Structural Health Monitoring of Concrete Bridges in Guilan ...
4'nInternational Confcrcnce oflranian OpcrationsResearch Society May 18-19,201I Faculty Mathematical...
-
Upload
cathleen-edwards -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of 4'nInternational Confcrcnce oflranian OpcrationsResearch Society May 18-19,201I Faculty Mathematical...

4'nInternationalConfcrcnce oflranian OpcrationsResearchSocietyMay 18-19,201I
Faculty Mathematicalof Sciences, University Guilanof
A new Nefwork DEA modelRoza Azizi., lslamic Azad University, Karaj Branch - Departmcnt of Mathematics- [email protected]
Reza Kazemi Matin, Islamic Azad University, Karaj Branch - Depaftment of Mathematics- [email protected]
Abstract: In recent years, there have been various researches which handle network systemsin DEAliterafure. Network systems are the systems which consume some inputs to produce some outputs
which some of them in some processesare used as the inputs of some of the other processes(intermediateproducts) to produce the final outputs. Most of the current approachesdid not have anyspecified model foi all the casesof network systems.In this paper a brief review of Kao approach isgiven and a new model for network systemswill be presentedwhich computesefficiency measurefor
all the casesof nefwork systems.Ke).words: Network systems,Specifiedmodel, Efficiency measure.
1. INTRODUCTION 2. REVTEWoN K^o (2009) APPROACH
DEA is a mathematical programming approach for Based on the most common notations in DEA literature,measuring the efficiency and the performance of any let f\flJ0 : 1 , . . . , n ) c o n s u m e i n p u t s x U ( i : 1 , . . . , m ) to
organizations, such as, commercial, educational, servingand etc. produceoutputsYo (r:1,...,s).
The conventional DEA models, consider each DMU asModcl (1) shows the multiple form of CCR rnodel
a black box without any look to the subsystemsactivities.which is firstly presented Chameset al. (i978).by
In rcccnt years, a number ofDEA studieshave focused onZu't '"systems with network structure. For example, Fare and
0. - Mtu +-Grosskopf (2000) divided network systemsto four cases,LV ,T,.
Static non-network model, Fixed but allocative Inputs,Static nctwork model, Dynamic network model, Lu'Y,
j=t.....rt (l)s.1 <lexplanation of these cases and examples of them are rn +*/,''^ tthcir paper. Sexton and Lewis (2003) study the Major i
League Baseball performance in a two-stage process. In v,,u,Z0 r - 1 , . . . , s , i =\ , . . . , n ttheir study money is used in the form of player salaries as The CCR model is based on the constant returns to
inputs to acquire talent as outputs of first stage and in scale (CRS) assumption for the production set. Model (l)second stage talent is used as inputs to win games as final is in its input-oriented version. The efficiency score of
outputs. And in 2004 they study the Major League this model is between zero and one.p\,fll.is calledBaseball performance in network structure. Another study
"efficient" respect to this model if and only if itsis Kao (2009) which divided network systems to series,computed efficiency scorebe equal to one.parallel, and systems which do not have thcse two
Model (1) cannot show logical efficiency score forstructures.network systcmsbecauseit does not consider the productsIn the systems which do not have series or parallel
which are produced and consumed between processesstruchrres, most of thc authors like Kao and Fare and(intermediate products). So, it is necessary to introduceGrosskopf (2000), did not introduce any specified model
the model which can use intermediateproducts.for this case and just wrote the restrictions of eachKao (2009) has been divided network systems to threeprocessesin their model and this way for the time when
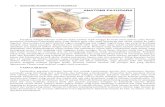
caseswhich will be presentedas the follows:there are a few processesor a few inputs or outputs need1. Seriessystemmuch lime and thc possibility of error is high.
Figure I shows a system consisting of p (p: I ,. . .,q)In this paper, we introduce the model which isprocesses connectedin senes.appiicable for series and parallel systems, and also for
network systems which do not have series or parallelstructures.
Based on the above discussion and to introduce themethod to find the efficiency measure of all the casesof
Figure Seriesl. systemsys:ems with network structures, the rest of this paper willzlis the dth intermediate product which is consumedunfold as following. Section 2 is devoted to a brief revrew
of Kao (2009) paper. A new Nehvork DEA model will in pth process andwlis the weight of dth intermediateintroduced in section 3, which have the ability of finding
product in pth process.Kao (2009) have been introducedthe efficiency measureof all the network systems,
seriesmodel as follows:
663