3. Golgi Apparatus - KOCWcontents.kocw.net/KOCW/document/2011/konkuk/LeeHoonTaek/...3. Golgi...
Transcript of 3. Golgi Apparatus - KOCWcontents.kocw.net/KOCW/document/2011/konkuk/LeeHoonTaek/...3. Golgi...


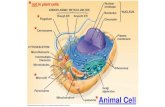
3. Golgi Apparatus A. Anatomy
- cis face: entry site
- trans face: exit site
B. Major functions
1) Retrieve proteins from ER to process further and transport to
their final destinations: lysosomes, PM, or secretions
2) Synthesize glycolipids & sphingomyelin

C. Protein glycosylation
1) N-linked glycosylation
• Further addition of N-linked acetylglucosamine
• Removal of some monnose molecules and
addition of some galactoses and silaic acids

- Processing of lysosomal proteins different from that of secreted & plasma memb proteins
(i) Phosphorylation of 6th position of mannose residue (by UDP-GlcNAc → UMP)
How the phosphorylating enzyme (GlcNAc phospho- transferase) recognize the lysosomal protein?
by signal patch of lysosomal protein
(ii) Mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) is recognized by M6P receptor in trans Golgi, then
lysosomal enzymes are transported to lysosome.
(iii) M6P receptor binds its specific oligosaccharide at pH 7 in trans Golgi network
and releases it at pH 6, which is pH in interior of late endosomes.

2) O-linked glycosylation:
3) Addition of GAG (Glycososaminoglycan) to produce proteoglycan.
: Many proteoglycans are secreted to become components of extracellular matrix
while others remain anchored to plasma memb.
4) Roles of glycosylation
a) glycosylation of proteins is only in eukaryotic cells.
b) renders glycoproteins resistant to protease digestion.
c) seems not related to intracellular transport.
Addition of sugars to OH groups of serine or
threonine side chains

D. Synthesis of sphingomyelin and glycolipids
from ceramide synthesized in ER
E. 3 export pathways from Golgi apparatus
: what mechanism is involved in choosing one of 3 pathways is not explained.
Constitutive
secretion
Regulated
secretion
Lysosome

1) Constitutive secretory pathway:
a) continual unregulated secretion from cell
b) also account for incorporation of new proteins and lipids into PM
c) Default pathway
d) In the polarized cell (such as epithelial cell), destination to either apical or
basolaterial memb seems to be determined by types of constituitive vesicle.

2) Regulated secretion
a) release of hormones, neurotransmitters, and digestive enzymes
b) proteins for this secretion may have signal patch
3) Specially targeted intracellular pathways
- proteins targeted to lysosome, etc.

F. The mechanism of vesicular transport -Clathrin-coated vesicle
(i) ① uptake of extracellular molecular from PM by endocytosis
② transport molecules from Golgi to lysosomes
(ii) By receptor & adaptor proteins: directs specific proteins into coated vesicle
(e.g.) M6P receptor + AP-1 adaptor protein → lysosomal proteins are packaged into vesicles

Review
- Golgi apparatus
Preview - Lysosome
- Nucleus