3.1 Cell Theory Sponge: Set up Cornell Notes on pg. 25 Topic: 3.1 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells...
-
Upload
emmett-smeaton -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of 3.1 Cell Theory Sponge: Set up Cornell Notes on pg. 25 Topic: 3.1 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells...
- Slide 1
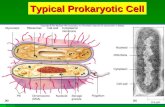
3.1 Cell Theory Sponge: Set up Cornell Notes on pg. 25 Topic: 3.1 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Essential Question: Describe the difference between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells. Dont forget to add it to your T.O.Contents! 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Describe the difference between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells 3.1 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life Slide 2 3.1 Cell Theory What do you think about when you hear the word cell? (Think of more than one type) What do these cells have in common? On the top of pg. 24: Slide 3 3.1 Cell Theory These are some things that you may think of when you think of a cell: Cell phone jail cell monks cell cell They have/are: structure, small, things inside, matter, mass, made of atoms, used by humans Slide 4 3.1 Cell Theory Main Ideas Early studies led to the development of the cell theory Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. Slide 5 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. Macrophages- play an important role in your immune system- take in a digest foreign materials (red= bacteria) Slide 6 3.1 Cell Theory Objective 1c. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. Slide 7 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. First to identify cells and named them Made better lenses for microscopes First to note that plants are made of cells Concluded that ALL living things are made of cells Proposed that all cells come from other cells Slide 8 3.1 Cell Theory Robert Hooke In 1665 he used the three-lens compound microscope to examine thin slices of cork He observed that cork is made of tiny, hallow compartments These compartments reminded Hooke of small rooms found in monasteries (where monks live), so he named them cells. Slide 9 3.1 Cell Theory More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. Slide 10 3.1 Cell Theory Cells cork Red blood cells Slide 11 3.1 Cell Theory How does the size of a cell in a blue whale compare to the size of the cell in a tadpole? Slide 12 3.1 Cell Theory How does the size of a cell in a blue whale compare to the size of the cell in a tadpole? A: Most cells in a whale are the same size as in a tadpole! So what makes a blue whale so much bigger? A whale has far more cells. Slide 13 3.1 Cell Theory The Cell theory has three principles. 1. All organisms are made of cells. Slide 14 3.1 Cell Theory 2. All existing cells are produced by other living cells. Slide 15 3.1 Cell Theory 3. The cell is the most basic unit of life. Slide 16 3.1 Cell Theory One of the 3 principles of cell theory is that ALL existing cells are produced by other existing cells. Apply this principle to a cut on your arm. (Explain what is happening throughout the healing process) Slide 17 3.1 Cell Theory One of the 3 principles of cell theory is that ALL existing cells are produced by other existing cells. Apply this principle to a cut on your arm. Answer You get a cut You start to bleed You form a scab Messages are sent to skin cells to replicate Skin cells replicate through mitosis New skin cells are created Scab falls off You are healed! Slide 18 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics: Slide 19 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics: Cells tend to be microscopic. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) Slide 20 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics: Cells tend to be microscopic. All cells are enclosed by a membrane. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) cell membrane Slide 21 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics Cells tend to be microscopic. All cells are enclosed by a membrane. All cells are filled with cytoplasm. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) cell membrane cytoplasm Slide 22 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. The nucleus holds the DNA Have membrane-bound organelles May be multi-cellular or single-celled organisms nucleus cell membrane organelles Draw and label picture on top of p. 24 Slide 23 3.1 Cell Theory Organelles: structures that are specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell. The nucleus is usually the largest and most visible organelle. Slide 24 3.1 Cell Theory Things that have Eukaryotic Cells: PLANTS ANIMALS FUNGI Slide 25 3.1 Cell Theory Cytoplasm: is a jellylike substance that contains dissolved molecular building blocks- such as proteins, nucleic acids, minerals, and ions Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) Slide 26 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. do not have membrane- bound organelles DNA is in the cytoplasm All are microscopic, single-celled organisms cell membrane cytoplasm Draw and label picture on top of p. 24 Slide 27 3.1 Cell Theory Things that have prokaryotic cells Bacteria Archaea Slide 28 2.1 Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 3.1 Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic/Virus Video Notes On pg. 26: Title your paper Title of videos: Intro to cells #1 Intro to cells #2 What is a cell? Bacteria The littlest Assassins How viruses work Intro to cells # 1: Intro to cells #2: What is a cell?: Bacteria: The littlest Assassins: How Viruses Work: Leave room for at least 3 bullets each!!!! Add to T.O.Contents Slide 29 3.1 Cell Theory Viruses Virus- An infective agent that typically consists of a DNA or RNA strand in a protein coat. multiply only within the living cells of a host Antibiotics will not work on them Vaccines prevent them EX: Herpes virus Influenza Chickenpox Ebola virus Draw and label picture on top of p. 24 Protein Coat Slide 30 3.1 Cell Theory Movies about Viruses I am Legend 28 weeks later The Stand (book) Osmosis Jones The Happening Slide 31 3.1 Cell Theory On the bottom of pg. 24: Draw a double-bubble map comparing and contrasting Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells Slide 32 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells No nucleus Has a nucleus No membrane- bound organelles Has membrane- bound organelles Cells tend to be microscopic All cells are enclosed by a membrane All cells are filled with cytoplasm. All are produced by other cells Basic unit of life Always single celled Slide 33 3.1 Cell Theory Homework In the middle section of pg. 24: Draw a tree map classifying Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells, and Viruses Cells and Viruses Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Viruses Slide 34 3.1 Cell Theory Draw a tree map classifying Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells, and Viruses Cells and Viruses Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Viruses No organelles DNA in cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Multi-cellular And Single-cellular Single-cellular No nucleus DNA in nucleus DNA in protein Coat Needs a host Antibiotics do not work on them Vaccines prevent