T1 x 100
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
14/66
Conclusion
1. We are chemical engines.
2. The major chemical fuel for physiological
processes is ATP.
3. Wedo not storeATP.
4. We are never 100 % efficient.
5. During physiological processes, heat is
released.
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
15/66
Question for thought:
1. How does a shark detect its prey?
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
16/66
Question for thought:
2.How to detect survivors in rabblesafter the collapse of a building?
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
17/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
18/66
What is homeostasis?
Why is it important to maintain thesteady state concentrations of various
biochemicals and ions in the
extracellular fluid and inside the cell?
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
19/66
Equilibrium
Steady State
Homeostasis - regulates internal environment,
maintains steady state.
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
20/66
What is a negative feedback mechanism?
What is a positive feedback mechanism?
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
21/66
Homeothermy
Heat Gain1. Muscular Activity
(Shivering,
exercise,
unconscious
muscle tension)2. Hormonal
stimulation of
metabolism
3. Food intake
4. Basal metabolic
heat
Heat Loss1. Evaporation
(from lungs,
skin and
sweating)
2. Conducting
and radiation
370C
35 39
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
22/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
23/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
24/66
Fever-resetting
of thermostat in
hypothalamus
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
25/66
Why would one feel cold during the onset of a
fever and feel hot as one recovers?
At the onset of a fever, the thermostat at the
hypothalamus sets the body temperature at a higher
level
In order to bring the core temperature to a new highlevel :
1) blood vessels in the skin constrict,
pale dry skin, decrease heat loss.2) metabolism may step up.
Temp sensors are located in the skin
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
26/66
Temperature receptors of our body actually
sense the temperature of the skin and not
the core temp.
Since less heat goes through the skin
during the onset of a fever, one feels
cold!!!
When fever is on decline, one feels hot
and the reverse sequence of events
occurs.
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
27/66
Should you were more clothingand keep your body warm when
you are building up a fever?
Fever and 5Cs
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWg
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWghttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWghttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWghttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWg -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
28/66
Fever
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWg&feature=fvsr
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWg&feature=fvsrhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WjmnrNinpWg&feature=fvsr -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
29/66
Normal setting of thermostat in hypothalamus
High environmental temperature
Low environmental temperature
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
30/66
Temperature
Temperature
receptors
Skin
temperatureset at 370C
sweat
Skin
BloodFlow
Shivering
hormone in
circulation
Heat loss byevaporation
Heat loss by
conduction
and radiation
Heat
production
(-)
COMPENSATION
BodySkin
Hypothalamus
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
31/66
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ncF6RSRmBcM
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
32/66
Sweat gland
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1tpwDvfjh4
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BzAIeHKrcK8
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1tpwDvfjh4&NR=1http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BzAIeHKrcK8http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BzAIeHKrcK8http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1tpwDvfjh4&NR=1http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1tpwDvfjh4&NR=1 -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
33/66
Saunas
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
34/66
Hot tub
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
35/66
What happens if you enter a 45oC room?
Hypothalamus set body temp. at 37oC
Blood pressurecardiac output
Blood vessel dilation
blood flow to skinTemp
sweat plasma volume
Blood pressureAldosterone secretion
Na+ reabsorption
ADH secretion
urine production
output from heart
sweating
until your system collapses.Temp. rise
Faint
If blood supply to brain becomes low
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
36/66
Fainting after
strenuous
exercise
Sweating
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
37/66
Temp Metabolism Heatproduction
(+)
Reinforcement
Positive feedback destabilize the
system
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
38/66
Heat Stroke and dehydrationhttp://www.umm.edu/non_trauma/dehyrat.htm
http://www.umm.edu/non_trauma/dehyrat.htmhttp://www.umm.edu/non_trauma/dehyrat.htm -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
39/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
40/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
41/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
42/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
43/66
Death by hypothermia
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fgqfQuivDrU&feature=endscreen
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
44/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
45/66
Blood pressure
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
46/66
Blood pressure and heart
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
47/66
Blood pressure and heartBlood pressure and heartBlood pressure and heart
Blood pressure and diameter of blood vessel
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
48/66
(-)
COMPENSATION
Heart
Cardiac
OutputBlood
PressureResistance
Arterioles
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
COMPENSATION
(-)
CNS Motornerve
Motor
nerve
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
49/66
Hypertension
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnyfElxkBlI
Problem:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnyfElxkBlIhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnyfElxkBlI -
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
50/66
Problem:
Hypertension can be divided into 2 types.
Primary (essential) hypertension is due to unknown
cause.Secondary hypertension is due to abnormal hormonal
production.
1.increase workload for heart,
increase in volume of heart muscle (left ventricle),
increase O2 demand,
limitation of coronary circulation,
ischemia,
heart attack.
2. increase chances of arteriosclerosis and hemorrhages.
3. kidney failure
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
51/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
52/66
Fainting afterstrenuous
exercise
Sweating
and blood
pressure
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
53/66
Hypotension
(fainting)
1. orthostatic
2. shock
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
54/66
What happens if you enter a 45oC room?
Hypothalamus set body temp. at 37oC
Blood pressurecardiac output
Blood vessel dilation
blood flow to skinTemp
sweat plasma volume
Blood pressureAldosterone secretion
Na+ reabsorption
ADH secretion
urine production
output from heart
sweating
until your system collapses.Temp. rise
Faint
If blood supply to brain becomes low
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
55/66
Blood Hypothalamus Posterior
pituitaryKidney
Blood Hypothalamus Posterior
pituitaryKidney
osmotic
content
(soluteconcentration)
depress
osmo-
regulator
release
of ADH
H2O
reabsorption
osmotic
content
(soluteconcentration)
stimulate
osmo-
regulator
release
of ADH
H2O
reabsorption
COMPENSATION
COMPENSATION
(-)
(-)
H2O
intake
H2O
loss
H2O
intake
H2O
loss
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
56/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
57/66
Body
FluidsKidney Kidney
Plasma
Proteins
Volume Bloodpressure Secretionof Renin Formation ofAngiotensin
Secretion of
Aldosterone
Adrenal
Cortex
Na+ & H2O
reabsorption
KidneyCOMPENSATION
(-)
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
58/66
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
59/66
What happens after you go for a blood
donation?
parasympathetic
sympathetic cardiac output
resistance
Blood volume Blood pressure secretion of renin
Na+ reabsorption secretion of
aldosterone
formation of
angiotensinPlasma solute
conc
release
of ADH H2O
reabsorption
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
60/66
End
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
61/66
Learning = new information + new
skills + new experience
Learning =making new connections
between information, skills andexperience
Learning = un-learn + re-learn
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
62/66
Conception
Configuration
Contradiction
Confusion
Reconfiguration
Culmination
Celebration
Thinking
Thinking
Doing
Learning activities:
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
63/66
Learning is not passive listening
To understand the topic
To reformulate material
To use it
To analyse it, filterif necessary
To re-structure it, build connections
To question it, doubt
To search and weigh evidence
To rejectthose parts of it that dont stand scrutiny
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
64/66
Wonderment, Inquisitiveness,
Curiosity
All thinking begins with wonderment
---Socrates---
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
65/66
Exploration
-
7/28/2019 7 Body Temperature and Heat Stroke Jan 2013 (1)
66/66
Thank you,
and see you inBL3262 orUROPS