5.Physiology of Blood
-
Upload
muhammad-falat-shofiudin -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of 5.Physiology of Blood
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
1/27
Dr.G.MoinuddinGhori,PhD
Deptt.of Physiology,College of
Medicine,King Saud Bin AbdulazizUniversity for Health Sciences,RIYADH
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
2/27
8% of Body weight,
5-6 L in males & 4-5 L in females
FUNCTIONS:--1)Respiratory function
2)Nutritive function
3)Excretory function4)Hormone transport
5)Water & Electrolyte balance
6)Prevent the body against bacteria & Blood loss
7)Temp. regulation
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
3/27
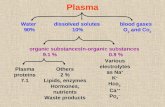
PLASMA:-- 55
58 %
(Water 91.0%, Plasma proteins 7.0%, Mineral Salts 0.9% &2.1 % others as Glucose, Cholesterol ,Gases)
Plasma proteins Albumin,Globulin,Fibrinogen &Prothrombin
FORMED ELEMENTS (BLOOD CELLS):-- 42 - 45 %
( RBCs or Erythrocytes, WBCs or Leukocytes, Platelets orThrombocytes)
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
4/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
5/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
6/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
7/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
8/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
9/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
10/27
Embryo (Yolk sac) Few weeks
Middle Trimester ( Liver,Spleen,Lymph nodes)
Later part of Pregnancy( Bone marrow ofSkull,Vertibrae,Ribs, Sternum)
After Birth (Skeleton & Girdles)
Production Stimulated in (Anemia,Hypoxemia)
Production Inhibited in (Supernormal level)
Production Regulated by (Erythropoietin hormonefrom Kidney)
RBC life span
120 days
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
11/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
12/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
13/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
14/27
All WBCs originate from Hemocytoblasts
The Myeloblasts develop into Eosinophils
Monoblasts develop into Monocytes
Lymphoblasts develop into Lymphocytes
PLATELETS:-- Originate fromHemocytoblasts(Fragments of Megakaryocytes,Useful for stoppage of bleeding or blood clotting)
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
15/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
16/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
17/27
A series of reactions for stoppage of bleeding
Three phases occur in rapid sequence:--1. Vascular spasmsimmediatevasoconstriction in
response to injury,initiated by local pain receptors
2. Platelet plug formation-- as a result of plateletaggregation
3. Coagulation a set of reactionsin which blood istransformed from a liquid to gel (follows Intrinsic &
Extrinsic pathways)Final 3 steps are:-Prothrombin activator is formed
-Prothrombin is converted into Thrombin
-Thrombin converts FIBRINOGEN into FIBRIN
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
18/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
19/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
20/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
21/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
22/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
23/27
Whole blood transfusion is required, when largequantity of blood is lost
Before transfusion,matching of blood isessential to avoid reaction due to mis- match ofblood
Human blood have 30 varities of naturallyoccuring RBC antigens
Antigens of ABO & Rh blood groups cause strongreaction ,if not matched before transfusion
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
24/27
ABO Blood group consists of:--
Two ANTIGENS (A & B) on surface of RBCs &
Two ANTIBODIES (Anti-A & Anti-B) in the plasma
Presence of Rh factor on RBCs surface is indicated asRh+
TRANSFUSION REACTION occurs when mis-matchedblood is infused. Donors cells are attacked by the recipientanti bodies causing clumping of cells which results bloodflow block
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
25/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
26/27
-
7/30/2019 5.Physiology of Blood
27/27
Type AB blood group is called
Universal recipient as it can receive
blood from Type A blood group as
well as Type B blood group
Type O blood group is calledUniversal donor as it can give blood
to both Type A and TypeB blood
groups