5-1 - mathppt.com · y =ax2 +bx+c Quadratic Equation Quadratic Term Constant Term Objective - To...
Transcript of 5-1 - mathppt.com · y =ax2 +bx+c Quadratic Equation Quadratic Term Constant Term Objective - To...

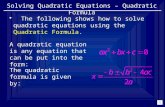
y = ax2 + bx + cQuadratic Equation
QuadraticTerm
ConstantTerm
Objective - To transform quadratic functions.
e ea
+a opens up-a opens down
skinny parabola a >1
wide parabola0< a <1
c
+c shifts up-c shifts down
y-intercept
yGraph f (x) = x2
x y
-32
94
x
-2-10123
410149
Vertex(0,0)Axis of
Symmetryx = 0
y
Graph f (x) = x2 − 5
x y
-3-21
−3( )2 − 5 = 4−2( )2 − 5 = −1
1( )2 5 4x
-10123
Vertex(0,-5)
Axis ofSymmetry
x = 0
−1( ) − 5 = −40( )2 − 5 = −51( )2 − 5 = −42( )2 − 5 = −13( )2 − 5 = 4
y
Graph f (x) = −x2 + 4
x y
-3-21
Vertex(0,4)
Axis ofSymmetry
x = 0− −3( )2 + 4 = −5− −2( )2 + 4 = 0
1( )2 + 4 3x
-10123
− −1( ) + 4 = 3− 0( )2 + 4 = 4− 1( )2 + 4 = 3− 2( )2 + 4 = 0− 3( )2 + 4 = −5
Translations of Quadratic Functions
y
Horizontal Translation
2( ) ( )f xh hx
f (x) = x2
x( ) ( )− = −f xh hx
h < 0 moves left
h > 0 moves right
Translations of Quadratic Functions
y
Vertical Translation
2( ) +kf x x k
f (x) = x2
x
( ) − = +kf x x k
k < 0 moves down
k > 0 moves up
Lesson 5-1
Algebra 2 Slide Show: Teaching Made Easy As Pi, by Mike Mills and James Wenk © 2010

Translations of Quadratic Functions
y
Reflection
f (x) = x2
f (x) = x2
x
− f (x) = −x
Stretches and Compressions
y
Horizontal Stretch
f (x) = x2
2
x2
21 1⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞=⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟⎝ ⎠ ⎝ ⎠
xb
f xb
b > 1 stretches
0 < b < 1 compresses
Stretches and Compressions
y
Horizontal Compression
f (x) = x2
x ( )2 2• =f xa ax
a > 1 stretches
0 < a < 1 compresses
y = a(x − h)2 + k
Vertex Form of a Quadratic Equation
vertex (h,k)axis of symmetry x = h
Lesson 5-1 (cont.)
Algebra 2 Slide Show: Teaching Made Easy As Pi, by Mike Mills and James Wenk © 2010