4. 555 timer
-
Upload
facebook-hacker-cup -
Category
Business
-
view
4.197 -
download
7
description
Transcript of 4. 555 timer

CHAPTER 4CHAPTER 4555 TIMER

555 TIMER555 TIMER555 timer is an integrated circuit
that very stable.Use as monostable multivibrator,
astable multivibrator, analog square wave signal generator, achometer frequency meter and others.
Basically, 555 timer operate in 2 mode,MonostableAstable

FUNCTION OF EACH PIN TIMER FUNCTION OF EACH PIN TIMER REFER TO MONOSTABLE REFER TO MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATORMULTIVIBRATOR
PIN 1 : GROUND -all the measure voltage must refer to this pin PIN 2 : TRIGGER
- It is used to set the flip-flop. - Output is LOW if voltage at pin > 2/3 Vcc- When negative trigger pulse is 1/3 Vcc, output at
comparator 2 cause the timer output HIGH. PIN 3 : OUTPUT
- Output can connect at 2 output pin, pin 3 and pin 1 or pin 3 and pin 8.
- When output LOW, current will flow through load that connected between pin 3 and pin 8 to output terminal, know as SINK CURRENT.
- Current flow through load that connected between pin
3 and pin 1, known as SOURCE CURRENT.- Maximum current for source current and sink current
is 200mA.

CONTINUE…..CONTINUE….. PIN 4 : RESET
- Reset with negative pulse
- When the reset pin is not used, the pin is connected to +Vs to avoid false trigger.
PIN 5 : CONTROL VOLTAGE- Normally is connected to earth through 0.01µF capacitor
- If output voltage is connected to pin 5, the output waveform bandwidth can be
changed.
- 0.01µF capacitor can avoid from noise problem.
PIN 6 : THRESHOLD VOLTAGE- Input for inverting pin at comparator 1
- When voltage at this pin ≥2/3 Vcc, output at comparator 1 is HIGH, output timer
LOW.
PIN 7 : DISCHARGE- This pin is connected internally to collector at transistor Q1.
- When output HIGH, Q1 OFF, circuit open
- When output LOW, Q1 saturated capacitor C discharge through Q1.
PIN 8 : SUPPLY VOLTAGE, Vcc- +5 V to 18V

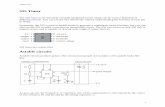
555 TIMER INTEGRAL 555 TIMER INTEGRAL CIRCUITCIRCUIT

MONOSTABLE MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATORMULTIVIBRATOR
Known as shoot multivibrator Pulse generator circuit which the period is calculated
from RC network and connected to external of 555 timer Stable when the output logic LOW (logic = 0) When a pulse is trigger at pin 2 (normally negative
trigger pulse), timer output will change to HIGH (+Vs) for a while and change to LOW (stable condition). The condition will continue LOW until pulse is trigger again.
The timing period is triggered (started) when trigger input (555 pin 2) is less than 1/3 Vs, this makes the output high (+Vs) and the capacitor C1 starts to charge through resistor R1. Once the time period has started further trigger pulses are ignored.
The threshold input (555 pin 6) monitors the voltage across C1 and when this reaches 2/3 Vs the time period over and the output becomes LOW,
At the same time discharge (555 pin 7) is connected to 0V, discharging the capacitor ready for the next trigger.

CONTINUE….CONTINUE….CONNECTION FOR MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATORCONNECTION FOR MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR

CONTINUE….CONTINUE…. Operation for monostable multivibrator :
¤ Assume initial output is LOW, circuit at stable condition, transistor Q1 ON, capacitor is connected to ground.
¤ When negative pulse is triggered to PIN 2 , transistor
Q1 OFF (Q1 open circuit), capacitor C start charging through resistor R1 and output is HIGH.
¤ When voltage at capacitor, C reach 2/3 Vs, output will
change to LOW through flip flop. At the same time, flip flop output will make the Q1 ON. Capacitor will discharge through transistor Q1.
¤ Monostable output will remain LOW until another trigger
pulse is triggered to pin 2.

ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATORASTABLE MULTIVIBRATORCONNECTION FOR CONNECTION FOR ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR

CONTINUE…CONTINUE… Known as free running multivibrator. Do not have stable condition, the condition always
change. Astable do not need trigger pulse for external to
change the output. The period for LOW and HIGH can be calculated based on
resistor and capacitor value that connected at outside of timer.
Operation for astable multivibrator :i) Assume the initial is HIGH. Transistor Q1 OFF and capacitor is charging through resistor RA and RB.ii) When capacitor voltage reach 2/3 Vee, Comparator 1 will trigger flip flop and output change from change from HIGH to LOW. Resistor RB and transistor Q1.iii) When the capacitor voltage reach 1/3 Vee, comparator output 2 will trigger flip flop so the timer output is HIGH. The cycle is repeated.
Period for capacitor charging from 1/3 Vcc to 2/3 Vcc same as period for HIGH output at timer.
Period for capacitor discharging from 2/3Vcc to 1/3 Vcc same as period for LOW output at timer.

FORMULA FOR TIMERFORMULA FOR TIMERTH = 0.693 (RA+RB) CTL = 0.693 (RB) C
Period, T = TH + TL = 0.693 (RA + 2RB) CFrequency, f = 1/T
= 1/ (TH + TL) = 1.44 / ((RA + 2RB) C)
% Duty Cycle = [TH / (TH + TL) ]x 100 = [(RA + RB) / (RA + 2RB)] x100

555/556 Inverting Buffer 555/556 Inverting Buffer (Schmitt trigger) or NOT (Schmitt trigger) or NOT gategate
The buffer circuit's input has a very high impedance (about 1MΩ) so it requires only a few µA, but the output can sink or source up to 200mA.
This enables a high impedance signal source (such as an LDR) to switch a low impedance output transducer (such as a lamp).
It is an inverting buffer or NOT gate because the output logic state (low/high) is the inverse of the input state:
- Input low (< 1/3 Vs) makes output high, +Vs - Input high (> 2/3 Vs) makes output low, 0V
555 inverting buffer or NOT gate555 inverting buffer or NOT gate
NOT gate symbolNOT gate symbol

CONTINUE…CONTINUE…When the input voltage is between 1/3 and 2/3
Vs the output remains in its present state. This intermediate input region is a deadspace
where there is no response, a property called hysteresis, it is like backlash in a mechanical linkage. This type of circuit is called a Schmitt trigger.
If high sensitivity is required the hysteresis is a problem, but in many circuits it is a helpful property.
It gives the input a high immunity to noise because once the circuit output has switched high or low the input must change back by at least 1/3 Vs to make the output switch back.

555/556 Bistable (flip-555/556 Bistable (flip-flop) - a memory circuitflop) - a memory circuit
The circuit is called a bistable because it is stable in two states: output high and output low. It is also known as a 'flip-flop'.
It has two inputs: Trigger (555 pin 2) makes
the output high. Trigger is 'active low', it functions when < 1/3 Vs.
Reset (555 pin 4) makes the output low. Reset is 'active low', it resets when < 0.7V.
The power-on reset, power-on trigger and edge-triggering circuits can all be used as described above for the monostable.