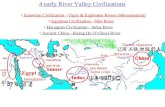
2lecture Egyptian Civilization
-
Upload
haider-manzoor -
Category
Documents
-
view
234 -
download
0
Transcript of 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
1/33
EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
Surroundings
Religion
Art Sculpture
Pottery
Furniture
Glass Clothing
Hieroglyphs
Papyrus
Holy animals
Products
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
2/33
SURROUNDINGS
To its north side is the
Mediterranean sea. To its west there is a large
Libyan desert.
To its east is the red sea.
Along its coast there is amountain range going fromnorth to south.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
3/33
EGYPTIAN HISTORY
Egypt is one of the most fertile areas of Africa, andone of the most fertile of the countries around theMediterranean Sea. Because it is so fertile, peoplecame to live in Egypt earlier than in most places,
probably around 40,000 years ago. At first there were not very many people, but
gradually Egypt became more crowded, so there wasmore need for a unified government.
Around 3000 BC (5000 years ago), Egypt was firstunified under one ruler, who was called the Pharaoh.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
4/33
CULTURE
The Culture of Egypt enjoys an international
reputation for its
uniqueness,
Majesty (dignity) and
technological skills.
Tourists from all over the world come to Egypt
to enjoy the beauty and splendor of culturethat is more than 7000 years old and is
harmonious fusion of the Egyptian,
Mediterranean, Greek and Arabic Cultures.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
5/33
PYRAMIDS: The highlight of the Egyptian Culture isthe pyramids. There are several pyramids in Egyptthat have created a lot interest in the minds of notjust historians and archaeologists but also tourists.The Pyramids are the single largest selling point oftourism industry in Egypt.
PAINTING:The paintings have also been associatedwith the Culture of Egypt. The paintings have alwaysbeen an integral part of the monuments of Egypt,which were ornamented with symbolic drawings.Modern artists in Egypt keep the culture of paintingalive with their skills.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
6/33
ANCIENT EGYPTIAN ART
Ancient Egyptian art refers to the style of
painting,
sculpture,
crafts and architecture developed by the civilization in the lower
Nile Valley from 5000 BC to 300 BC.
Ancient Egyptian art as expressed in painting and
sculpture was both highly stylized and symbolic. Much of the surviving art comes from tombs and
monuments and thus there is an emphasis on life afterdeathand the preservation of knowledge of the past
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
7/33
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
8/33
SYMBOLISM
Symbolism also played an important role inestablishing a sense of order.
Symbolism, ranging from the pharaoh's regalia(symbolizing his power to maintain order) to theindividual symbols of Egyptian gods and goddesses,is omnipresent in Egyptian art.
Animals: Animals were usually also highly symbolicfigures in Egyptian art.
Colors:Colors were more expressive rather thannatural: red skin implied vigorous tanned youth,whereas yellow skin was used for women or middle-aged men who worked indoors
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
9/33
blue or gold indicated divinity because of its
unnatural appearance and association with
precious materials
the use of black for royal figures expressed thefertility of the Nile from which Egypt was
born.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
10/33
MATERIALUSED
There were different types of materials used inEGYPT namely,
COPPER: Until the New Kingdom most of the copper
used in Egypt was seemingly mined in the easterndesert or Sinai.
GOLD: Egypt was richer in gold than any othercountry of the region, especially after the conquest
of Nubia.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
11/33
ELECTRUM:Electrum is a gold-silver alloy which
occurred naturally. It had a silver contents somewhathigher than twenty percent. It was mostly imported
from countries south of Egypt: Punt, Emus, the south
countries.
SILVER:Egypt had little silver which was not part ofgold deposits. Silver was imported from western
Asia.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
12/33
BRONZ
E:T
he introduction of bronze was ahuge improvement in tool and weaponmanufacture. Unlike iron which was a difficultmaterial to work with, bronze technologies
were similar to the techniques improvedduring the copper age: It could be cast,hammered cold, improved its toughness.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
13/33
IRON:Iron is a very common element and in
Egypt iron ores occur in the mountainous
areas of the eastern desert and Sinai.
LEAD:Lead was of minor importance. Too soft
for making tools or weapons
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
14/33
RELIGION
Egyptians were polytheistic (theybelieved In many Gods).
Pharaoh was believed to be the
representative on earth of thegod, or may be a kind of Godhimself.
Everything of Egypt belonged to
the pharaoh.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
15/33
ART Most of what we know about Egyptian art comes from
the paintings. Paintings showed all sorts of things that people did in
their regular lives.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
16/33
SCULPTURE
Egyptian sculptor used stone as it was the most plentiful and
permanent,
available in a wide variety of colors and
hardness.
Sculpture was often painted in vivid hues as well.
Egyptian sculpture has two qualities that are
distinctive; it can be characterized as cubic and
frontal.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
17/33
SEATED MAN
2465-2323 B.C. Old Kingdom, Dynasty 5; Polychromed limestone;
height40
cm (15
3/4
in.)
The Seated Man is arepresentation of someone wholived in the Pyramid Age, during
the Old Kingdom.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
18/33
SEATED SCRIBE
1350 B.C.
New Kingdom, Dynasty 18
Basalt
height 6.4 cm (2 1/2 in.)
The small Seated Scribe was oncepart of a votive offering to Thoth,the patron god of writing. It is aparticularly graceful example ofthe artistic production.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
19/33
SEBEK EM HAT, A
LEADER
OF PRIESTS
ca. 1780 B.C.
Middle Kingdom, late Dynasty 12-early Dynasty 13
Limestone 48.3 cm (19 in.)
The subject of the standing
statue of Sebek em hat can beidentified as a leader of a groupof priests in a temple.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
20/33
POTTERY
Ancient Egyptians used carved small pieces of vasesand several other objects.
They also discovered the art of covering pottery with
enamel. Different types of pottery items were deposited in
burial chambers of the dead.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
21/33
FURNITURE
Common pieces of furniturewere small 3 and 4 leg stools
The ever present stool wasmade from wood, and had aleather or woven seat.
Wealthy people had theirstools and all furniture ingeneral was richly decoratedwith gold or silver leaf.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
22/33
GLASS
Glass-making technology initiallybegan in Egypt with themanufacture of small beads in thepre-dynastic era.
The technology was a result of theprocess of firing clay pots. Thesand and slag (fused material)utilized in making clay pots meltedtogether to make glass.
It was determined that when metaloxides were added to the glassnugget (pieces), various color hue(shades) resulted.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
23/33
CLOTHING
Both men and women in Egyptwore tunics which were sewnto fit them.
These tunics were like a longt-shirt which reached to theknees (for men) or to theankles (for women).
They were usually made oflinen and were nearly always
white. Men working outside usually
wore short skirts instead oftunics.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
24/33
When dressed up fancyboth men and womenwore blue and green eyeshadow and black kohl(eyeliner).
Both men and womenwore gold jewelry ifthey could afford to.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
25/33
HIEROGLYPHS
H
ieroglyphs are"sacred-drawings.
They are basicallydrawings of familiarobjects, simplified to
make them easier todraw.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
26/33
PAPYRUS
material on which to write,
prepared from thin strips of the
pith of this plant laid together,
soaked, pressed, and dried, used
by the ancient Egyptians, Greeks,and Roman
The first use of papyruspaper is believed to havebeen 4000 BC.
The raw material of papyruspaper comes from the plant
Cyperus papyrus.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
27/33
CANOPIC JARS
1070-712 B.C.
Egyptian, Dynasty 21-22
Limestone
height 48.3 cm (17 1/2-19 in.) Their internal organs were separately treated and,
during much of Egyptian history, placed in jars of clayor stone. These so-called Canopic Jars were closed
with stoppers fashioned in the shape of four heads--
human, baboon(monkey), falcon, and jackal --representing the four protective spirits called theFour Sons of Horus.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
28/33
FALCON OF HORUS
664-525 B.C.
Late Period, Dynasty 26
Bronze
height 39.4 cm (15 1/2 in.)
The Falcon of Horus wearing the double crown ofUpper and Lower Egypt is an image of royal kingship.The king was associated with the sky god as the"Living Horus," and he was thought to represent the
rule of the gods on earth. Statues such as this weresometimes used as containers for the preservedremains of the animal or bird they represented.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
29/33
HOLY ANIMALS
Sacred Cat of Bast
Falcon of Horus
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
30/33
SACRED CAT OF BAST
664-525 B.C.
Late Period, Dynasty 26 Bronze
height 26.4 cm (103/8 in.)
The Sacred Cat of Bast is
associated with the goddess Bastor Bastet, and she was sometimesrepresented as a human figurewith the head of a cat. The
natural grace, and perhaps themotherly qualities of the cat,suggested to the Egyptians someaspect of the goddess.
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
31/33
BOWL WITH HUMANFEET
Predynastic Period
37503550 B.C. Ceramic H. 3 7/8 in. (9.8 cm) Dia. 6 in. (15.3 cm)
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
32/33
VESSEL
Predynastic Period,
Naqada II 34503300 B.C.
Painted pottery
H. 11 3/4 in. (29.8 cm)
-
8/8/2019 2lecture Egyptian Civilization
33/33
COMB
Predynastic Period 3200 B.C.
Ivory
H. 2 1/4 in. (5.7 cm)